Primer group, kit and method for identifying poisonous mushroom Amanita concentrica
A technology of primer sets and kits, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, and resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve problems such as less attention and research, difficult morphological identification, life safety and health risks, etc. To achieve the effect of strong detection specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1. Design of primers and probes
[0049] 1. Select the mushrooms to be tested
[0050] Mushroom samples for testing: wet samples were stored at -20°C, dry samples were stored at room temperature, and the mushroom samples used for testing are shown in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1 Types of mushroom samples tested
[0052]
[0053] 2. Design of specific primers for the poisonous mushroom Amanita amanita
[0054] DNA analysis of the ITS genes of seven kinds of mushrooms: Amanita chinensis, Amanita false brown cloud, Light red Amanita, Russula spp. Sequencing, the sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO.5~NO.11 in turn, combined with the BOLD system to retrieve the genome ribosome sequences of all tested mushrooms.
[0055]The obtained sequences were compared with DNAMAN software (a highly integrated molecular biology comprehensive application software developed by LynnonBiosoft, U.S.A.) to find the sites that can specifically distinguish the poisonous mushroom Amanitati...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2. Primer specificity and sensitivity verification
[0060] (1) DNA extraction
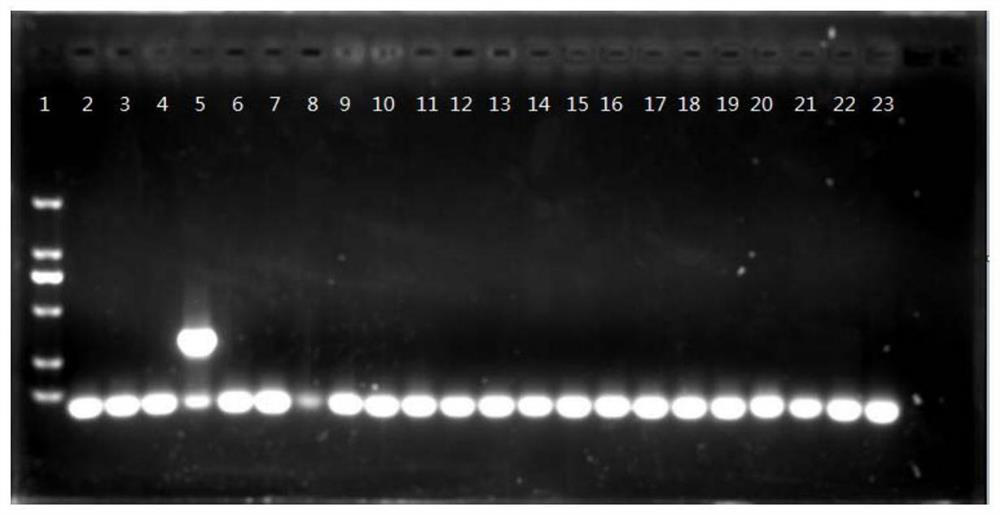
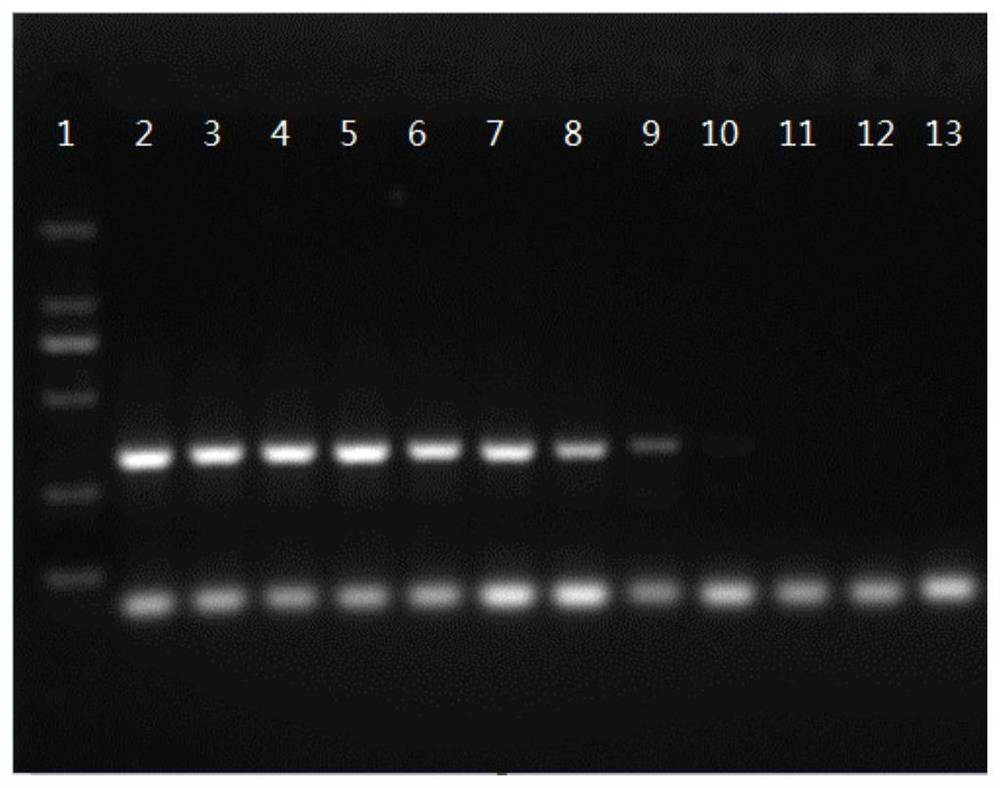
[0061] Genomic DNA was extracted from the mushroom samples in Table 1 using the "Plant Genomic DNA Extraction Kit" (purchased from Beijing Suolaibao Technology Co., Ltd.) for the specificity verification of the primers. For the specific operation process, refer to the instructions of the DNA extraction kit.
[0062] (2) Primer specificity verification:
[0063] Using the DNA extracted in step (1) as a template, PCR amplification was performed using the primers in Table 2 (amplification reagent 2×TaqPCR MasterMix was purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd., Cat. No. KT201), and by continuously adjusting the PCR reaction Reagent dosage and annealing temperature, time, etc. determine the final reaction system.
[0064]
[0065] After the amplification reaction is over, take 5 μl of PCR-specific amplification products and perform electrophoresis detection ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3. Real-time fluorescent PCR identification of poisonous mushroom Amanita ringscale
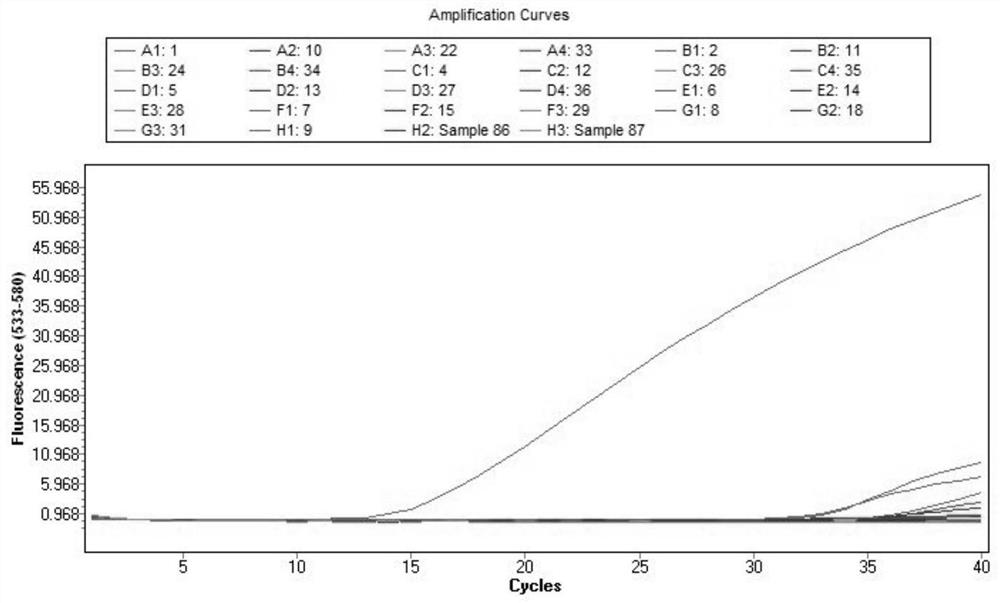
[0072] According to the method of embodiment 2, extract the genomic DNA of Amanita ring scale as real-time fluorescent PCR amplification template, and extract the genomic DNA of other mushroom species as contrast, with ddH 2 O is a negative control, and a real-time fluorescent PCR reaction was carried out using the Taqman fluorescent probe method.
[0073] The qPCR reaction system is: a total volume of 20 μl, including 10 μl of 2×T5 Fast qPCR Mix (Beijing Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Cat. No. TSE301), 1 μl of primers AconF / qAconR at a concentration of 10 μM, and 0.5 μl of probe AconU at a concentration of 10 μM , DNA template 1μl, the balance is ddH 2 O. The qPCR amplification program was: 95°C for 10min; 95°C for 10s, 60°C for 40s, 40 cycles; and finally cooling at 40°C for 30s.
[0074] The result is as image 3 As shown, the real-time fluorescent PCR amplification was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com