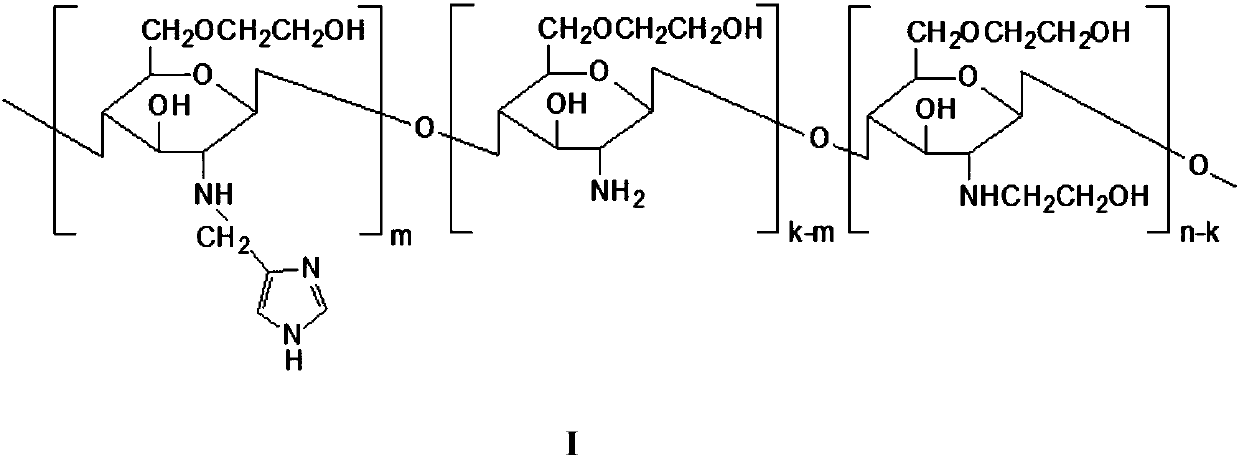
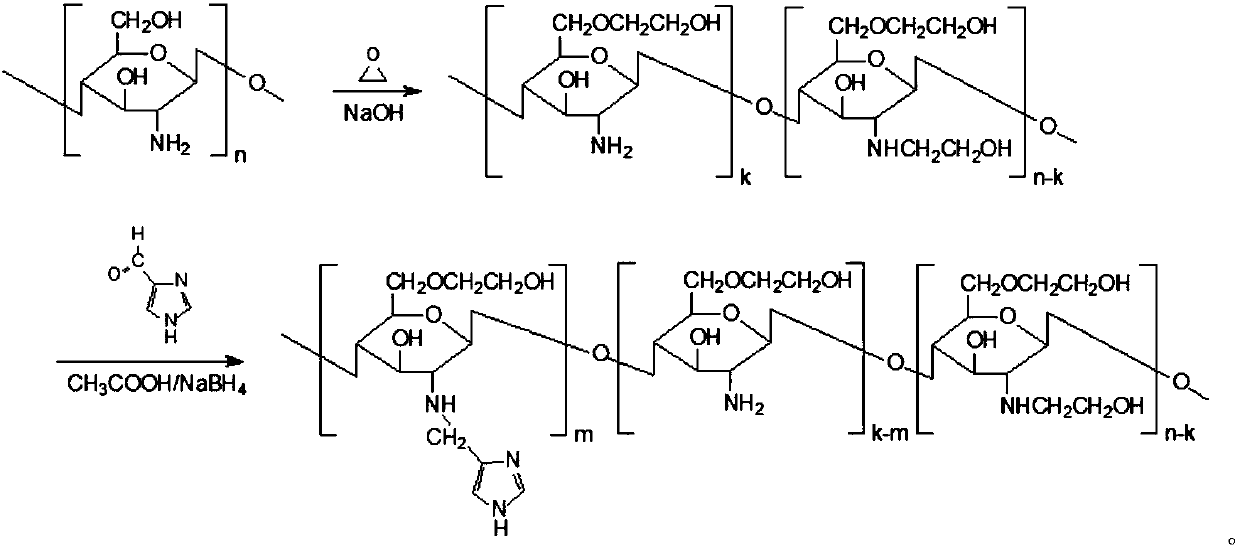
A chitosan derivative with endosome escape function and its preparation method and application
A technology of chitosan derivatives and escape function, which can be applied to medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulas, etc., and can solve the problems of poor drug loading effect and poor effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1 material synthesis
[0028] The material characterization method is as follows: by 1 H NMR and organic element analysis were used to determine the degree of substitution of imidazolylmethyl and hydroxyethyl, respectively. Determination of Critical Micelle Concentration of MHC Using Pyrene Fluorescence Spectrometry
[0029] 1. Synthesis of hydroxyethyl chitosan (HE-Cs): Weigh 1 gram of chitosan (50KDa 100KDa), add 10ml of 2% HAc, stir until completely dissolved, then add 10ml of 50% NaOH. Afterwards, the temperature was raised to 40° C. for 12 hours, and 10 ml of ethylene oxide was added after cooling down with ice, and the temperature was raised to 50° C. for 18 hours. Cool to room temperature and add 5mol / L HCl to adjust the pH to neutral. The obtained product was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min, filtered through a 0.8 μm microporous membrane, dialyzed and freeze-dried to obtain the product.
[0030] Elemental analysis shows that different ethylene ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 drug loading process optimization
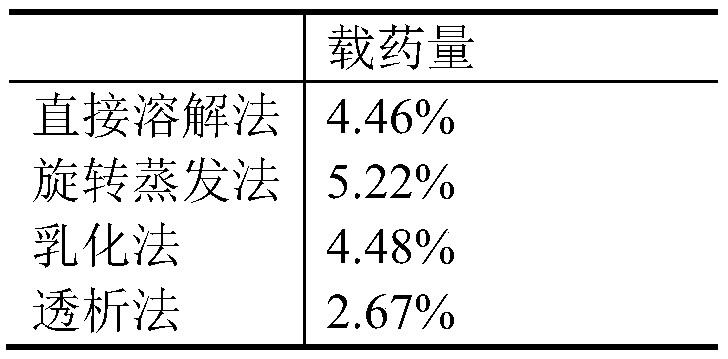
[0039] Taking quercetin as a model drug, the micelles prepared by direct dissolution method, rotary evaporation method, dialysis method and emulsification method with different drug loading were compared. Different solvents (ethanol, dimethyl sulfoxide, methanol), carrier concentrations (1%, 0.67%, 0.5%), and drug-carrier ratios (1:25, 1:10) of quercetin were compared using a single factor method. , 1:5) on the drug loading, the process was optimized with the drug loading as an index, and the drug-loading micelles reaching a certain concentration were made. The results are shown in Table 3 and Table 4 below.
[0040] Table 3 Drug-loaded micelles obtained by different preparation methods
[0041]
[0042] Table 4 single factor inspection process optimization results
[0043]
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Cellular uptake and intracellular endosome escape
[0045] Fluorescent probes with coumarin-6 (C6) as hydrophobic drugs are entrapped in micelles, and are observed and evaluated by laser confocal.
[0046] For the convenience of microscopic observation, MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in DMEM for 24 hours in a 24-well plate. After incubation with micelles for 4 hours, the cells were washed three times with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258 before fluorescence photography, and the cellular uptake of micelles was observed by fluorescence microscopy.
[0047] CLSM was used to observe the subsequent internalization of micelles and endosomal escape. MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in a glass-bottomed culture dish for 24 hours, washed three times with PBS at 2 hours, 4 hours and 12 hours after adding C6-MHC micelles, and then used LysoTracker TM Red staining, 4% paraformaldehyde fixation, CLSM observation.
[0048]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com