Patents
Literature
31 results about "Amanita" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
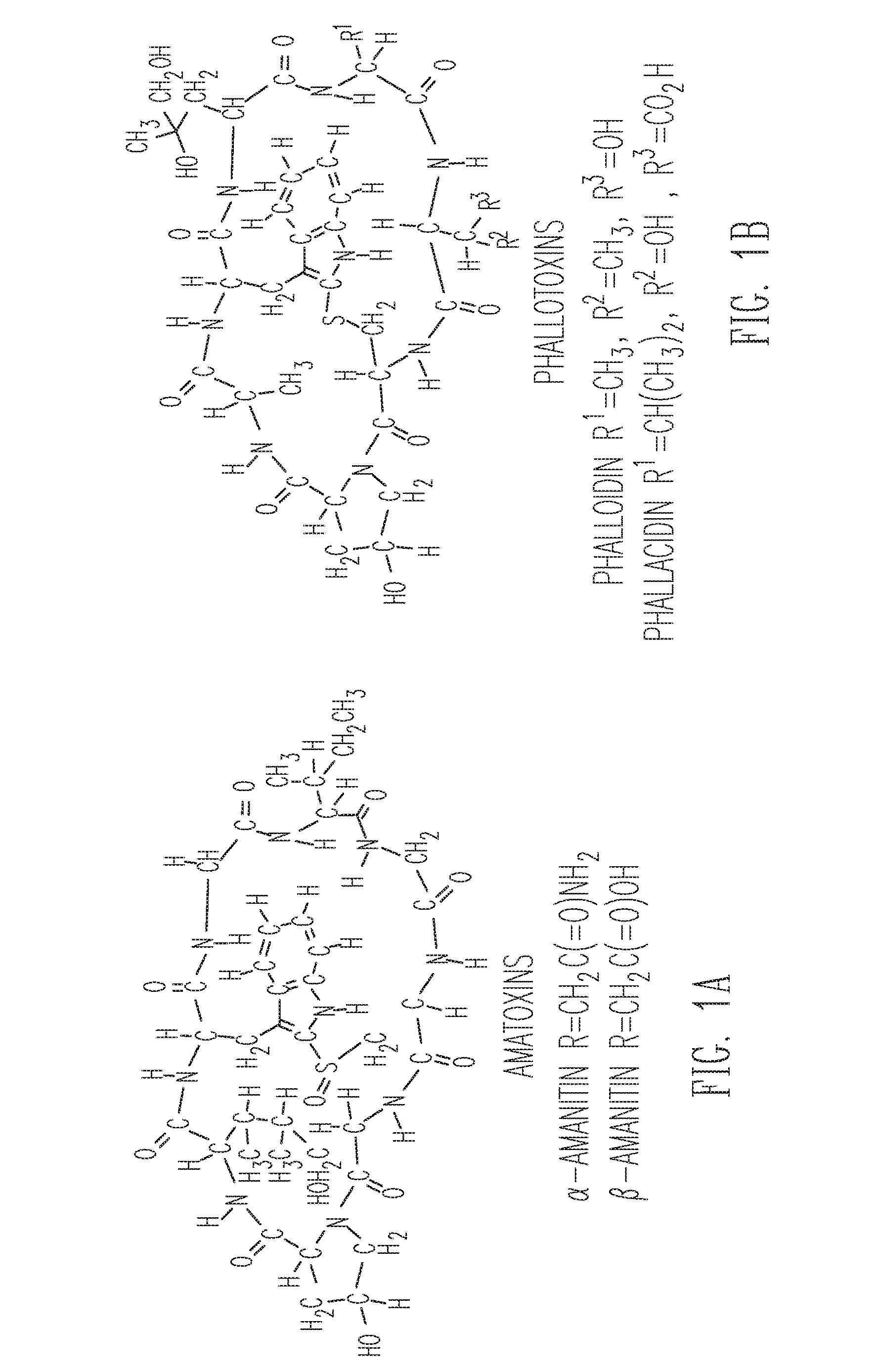
The genus Amanita contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is α-amanitin.
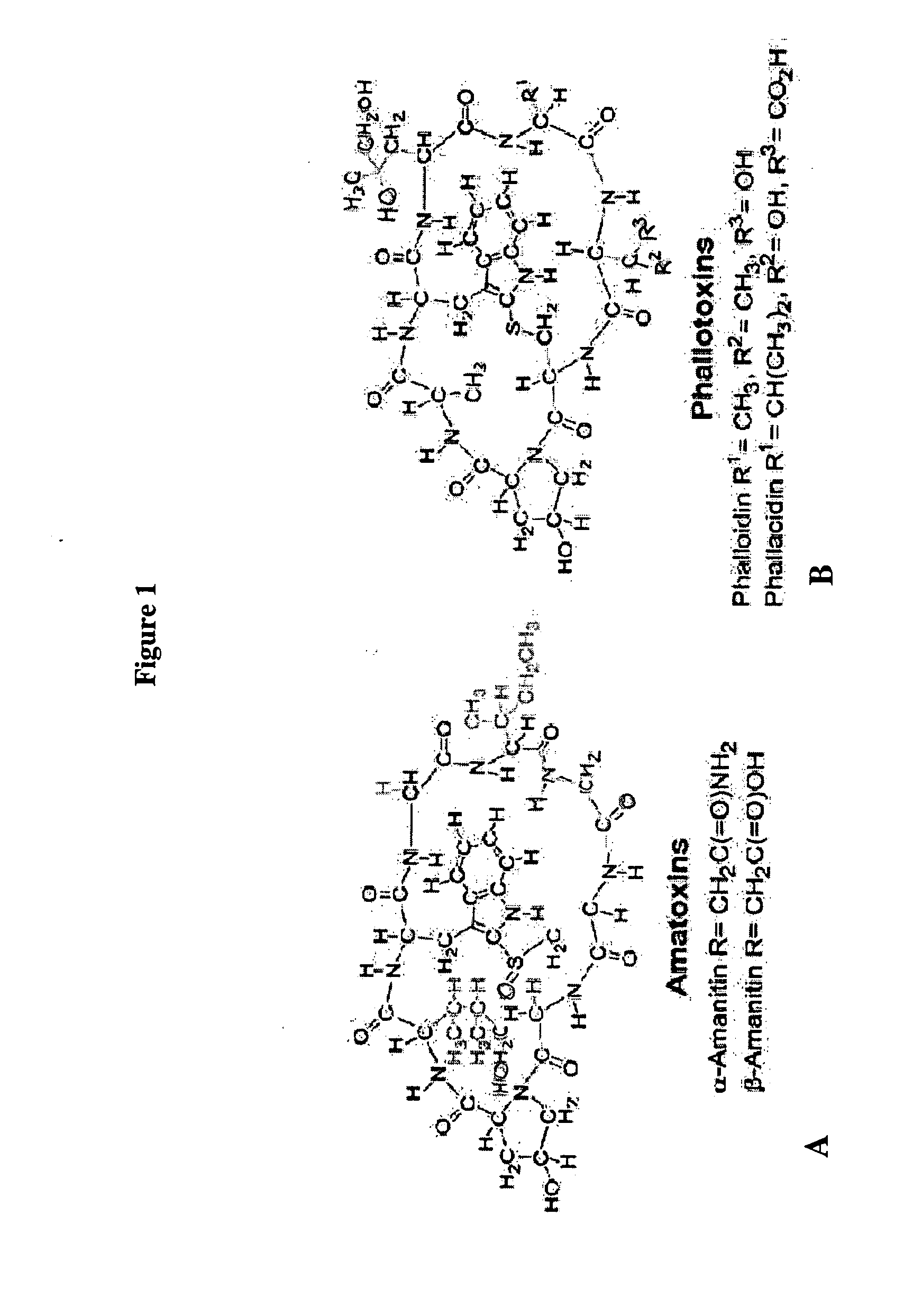
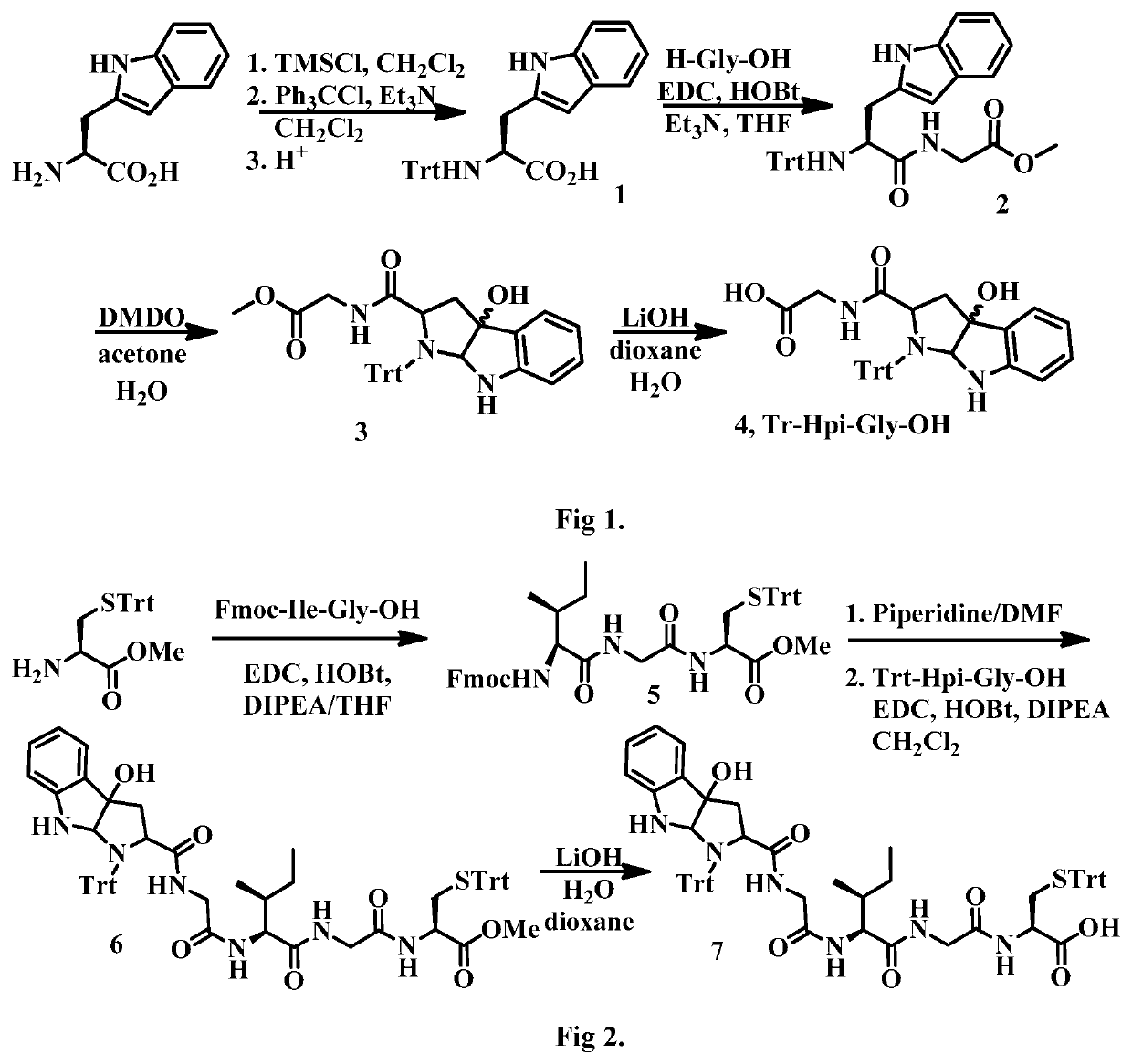
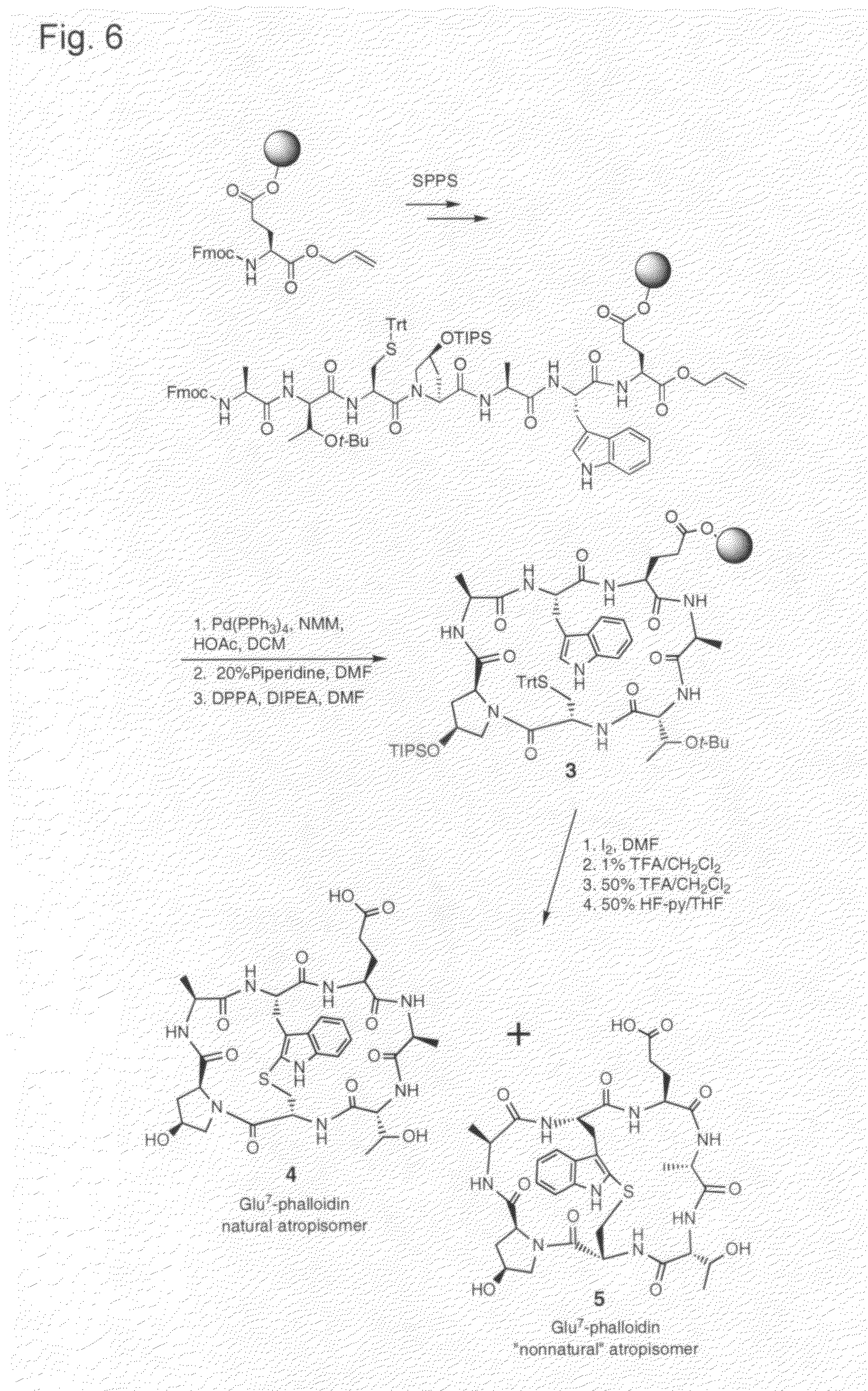
Identification And Use Of Genes Encoding Amatoxin And Phallotoxin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising genes and peptides associated with cyclic peptide toxins and toxin production in mushrooms. In particular, the present invention relates to using genes and proteins from Amanita species encoding Amanita peptides, specifically relating to amatoxins and phallotoxins. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention also relates to methods for detecting Amanita peptide toxin genes for identifying Amanita peptide-producing mushrooms and for diagnosing suspected cases of mushroom poisoning. Further, the present inventions relate to providing kits for diagnosing and monitoring suspected cases of mushroom poisoning in patients.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Russula vinosa Lindbl yield increasing fungi and using method thereof
InactiveCN101690454APromote recoveryIncreased fine root biomassHorticultureFertilizer mixturesFloraEconomic benefits
The invention provides russula vinosa Lindbl yield increasing fungi and a using method thereof, which belong to the technical field of russula vinosa Lindbl yield increase and solve the problems of low yield, high price, low quality and the like of wild russula vinosa Lindbl of the prior art. The russula vinosa Lindbl yield increasing fungi of the invention are a mixed flora of locally common ectomycorrhizal fungi and comprise Boletus brunneissimus Chiu, R. albida Peck, Boletus luridus and amanita yellow corner. Mycelia of various fungi of the russula vinosa Lindbl yield increasing fungi are cultured by a shaker culture method respectively; the mycelia are separate and used to prepare mycelium mixtures at a concentration of 50mg / L respectively; the mixtures are mixed uniformed in the same amount before inoculation to form the russula vinosa Lindbl yield increasing fungi; and on a woodland wherein russula vinosa Lindbl grows, the russula vinosa Lindbl yield increasing fungi are inoculated in dent pits by a root cutting and mycorrhization technique. In the method, ectomycorrhizal fungi flora is used to increase the biomass of thin roots of arbor, so the fruiting capacity, yield and quality of wild russula vinosa Lindbl are improved obviously and remarkable economic benefits are created. Thus, the method is suitable to be promoted and used in large areas.
Owner:INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Optimized culturing method for promoting growth of Amanitaflavipes mycelia
InactiveCN102696404APromote rapid proliferationShorten the growth cycleHorticultureBiotechnologyMycelium
The method relates to a culturing method for promoting growth of Amanitaflavipes mycelia, belonging to the technical field of culturing of macro fungi.. The culturing method is characterized in that mycelia are induced with mature sporocarps without pileus and a culturing medium is improved so as to provide a simple optimized culturing medium with short culturing circle, low cost and capability of promoting the fast growth of mycelia. Amanita belongs to special and precious economical macro fungi, is high in value and wide in application range and has potential application prospect in the field of development of new specific medicines such as anti-tumor, antibacterial and antiviral, sedative or narcotic medicines, but Amanita is hard to develop and use so far because of rear resource, difficulty in artificial acclimatization, inactive chemical synthetics of toxins and other problems. According to the method, Amanitaflavipes mycelia collected from Shishan, Wuding, Yunnan is used as the raw material and innovative breakthrough is made aiming at the problems limiting the culturing, such as difficulty in mycelium induction and slow growth of mycelia, thereby providing conditions for large-scale culturing and artificial acclimatization of Amanitaflavipes mycelia in the further.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Establishing method for indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides as symbiotic plant
InactiveCN102715089ABuild a symbiotic systemConvenient researchHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporocarp (fungi)
The invention relates to an establishing method for indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides which is a symbiotic plant, and belongs to the field of biotechnology (plant tissues and Fungus cultivation). An overwhelming majority of amanita belongs to ectomycorrhizal fungi, can not be yet subjected to artificial cultivation at present, and can be hardly developped and utilized; and growth and development of sporocarps of the amanita has a close relationship with cyclobalanopsis glaucoids which is a symbiotic plant. The establishing method is characterizedin that myceliums are induced through the sporocarps of amanita flavipes for reproduction; aseptic seedlings and potted seedlings are successfully obtained by using seeds of cyclobalanopsis glaucoides, collected in the field; reproduced myceliums are inoculated to the roots of the aseptic seedlings and the potted seedlings respectively; the result shows that inoculated seedlings are more exuberant than the non-inoculated seedlings and have more leaves, the leaves of inoculated seedlings are dark green, disease resistance of inoculated seedlings are reinforced; and therefore, the indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides is innovatively established, and a technological reserve is provided for future researches on symbiotic mechanism and mechanism generated in the sporocarps of amanita.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for co-culturing amanita subfrostiana mycelium by using mycorrhizal fungus and saprobic fungus
InactiveCN103667084AFast growthGood effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmanita chepangiana
The invention relates to a method for co-culturing an amanita subfrostiana mycelium by using a mycorrhizal fungus and a saprobic fungus, and belongs to the technical field of macro fungus culture. The method is characterized in that the mycorrhizal fungus lactarius piperatus and the artificially cultured saprobic fungus lentinus edodes are added directly in multiplication media, so that the growth rate of the amanita subfrostiana mycelium can be increased by 9-12 times, and the growth is accelerated obviously. According to the method, a tedious and complex process is not required, the reproduction speed of the mycelium can be increased only by adding a mixture of the two fungi into the media, the effect is obvious, the culture is simple and easy to implement, and the production cost is low. Amanita toxins have potential application in the field of development of novel specific medicines such as anti-tumor medicines, anti-microbial and antiviral medicines, sedative or anaesthetic medicines and like, while are difficult to develop and apply due to bottleneck problems that resources are rare and valuable, artificial acclimation is difficult and the like. The method performs innovation research aiming at pure culture restraining problems such as slower growth of the amanita subfrostiana mycelium and the like, and provides a basis for large-scale culture, artificial acclimation and culture in the future and the like of the mycelium.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Derivatives of amanita toxins and their conjugation to a cell binding molecule
Owner:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH
Solid-liquid alternating culturing method for mycelia of amanita rubrovolvata imai
The invention relates to a solid-liquid alternating culturing method for mycelia of amanita rubrovolvata imai and belongs to the technical field of culturing of macro fungi. The solid-liquid alternating culturing method for mycelia of amanita rubrovolvata imai is characterized by comprising the steps of: performing solid culturing on the induced and propagated mycelia for 4-6 generations and then performing the liquid culturing on the induced and propagated mycelia for 3-4 generations by using the solid-liquid alternating culturing method; then performing the solid culturing, wherein the growth speed of the mycelia is 8-10 times that of the mycelia before the liquid culturing, and the growth is speeded obviously. According to the invention, the propagation speed of the mycelia is speeded up by simply changing the culturing method, the operation is simple and easy to implement, the effect is obvious, and the production cost is low. The toxin of the amanita has potential application in the field of developing new specific medicines such as antineoplastic medicines, antibiosis and antiviral medicines, sedatives or narcotics, but is different to develop and apply due to the bottleneck problems such as the valuable and rare resource and the difficulty in artificial acclimatization so far. According to the invention, focused research is performed on the problems for limiting the pure culturing such as very slow growth of the mycelia of amanita rubrovolvata imai, and conditions are provided to the large-scale culturing of the mycelia, the artificial acclimatization cultivation in future and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Special culture medium for Chinese amanita and preparation method of special culture medium
InactiveCN107686386AHigh nutritional valueHigh in nutrientsCalcareous fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersBiotechnologyNutritive values
Owner:诸暨马谷亲科技有限公司
Extremely toxic mushroom rapid detection method
ActiveCN106568769ARapid McFarland Color ReactionMcFarland color reaction is easy to use and accurateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLepiotaTreatment design
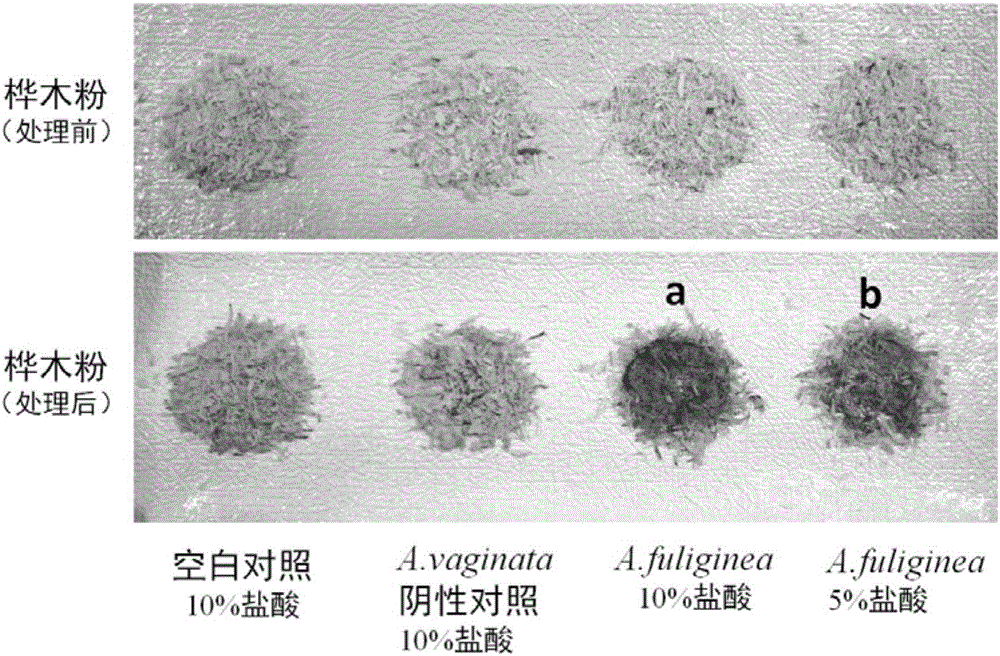
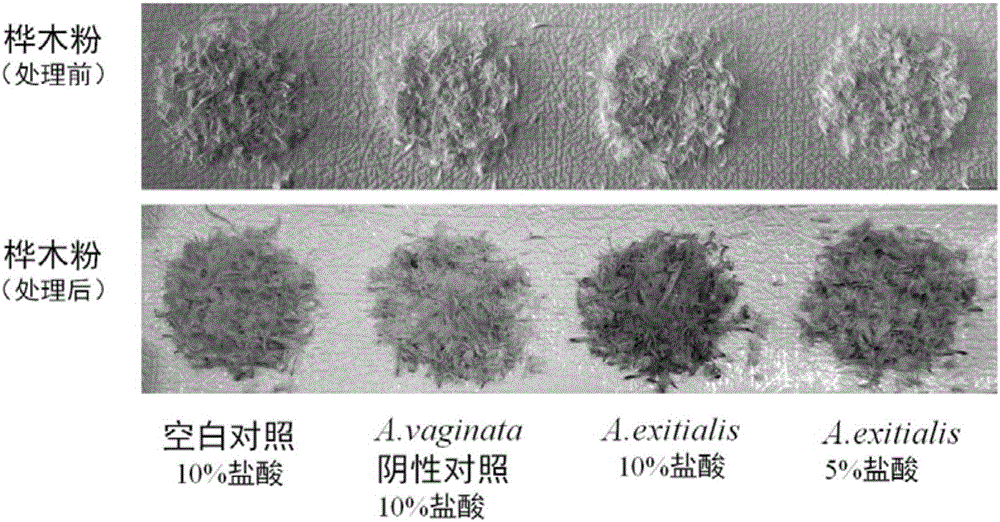
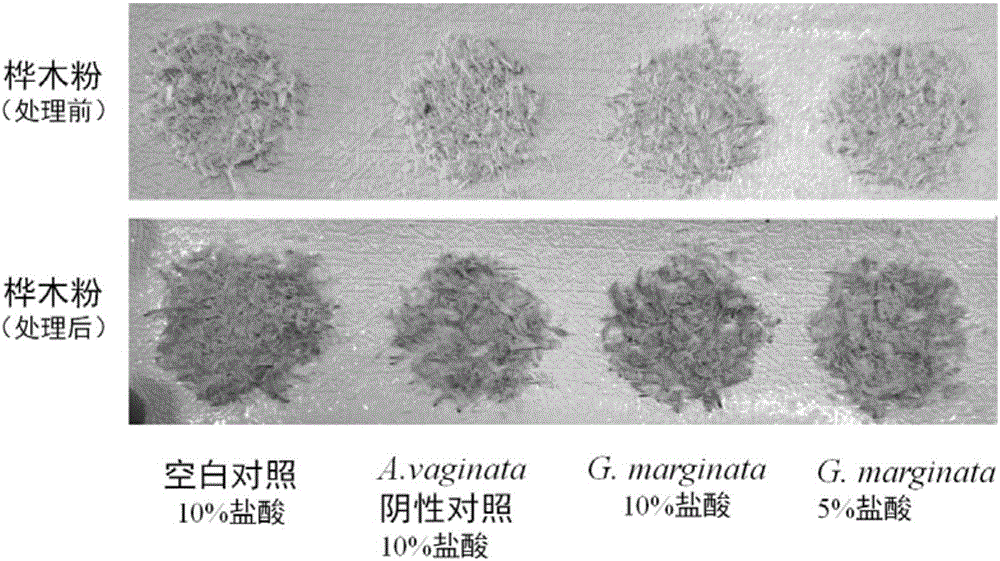
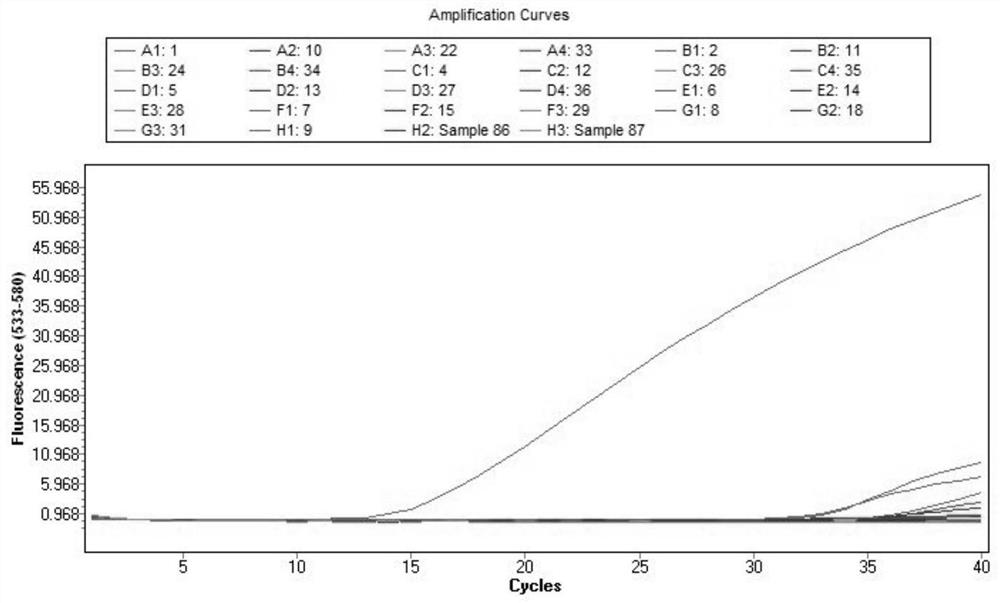
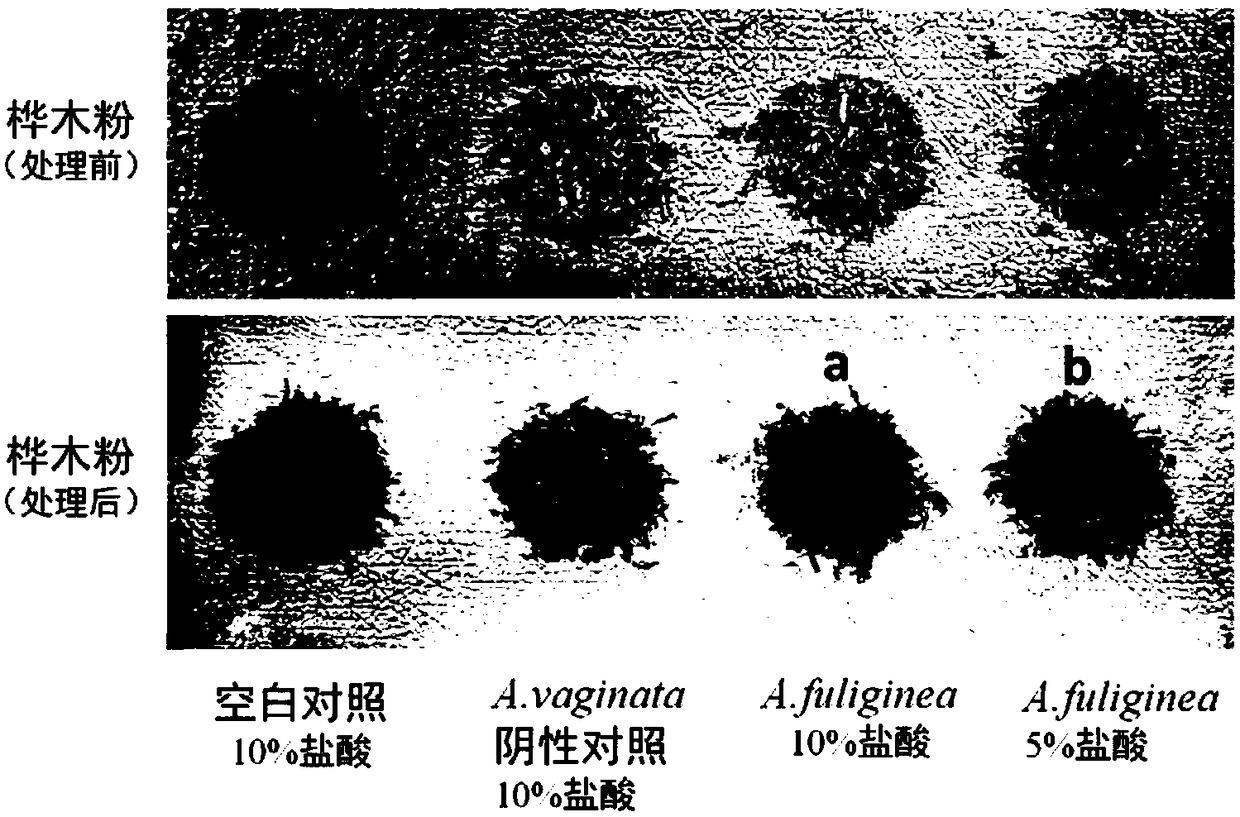
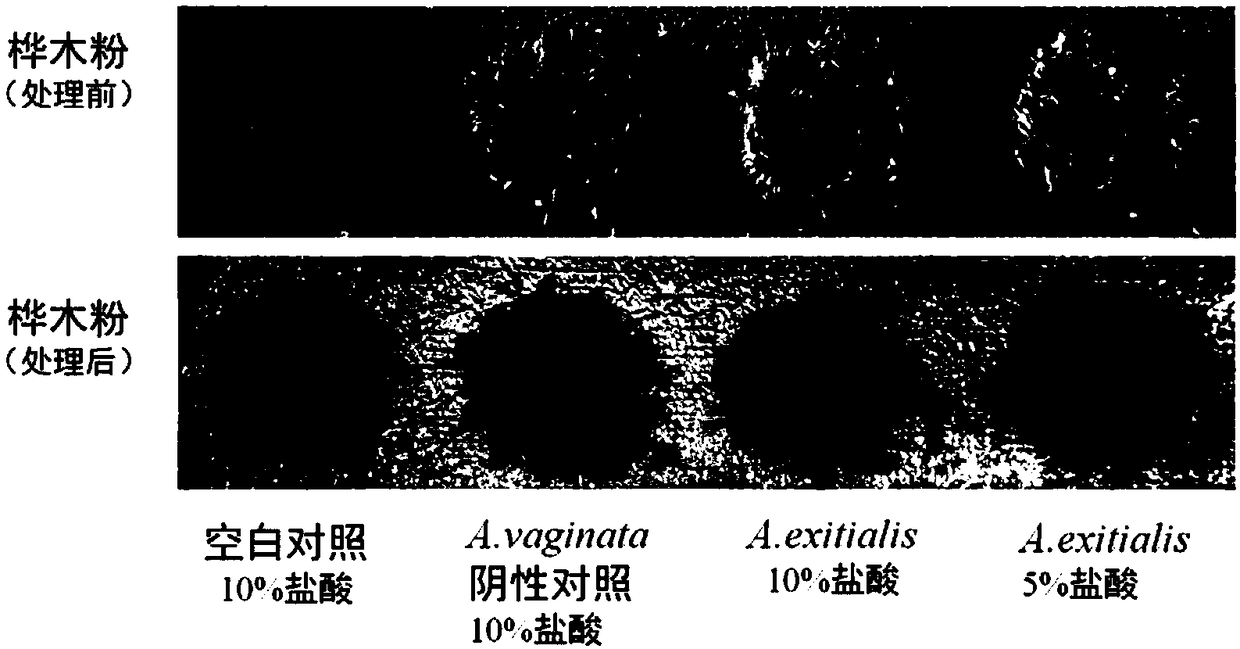
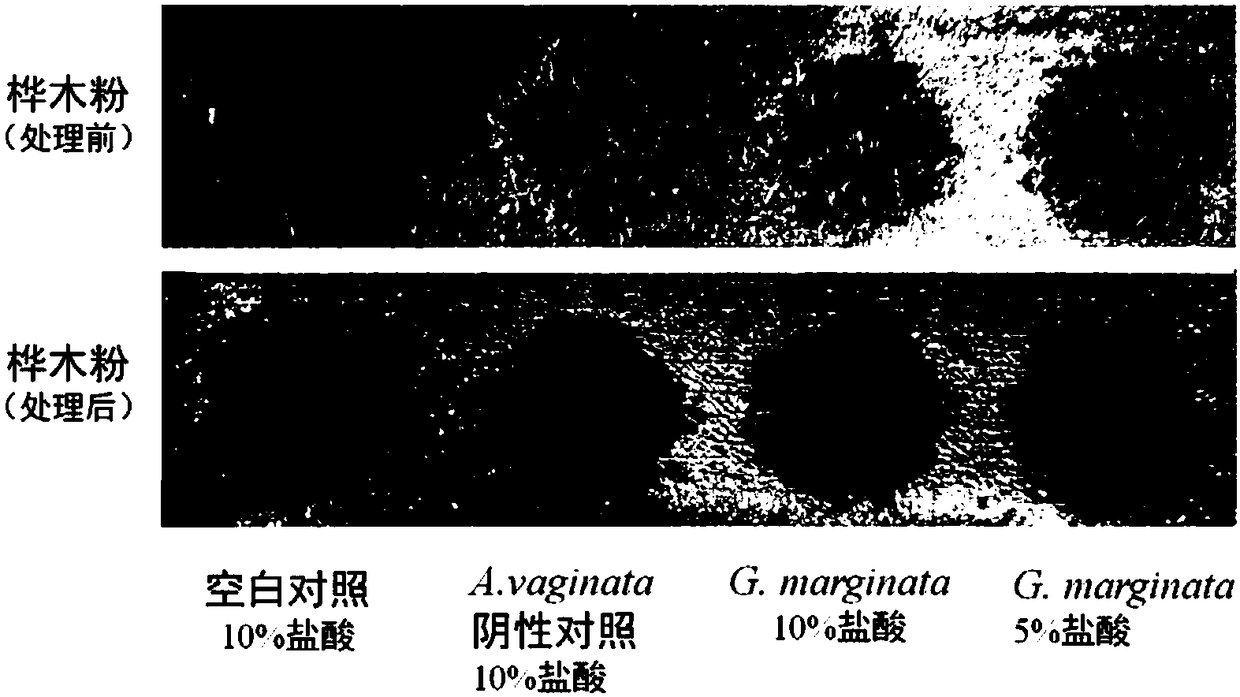
The invention provides a simple and rapid method for identifying extremely toxic mushrooms such as Amanita, Galerina, Lepiota, other mushrooms containing Amanitin, and the like. The method can also be used to detect pure Amanitin. Amanitin and lignin form a blue-green substance with a prominent characteristic in the presence of hydrochloric acid, and through the color development reaction, extremely toxic mushrooms can be rapidly identified within 10 to 30 minutes. The experiment results show that when the hydrochloric acid concentration is 5 to 15%, wood (birch, pine, etc.) can be used to effectively detect Amanitin, MgCl2 can improve the color developing effect; when the hydrochloric acid concentration is 15 to 25%, newspaper can effectively detect Amanitin, and the effect is better, when MgCl2 exists in the solution. The provided method can rapidly and accurately detect Amanita, Galerina, Lepiota, and other mushrooms containing Amanitin, and has an important meaning for mushroom poisoning prevention, understanding of mushroom poisoning reason, and treatment design.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
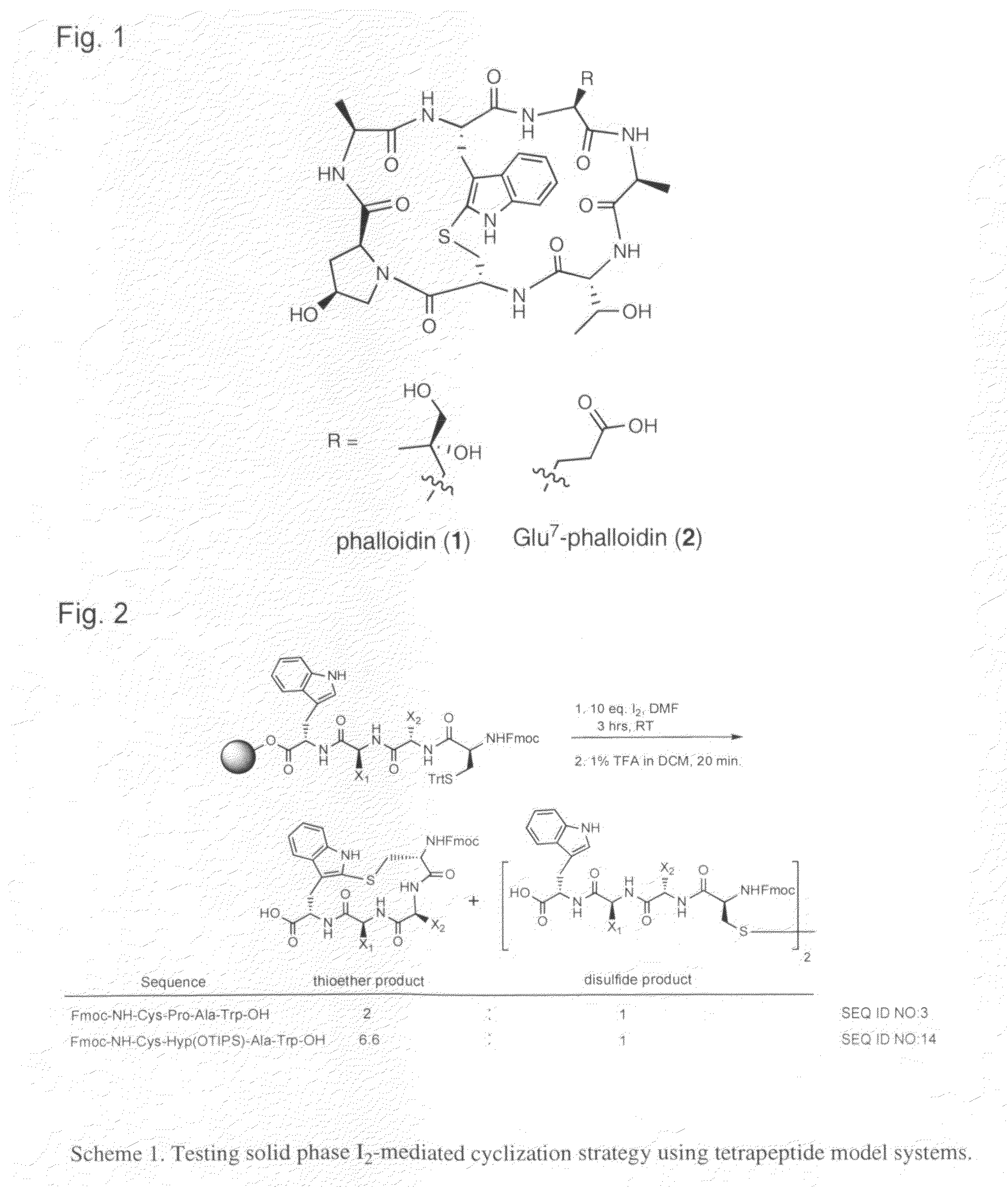
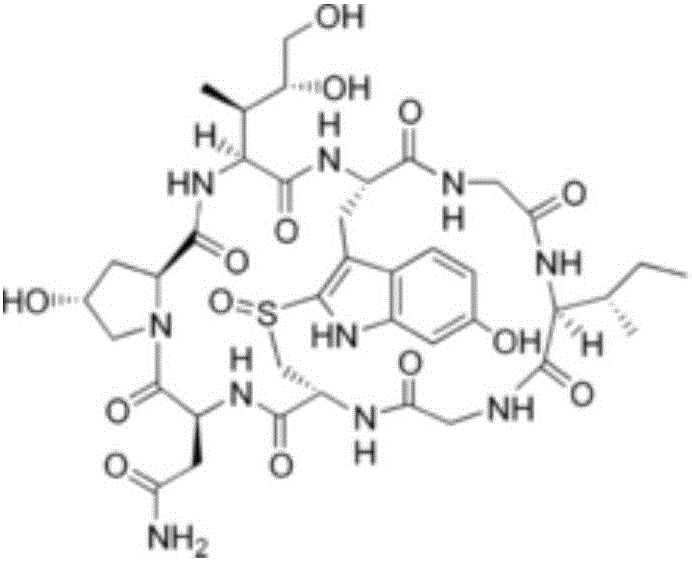
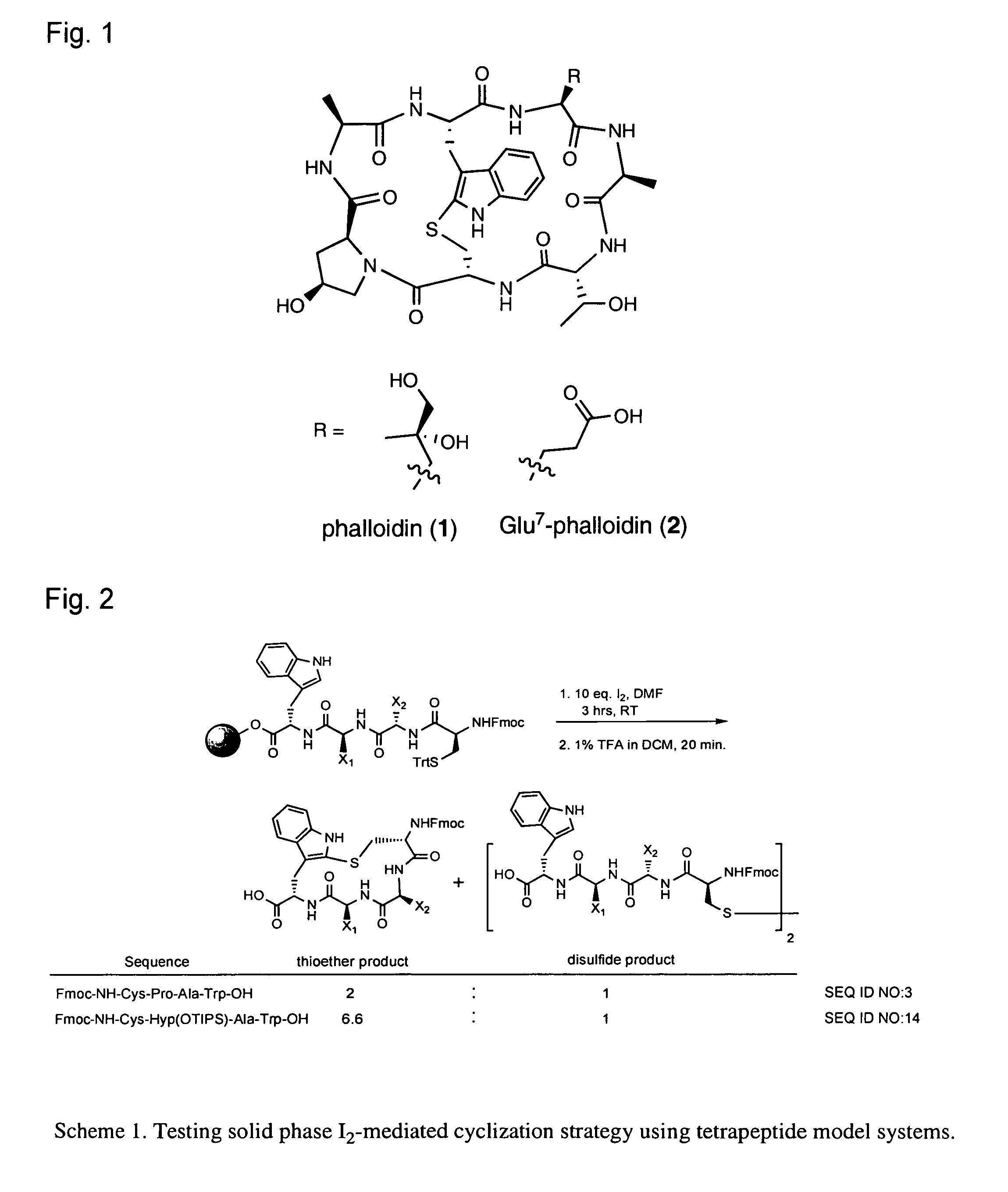
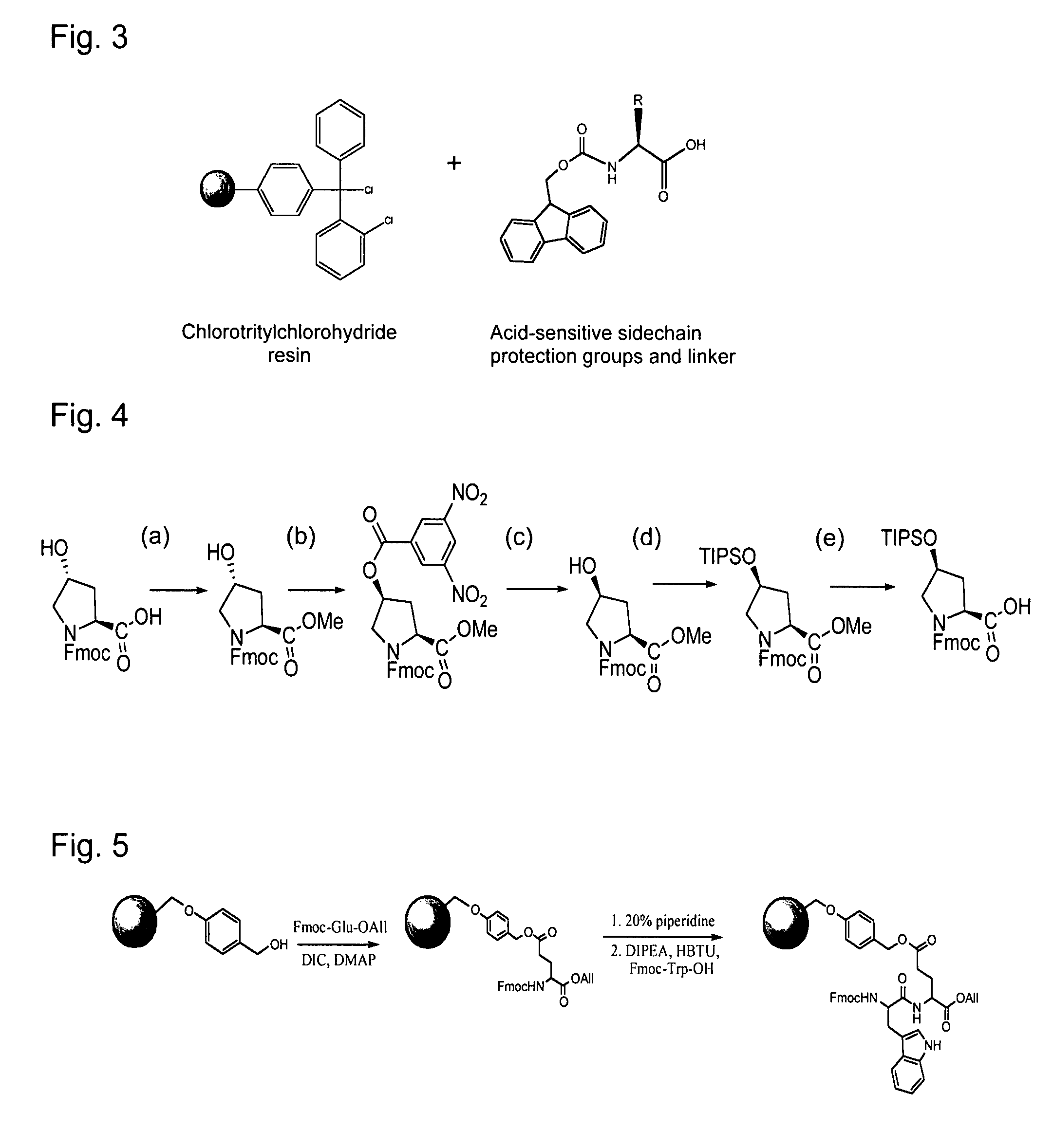
Phalloidin derivatives and methods for their synthesis
InactiveUS20120231996A1Serially reducedReduce in quantityBiocideAntimycoticsPhalloidinActinin binding
The invention provides a cyclomonomer having actin-binding activity. The cyclomonomer is of utility for the study of the molecular biology of actin polymerization. The cyclomonomer is also useful for the study of and treatment of the toxic effects of Amanita sp. poisoning.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
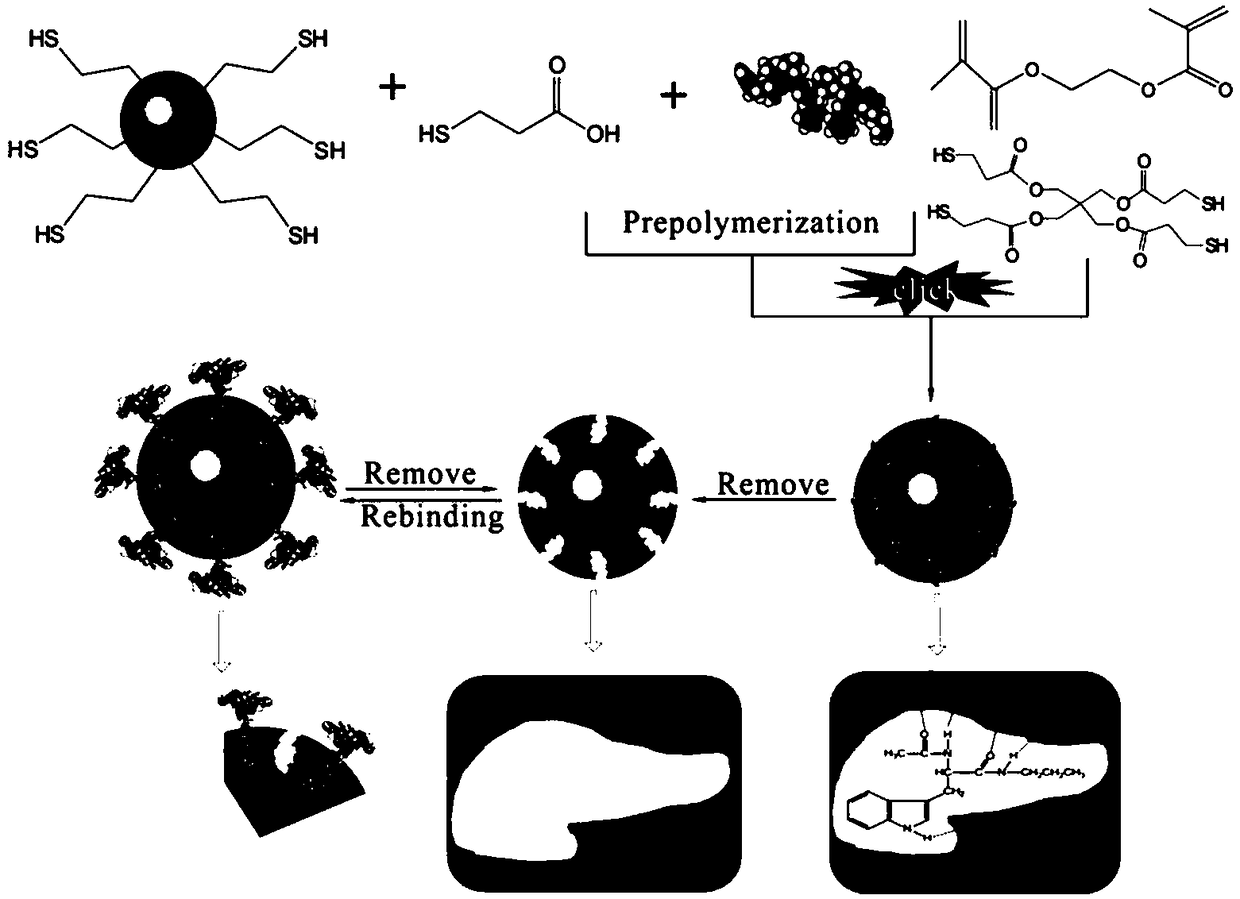
Preparation method of Alpha-amanita hemolysin molecular imprinting material
ActiveCN105885049AShorten the timeEasy to operateOther chemical processesCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention provides a preparation method of an Alpha-amanita hemolysin molecular imprinting material, and relates to the field of a separation material. The method comprises the following steps of S1, uniformly mixing a template molecule, a functional monomer, a cross-linking agent and a solvent; S2, performing sulfhydrylation treatment on the carrier surface; S3, adding a carrier obtained through the treatment in the S2 into a mixed solution prepared in the S1, and performing cross-linking polymerization with the functional monomer; S4, eluting the template molecule from the polymerized carrier surface; S5, performing vacuum drying on the molecular imprinting material obtained through treatment in the S4. The preparation method has the advantages that the experiment operation is simple and convenient; nitrogen introduction and oxygen removal are not needed; the reaction can be triggered by regulating the pH value of a reaction system by triethylamine; the reaction condition is mild; the time is short; the method shows great superiority than that of a traditional molecular imprinting preparation method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Identification and use of genes encoding amatoxin and phallotoxin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising genes and peptides associated with cyclic peptide toxins and toxin production in mushrooms. In particular, the present invention relates to using genes and proteins from Amanita species encoding Amanita peptides, specifically relating to amatoxins and phallotoxins. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention also relates to methods for detecting Amanita peptide toxin genes for identifying Amanita peptide-producing mushrooms and for diagnosing suspected cases of mushroom poisoning. Further, the present inventions relate to providing kits for diagnosing and monitoring suspected cases of mushroom poisoning in patients.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Toxic amanita species identification method based on DNA mini-barcode technology and application
The invention relates to the technical field of food quality and safety detection, and particularly discloses an amanita species identification method based on DNA mini-barcode and application. The method comprises the following steps: extracting toxic amanita genome DNA, then carrying out PCR amplification by utilizing self-designed DNA mini-barcode primers, sequencing a purified PCR product, comparing a DNA mini-barcode fragment sequence obtained by sequencing with a reference sequence in a public database, and carrying out species identification according to the matching similarity of the sequences. The method is simple and convenient to operate and high in accuracy, can identify an artificially simulated digested amanita sample, and has great application potential in analysis of amanita or vomit after mistaken eating and other scenes.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Phalloidin derivatives and methods for their synthesis
The invention provides a cyclomonomer having actin-binding activity. The cyclomonomer is of utility for the study of the molecular biology of actin polymerization. The cyclomonomer is also useful for the study of and treatment of the toxic effects of Amanita sp. poisoning.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Macro fungi insecticide for preventing and controlling aromia bungii
InactiveCN102090422AGood control effectImprove efficacyBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyLepiota helveola
The invention discloses a macro fungi insecticide for preventing and controlling aromia bungii, which contains the following components and the contents thereof: 40% of crude product of lepiota helveola phallotoxin toxins, 35% of crude product of amanita phalloides phallotoxin toxins and 25% of 10-mesh fungus chaff powder. The preparation method comprises the steps of: 1, screening of macro fungi; 2, liquid deep fermentation on a shaking table; 3, ultrasonication and refrigerated centrifugation of fermentation liquid; 4, extraction of crude products of phallotoxin toxins; 5, selection and treatment of a carrier; and 6, formation. The macro fungi insecticide for preventing and controlling aromia bungii has the characteristics of high lethality, strong selectivity, long effective time and high temperature resistance.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
Composition for preventing and controlling diseases and insect pests of atractylodes macrocephala and application of composition
The invention discloses a composition for preventing and controlling diseases and insect pests of atractylodes macrocephala and application of the composition. The composition is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 20 percent to 30 percent of macleaya cordata fruit pod juice, 20 percent to 30 percent of amanita phalloides juice and 40 percent to 50 percent of phytolacca americana fruit juice. The composition disclosed by the invention is prepared through preparing the macleaya cordata fruit pod juice, the amanita phalloides juice and the phytolacca americana fruit juice respectively and then mixing according to a certain ratio. The composition provided by the invention has the advantages simple preparation technology and low cost, and has remarkable prevention andcontrol effects on the diseases and insect pests of the atractylodes macrocephala.
Owner:湖南绿佰珍中药材股份有限公司
Amanitin Molecularly Imprinted Materials for Solid Phase Extraction of α-amanitin and β-amanitin
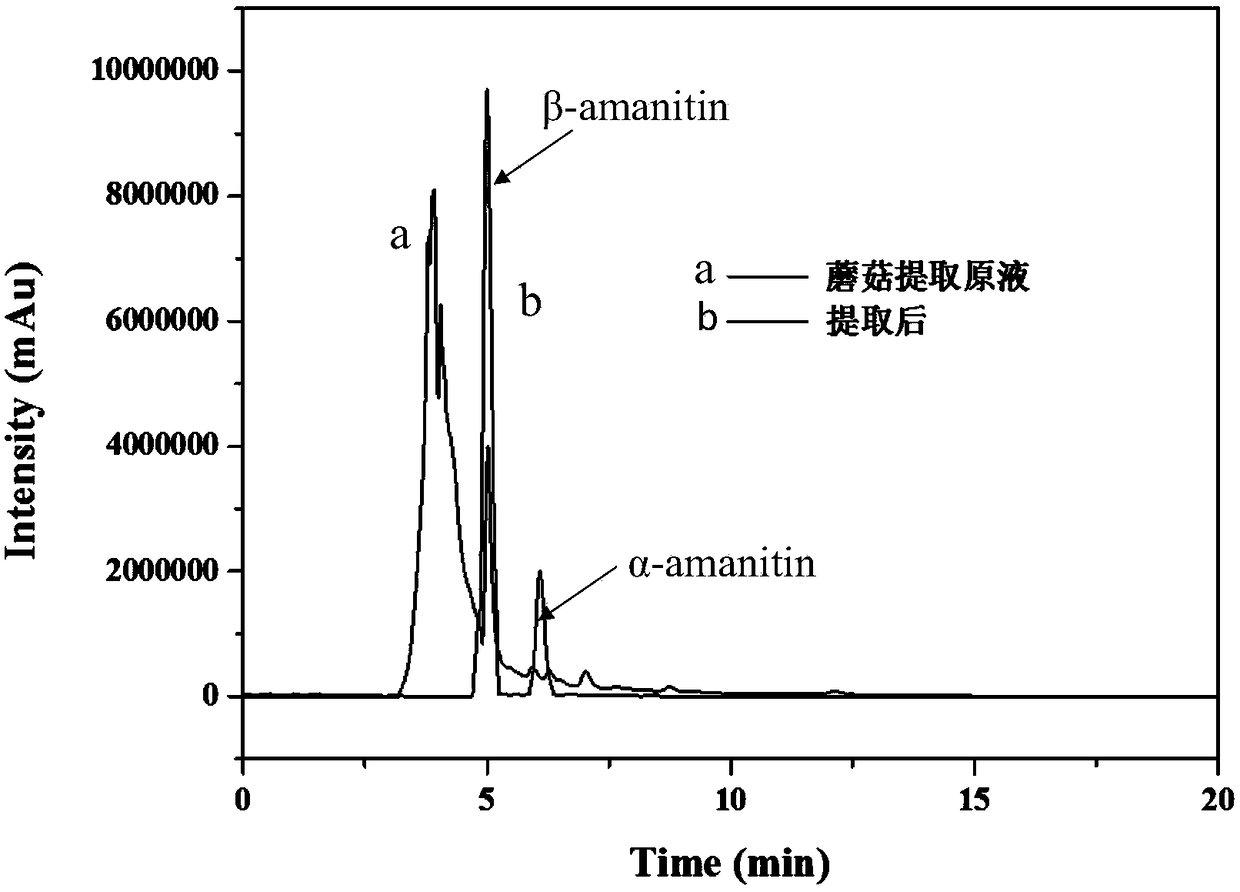
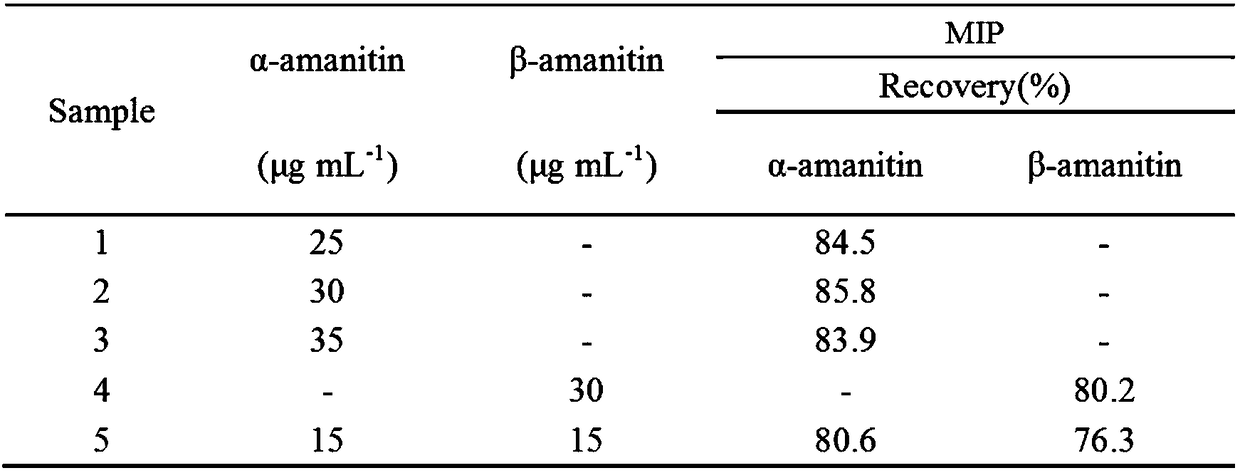
The invention discloses a method for solid-phase extraction of alpha-amanitin and beta-amanitin with an amanitin molecularly imprinted material. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the amanitin molecularly imprinted material with N-acetyl tryptophan propanamide serving as a template molecule is synthesized; secondly, a sample is pretreated, wherein alpha-amanitin and beta-amanitin in the sample to be detected are extracted, and a solution to be detected is obtained; thirdly, solid-phase extraction is carried out, wherein the amanitin molecularly imprinted material prepared in the first step is added into the solution to be detected, and the amanitin molecularly imprinted material is separated after oscillation; fourthly, alpha-amanitin and beta-amanitin in the amanitin molecularly imprinted material are eluted with a certain volume of an elution solvent, and eluant is collected; fifthly, the concentration of alpha-amanitin and the concentration of beta-amanitin in the eluant are measured with the HPLC. According to the method, the detection method of combining amanitin molecularly imprinted material extraction and the HPLC is established, and alpha-amanitin and beta-amanitin in the complex sample are enriched through the amanitin molecularly imprinted material, so that matrix interference is reduced, the sensitivity, accuracy, precision and selectivity of the method are improved, and the detecting sensitivity on alpha-amanitin and beta-amanitin is greatly improved.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
A method and application of poisonous Amanita species identification based on dna micro-barcoding technology
ActiveCN111575397BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenomic DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of food quality and safety detection, and specifically discloses a DNA micro-barcode-based identification method and application of Amanita species. The method extracts the genomic DNA of the poisonous Amanita, then uses self-designed DNA micro-barcode primers for PCR amplification, sequences the purified PCR products, and compares the sequences of DNA micro-barcode fragments obtained by sequencing with the reference sequences in the public database. The comparison is carried out, and the species identification is carried out according to the matching similarity of the sequences. This method is easy to operate and has high accuracy. It can identify Amanita samples after artificial digestion, and has great application potential in the analysis of Amanita or vomit after accidental ingestion.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
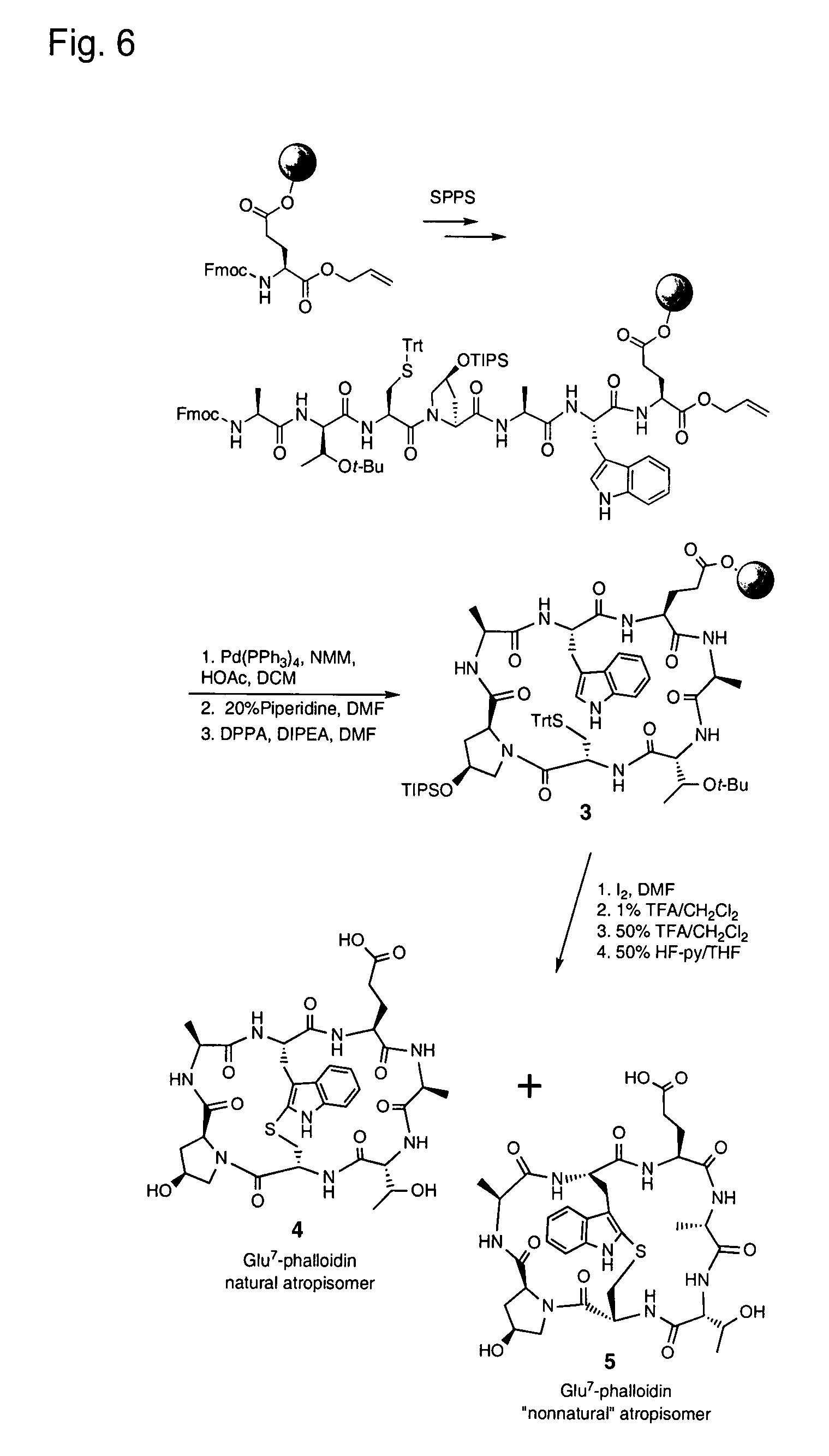
Derivatives of amanita toxins and their conjugation to a cell binding molecule
The present invention is related to novel cytotoxic agents, derivatives of Amanita toxins of Formula (I), wherein , - - - , R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, X, L, m, n and Q are defined herein, the preparation and the therapeutic uses in the targeted treatment of cancers, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
Owner:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH
Establishing method for indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides as symbiotic plant
InactiveCN102715089BBuild a symbiotic systemConvenient researchMicroorganismsHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporocarp (fungi)
The invention relates to an establishing method for indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides which is a symbiotic plant, and belongs to the field of biotechnology (plant tissues and Fungus cultivation). An overwhelming majority of amanita belongs to ectomycorrhizal fungi, can not be yet subjected to artificial cultivation at present, and can be hardly developped and utilized; and growth and development of sporocarps of the amanita has a close relationship with cyclobalanopsis glaucoids which is a symbiotic plant. The establishing method is characterized in that myceliums are induced through the sporocarps of amanita flavipes for reproduction; aseptic seedlings and potted seedlings are successfully obtained by using seeds of cyclobalanopsis glaucoides, collected in the field; reproduced myceliums are inoculated to the roots of the aseptic seedlings and the potted seedlings respectively; the result shows that inoculated seedlings are more exuberant than the non-inoculated seedlings and have more leaves, the leaves of inoculated seedlings are dark green, disease resistance of inoculated seedlings are reinforced; and therefore, the indoor symbiotic relationship of amanita flavipes and cyclobalanopsis glaucoides is innovatively established, and a technological reserve is provided for future researches on symbiotic mechanism and mechanism generated in the sporocarps of amanita.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
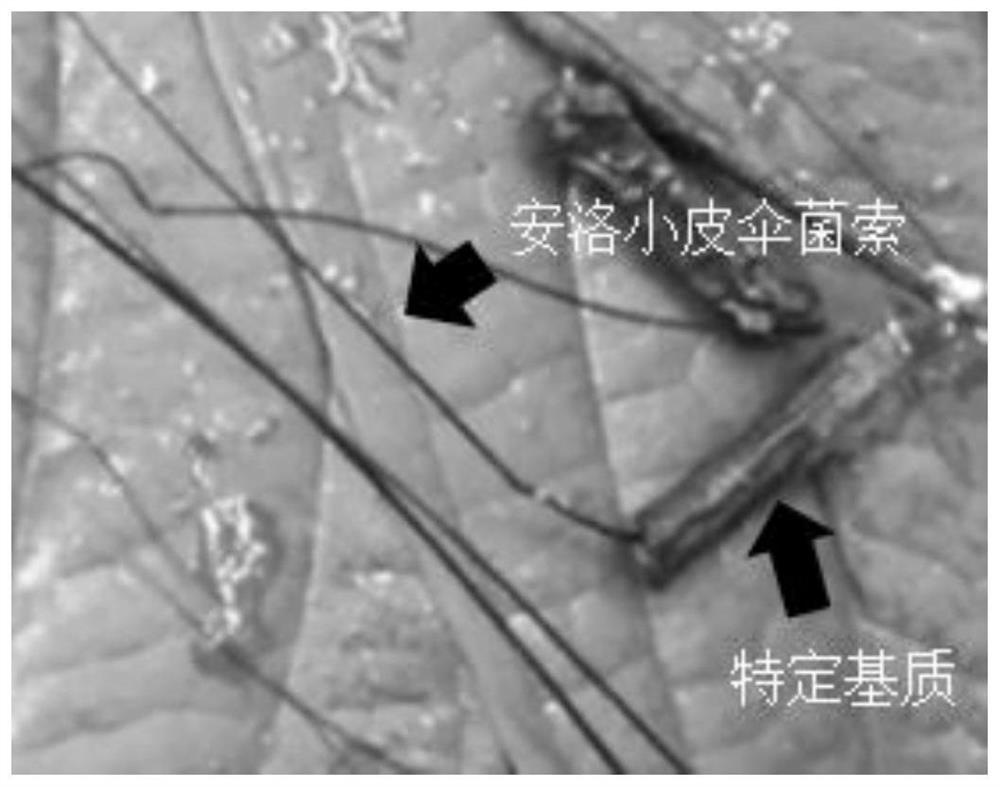
A kind of obtaining method of wild fungus of rare medicinal Anluo diphtheria
ActiveCN109055230BEfficient developmentEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyWild species
The invention relates to a method for obtaining wild strains of rare medicinal Dermophyllum anluo, which comprises: collecting wild Dermomycetes anluo; separating the strains; and purifying the strains. The present invention utilizes the wild Dermoderma anluo strain for the first time to obtain the Dermoderma anluo strain, which has the advantage of simple operation, and can use the obtained highly active strain of Dermoderm anluo to cultivate and ferment for the treatment of neuropathy. The research and development of more effective drugs for pain, bruises, etc. has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
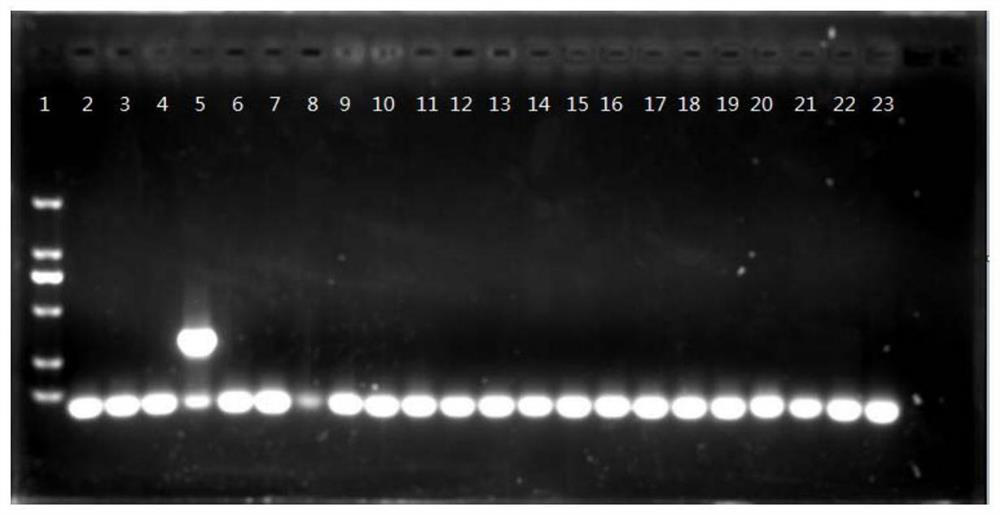
Primer group, kit and method for identifying poisonous mushroom Amanita concentrica
ActiveCN114058726AQuick distinctionRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideRapid identification
The invention discloses a primer group, a kit and a method for identifying poisonous mushroom Amanita concentrica, the primer group comprises a primer AconF and a primer qAconR, the nucleotide sequences of the primer AconF and the primer qAconR are as follows: AconF: GTCTCTCTTCTTGCTTGTTTC, and qAconR: AAATCCAAAACACACTCAAAAAGAGC; the identification method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting genome DNA of a sample to be detected; 2) carrying out PCR amplification on the extracted genome DNA by adopting the primer group or the kit; and 3) detecting whether the PCR amplification product contains a target amplification fragment, and identifying the sample containing the target amplification fragment as the Amanita concentrica. The invention establishes a poisonous mushroom Amanita concentrica rapid identification technical system with wide applicability, innovates the detection means and measures, and realizes rapid identification of toxic mushroom.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Method for co-culturing amanita subfrostiana mycelium by using mycorrhizal fungus and saprobic fungus
InactiveCN103667084BFast growthGood effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmanita chepangiana
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A rapid detection method for highly poisonous mushrooms
ActiveCN106568769BRapid McFarland Color ReactionMcFarland color reaction is easy to use and accurateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTreatment designLepiota
The invention provides a simple and rapid method for identifying extremely toxic mushrooms such as Amanita, Galerina, Lepiota, other mushrooms containing Amanitin, and the like. The method can also be used to detect pure Amanitin. Amanitin and lignin form a blue-green substance with a prominent characteristic in the presence of hydrochloric acid, and through the color development reaction, extremely toxic mushrooms can be rapidly identified within 10 to 30 minutes. The experiment results show that when the hydrochloric acid concentration is 5 to 15%, wood (birch, pine, etc.) can be used to effectively detect Amanitin, MgCl2 can improve the color developing effect; when the hydrochloric acid concentration is 15 to 25%, newspaper can effectively detect Amanitin, and the effect is better, when MgCl2 exists in the solution. The provided method can rapidly and accurately detect Amanita, Galerina, Lepiota, and other mushrooms containing Amanitin, and has an important meaning for mushroom poisoning prevention, understanding of mushroom poisoning reason, and treatment design.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Amanita amanita peptide detection method for non-disease diagnosis purpose
PendingCN114839284AExtended detection windowImprove the detection rateComponent separationICT adaptationPhallotoxinBinding state
The invention relates to the technical field of detection, in particular to a non-disease-diagnosis amanita peptide detection method. The detection method comprises the operation of detecting amatoxin in a to-be-detected sample, wherein the to-be-detected sample is prepared by performing protein degradation treatment on the to-be-detected sample. A to-be-detected sample used in the detection method is prepared after the to-be-detected sample is subjected to protein degradation treatment, and protein in the protein binding state amatoxin can be degraded through the protein degradation treatment, so that more free state amatoxin is released. Therefore, the free amatoxin contained in the used sample to be detected is composed of the original free amatoxin and the free amatoxin released by the protein binding state amatoxin, that is, the detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously detecting the free amatoxin and the protein binding state amatoxin contained in the sample to be detected; therefore, the detection window period of the amatoxin can be obviously prolonged, and the detection rate of the amatoxin is effectively increased.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心职业卫生与中毒控制所
Alternative solid-liquid culture method of Amanita hongtuo mycelium
InactiveCN103688753BReproduce fastFast growthHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyAmanita chepangiana
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Macro fungi insecticide for preventing and controlling aromia bungii
InactiveCN102090422BGood control effectImprove efficacyBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyLepiota helveola
The invention discloses a macro fungi insecticide for preventing and controlling aromia bungii, which contains the following components and the contents thereof: 40% of crude product of lepiota helveola phallotoxin toxins, 35% of crude product of amanita phalloides phallotoxin toxins and 25% of 10-mesh fungus chaff powder. The preparation method comprises the steps of: 1, screening of macro fungi; 2, liquid deep fermentation on a shaking table; 3, ultrasonication and refrigerated centrifugation of fermentation liquid; 4, extraction of crude products of phallotoxin toxins; 5, selection and treatment of a carrier; and 6, formation. The macro fungi insecticide for preventing and controlling aromia bungii has the characteristics of high lethality, strong selectivity, long effective time and high temperature resistance.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
Optimized culturing method for promoting growth of Amanitaflavipes mycelia
The method relates to a culturing method for promoting growth of Amanitaflavipes mycelia, belonging to the technical field of culturing of macro fungi.. The culturing method is characterized in that mycelia are induced with mature sporocarps without pileus and a culturing medium is improved so as to provide a simple optimized culturing medium with short culturing circle, low cost and capability of promoting the fast growth of mycelia. Amanita belongs to special and precious economical macro fungi, is high in value and wide in application range and has potential application prospect in the field of development of new specific medicines such as anti-tumor, antibacterial and antiviral, sedative or narcotic medicines, but Amanita is hard to develop and use so far because of rear resource, difficulty in artificial acclimatization, inactive chemical synthetics of toxins and other problems. According to the method, Amanitaflavipes mycelia collected from Shishan, Wuding, Yunnan is used as the raw material and innovative breakthrough is made aiming at the problems limiting the culturing, such as difficulty in mycelium induction and slow growth of mycelia, thereby providing conditions for large-scale culturing and artificial acclimatization of Amanitaflavipes mycelia in the further.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Primer group and kit for identifying ochrata ochrata and application of primer group and kit
PendingCN114182039ANo cross reactionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular identification
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular identification, in particular to a primer group and a kit for identifying Gyromitra infusus and application of the primer group and the kit. The primer group provided by the invention can specifically amplify the nucleic acid of the deer antler, and does not have cross reaction with the nucleic acid of the white beveled fungus, the deer antler, the morchella, the bodybell fungus, the brown tray verruca and the beveled beveled fungus which are easy to confuse, and the nucleic acid of other macro fungi such as the boletus amber, the choriomyelon, the amanita coleopleatus and the boletus mucilaginosus, so that the nucleic acid of the deer antler and the nucleic acid of the boletus mucilaginosus are not subjected to cross reaction; the specificity is strong, and the primer group can be used for identifying the ochracea ochracea. Furthermore, according to the identification method provided by the invention, the specific identification of the deer antler can be completed within 90 minutes by utilizing the primer group, the detection result can be directly observed by naked eyes, and the method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the sensitivity is high (the detection limit is 1ng / mu L), the method is suitable for a base layer, and the field detection can be realized.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
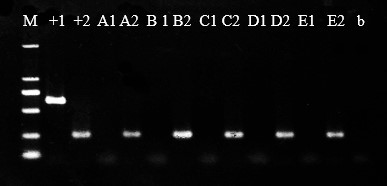
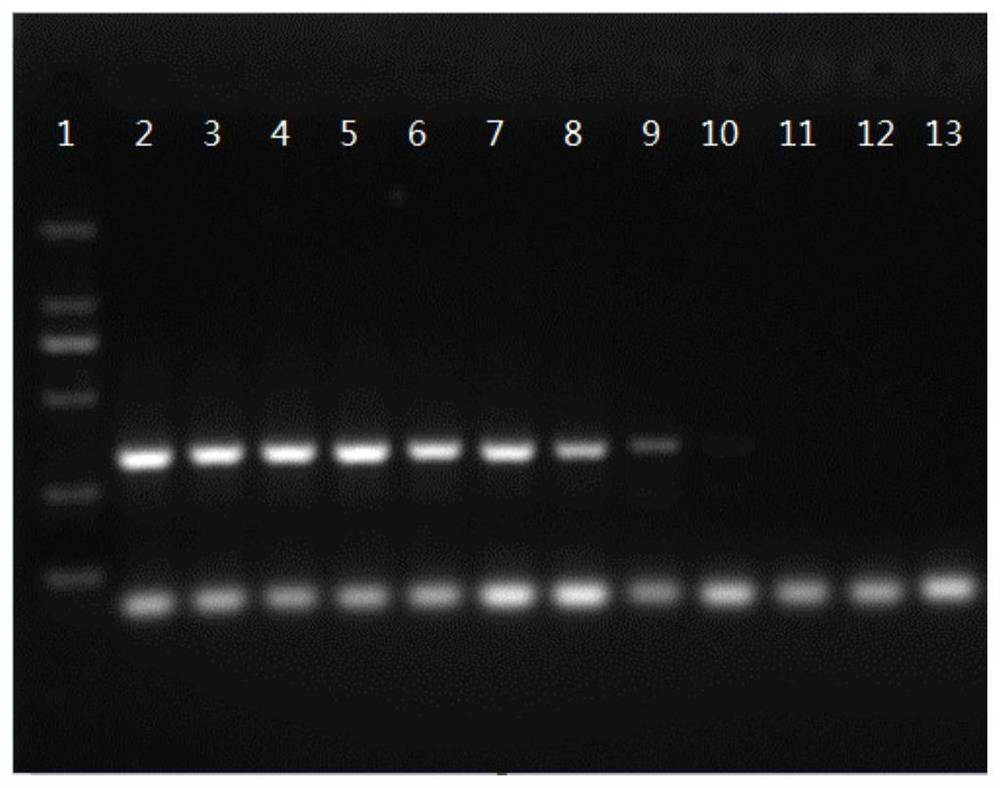
Nucleic acid molecular primer, method and kit for identifying Chinese amanita
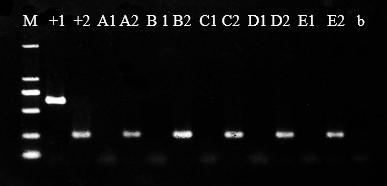
InactiveCN113502343ARapid molecular identificationStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAmanita chepangianaMolecular identification
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecular primer, a method and a kit for identifying Chinese amanita. The DNA sequence of the nucleic acid molecule primer is LG02.173F: 5 '-CGATGACGATGACGACTC-3'; LG02.173R: 5 '-ATTGGTGAGAGGCTTGGA-3'. The method for identifying the chinese amanita comprises the following steps: S1, extracting DNA of a to-be-detected sample of the Chinese amanita; S2, carrying out PCR amplification by taking the sample DNA as a template for PCR amplification and taking nucleic acid molecular primers LG02.173F and LG02.173R as amplification primers; and S3, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection on the PCR amplification product in the step S2. The nucleic acid molecular primer disclosed by the invention can be used for carrying out rapid molecular identification on the Chinese amanita sinensis sporocarp and strain, and has the advantages of good specificity, less material consumption, simple method and capability of completing inspection within 2 hours.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com