electromagnetic actuator
An electromagnetic actuator, electromagnetic field technology, applied in the direction of circuits, magnets, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of reduced response of moving output pins, increased sliding resistance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
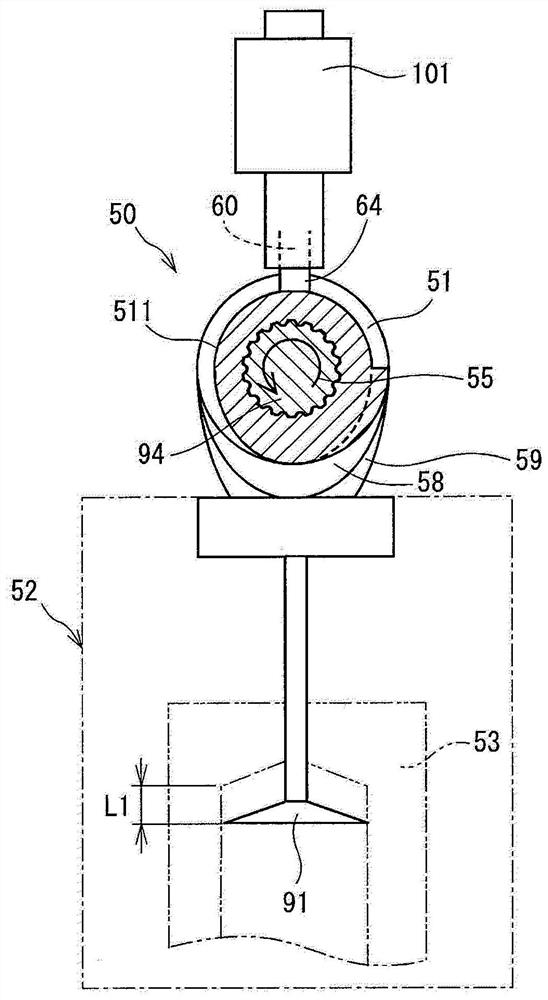
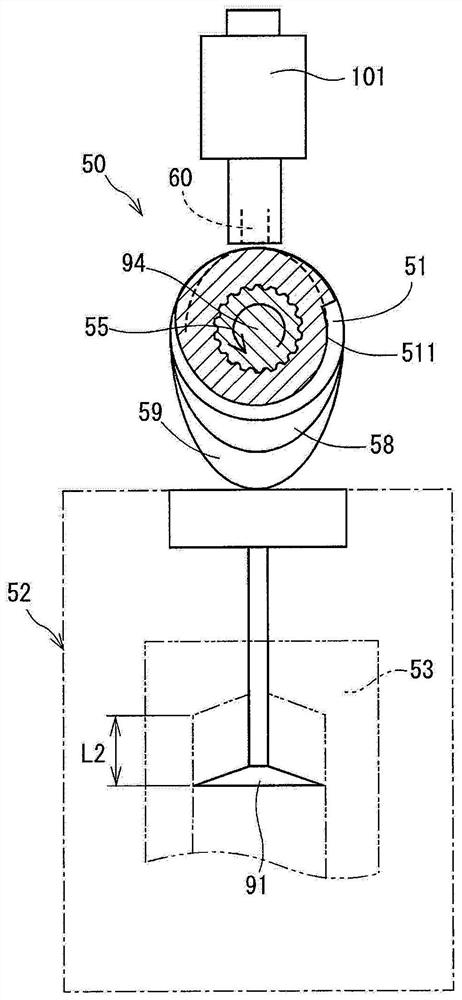
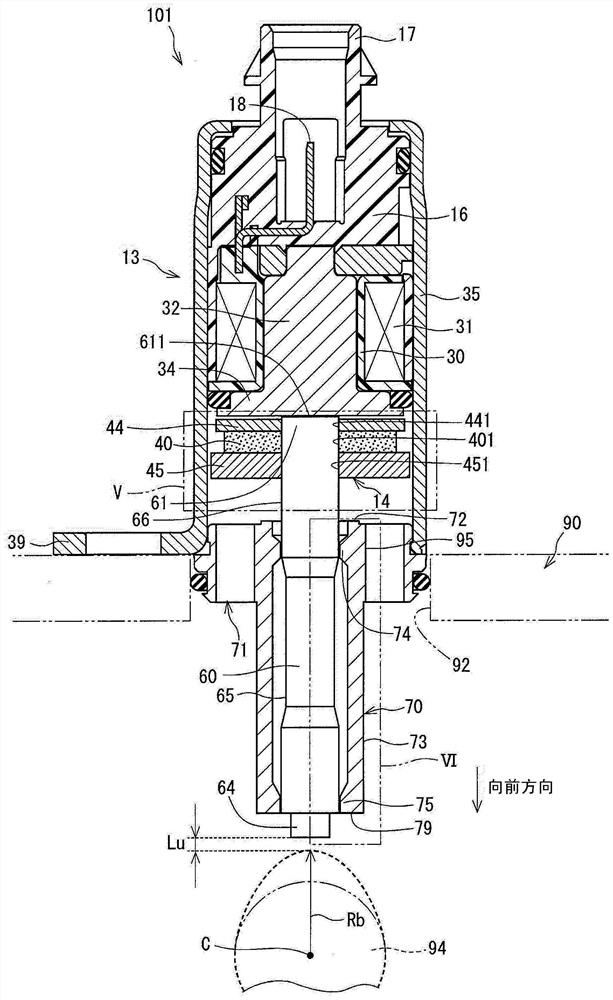
[0044] will refer to Figure 3 to Figure 10 The structure of the actuator 101 will be described.
[0045] Such as image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, the actuator 101 is composed of a stationary unit 13 and a movable unit 14 .
[0046] The stationary unit 13 is fixed on the engine head 90 and is composed of a coil 31 , a stator 32 , a yoke 35 and a guide member 70 .
[0047] In the coil 31 , a winding is wound around the outer circumference of the bobbin 30 . The bobbin 30 is made of resin and fitted to the stator 32 . The bobbin 30 insulates the winding of the coil 31 from the stator 32 .
[0048] The resin molding unit 16 is provided on the rear side of the bobbin 30 of the coil 31 , that is, on the side opposite to the movable unit 14 . The connector 17 is integrally formed with the resin molding unit 16 .
[0049] When power is supplied to the coil 31 from an external power source (not shown) via the terminal 18 of the connector 17 , the coil 31 generates a magnetic fi...
no. 2 approach
[0133] The electromagnetic actuator 102 of the second embodiment differs from the actuator 101 of the first embodiment in the position of the first support portion and the position of the radially inward recessed portion.
[0134] Such as Figure 11 As shown, when the output pin 60 is in its initial state, the first radially inner corner 742 of the first support portion 74 is located therein axially separated from the rear radially outer corner 653 of the output pin 60 in the rearward direction toward the output pin 60 The rear end 61 position. The same advantages as those of the first embodiment can also be obtained in the second embodiment.
no. 3 approach
[0136] The electromagnetic actuator 103 of the third embodiment differs from the actuator 101 of the first embodiment in the structure of the stationary unit and the structure of the movable unit.
[0137] Such as Figure 12 As shown, the actuator 103 of this embodiment has a stationary unit 113 and a movable unit 114 .
[0138] The movable unit 114 has an output pin 160 and an armature 180 .
[0139] The armature 180 is made of a magnetic material, and has a connection portion 181 on the front side and a flange portion 182 (magnet opposing portion 182 ) on the rear side. The armature 180 is movable together with the output pin 160 in the axial direction.
[0140] The main part of the armature 180 is located in the radially inner space of the coil 131 .
[0141] The connection part 181 has a connection hole 183 extending in the axial direction and having a bottom end. The rear end 61 of the output pin 160 is inserted into the connection hole 183 so that the output pin 160 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com