Calculation method for determining high-pressure physical parameters of foamy oil
A technology of physical parameters and calculation methods, which is applied in the direction of earthwork drilling, production fluid, wellbore/well components, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult gas dissolution, lack of system calculation method of foam oil high-pressure physical parameters, long stirring time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
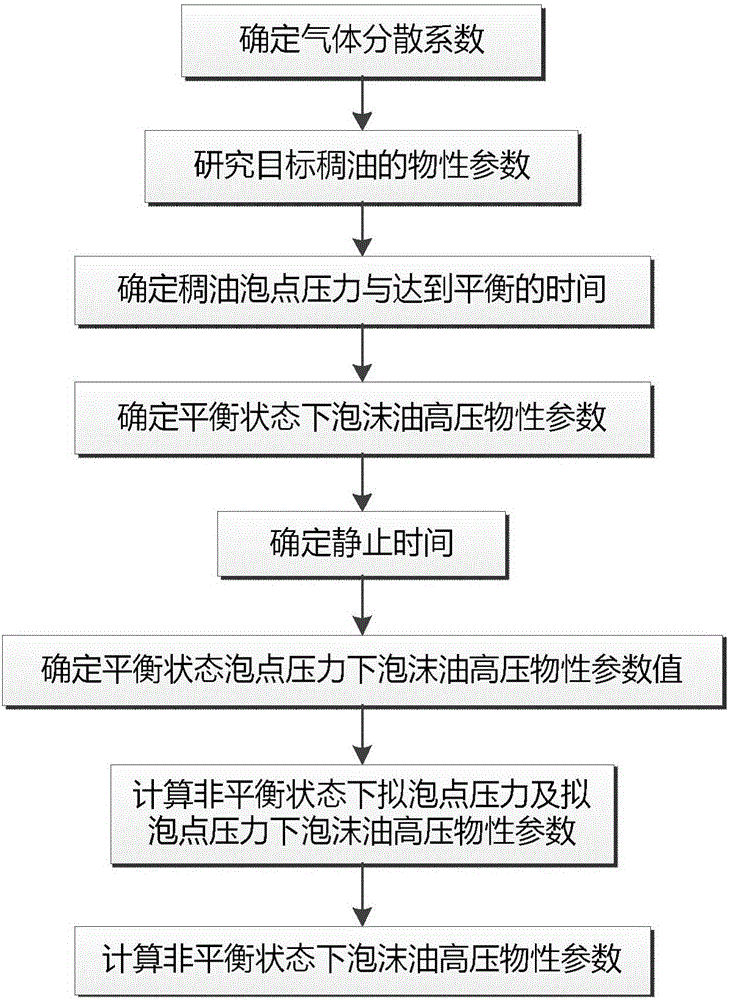
[0076] A calculation method for determining the high-pressure physical parameters of foam oil, the calculation flow chart is shown in figure 1 As shown, the calculation steps are as follows:
[0077] Step 1. Determine the gas dispersion coefficient α under different resting times according to the ratio of foam oil to dissolved gas to oil at different resting times;
[0078] Step 2. Determine the physical parameters of the special heavy oil under study, including: dissolved gas-oil ratio R at bubble point pressure sb , reservoir temperature T, dead oil density ρ STO ;
[0079] In this example 1, it is determined that the special heavy oil studied is the heavy oil sample 9, and the dissolved gas-oil ratio R at the bubble point pressure is sb 31m 3 / m 3 , reservoir temperature T is 43℃, dead oil density ρ STO 0.998g / cm 3 .
[0080] Step 3. Determine the bubble point pressure p of the special heavy oil b and the time t to achieve equilibrium after oil and gas are complete...
Embodiment 2
[0141] A calculation method for determining the high-pressure physical property parameters of foam oil as described in Example 1, the difference is that the gas dispersion coefficient α of heavy oil sample 1 is calculated by this method. According to the gas-oil ratio of foam oil dissolved in different static times obtained from indoor experiments, the gas dispersion coefficient α is determined at different static times. The calculation method is shown in formula (1):
[0142] α=(x-y) / x (1)
[0143] x is the total volume of dissolved gas in special heavy oil under a certain pressure, m 3 ; y is the volume of dissolved gas in foam oil under non-equilibrium state, m 3 .
[0144] In this embodiment, the gas dispersion coefficient α is calculated according to the formula (1) under different static times, see Figure 4 . Depend on Figure 4It can be seen that, no matter what the static time is, the free gas dispersion coefficient increases first and then decreases with the dec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com