Method of distinguishing mesenchymal stem cells and method of determining purity of mesenchymal stem cells
A quality stem cell, purity technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, embryonic cells, animal cells, etc., can solve problems such as non-existence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0046] Example 1: Flow Cytometry Analysis of Mixed Populations of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) and Fibroblasts
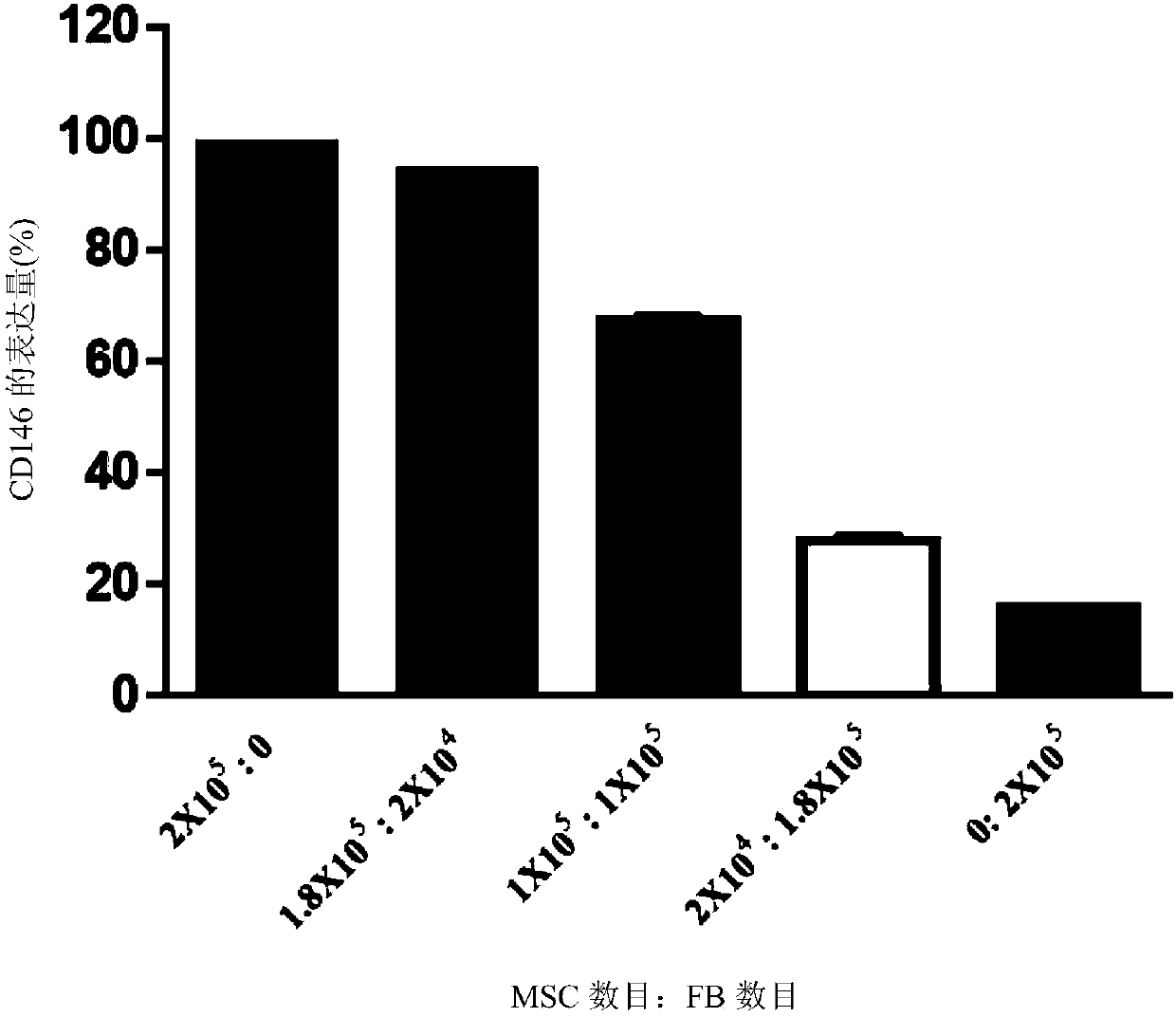
[0047] In order to prove that CD146 can be used as a biomarker for the separation of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and fibroblasts, MSCs and fibroblasts derived from umbilical cord were mixed at the following ratio (MSC : number of cells of fibroblasts) mix: 2x10 5 : 0, 1.8x10 5 : 2x10 4 , 1x10 5 : 1x10 5 , 2x10 4 : 1.8x10 5 , or 0: 2x10 5 . CD146 in each microcentrifuge tube was then analyzed by flow cytometry + group. refer to figure 1 , the results showed that through flow cytometry, CD146 detected by anti-CD146 antibody (anti-human CD146-V450, BD biosciences company) + The percentage of the population decreases proportionally to the increasing fibroblast population.
example 2
[0048] Example 2: The expression level of CD146 is still maintained as the number of subcultures increases
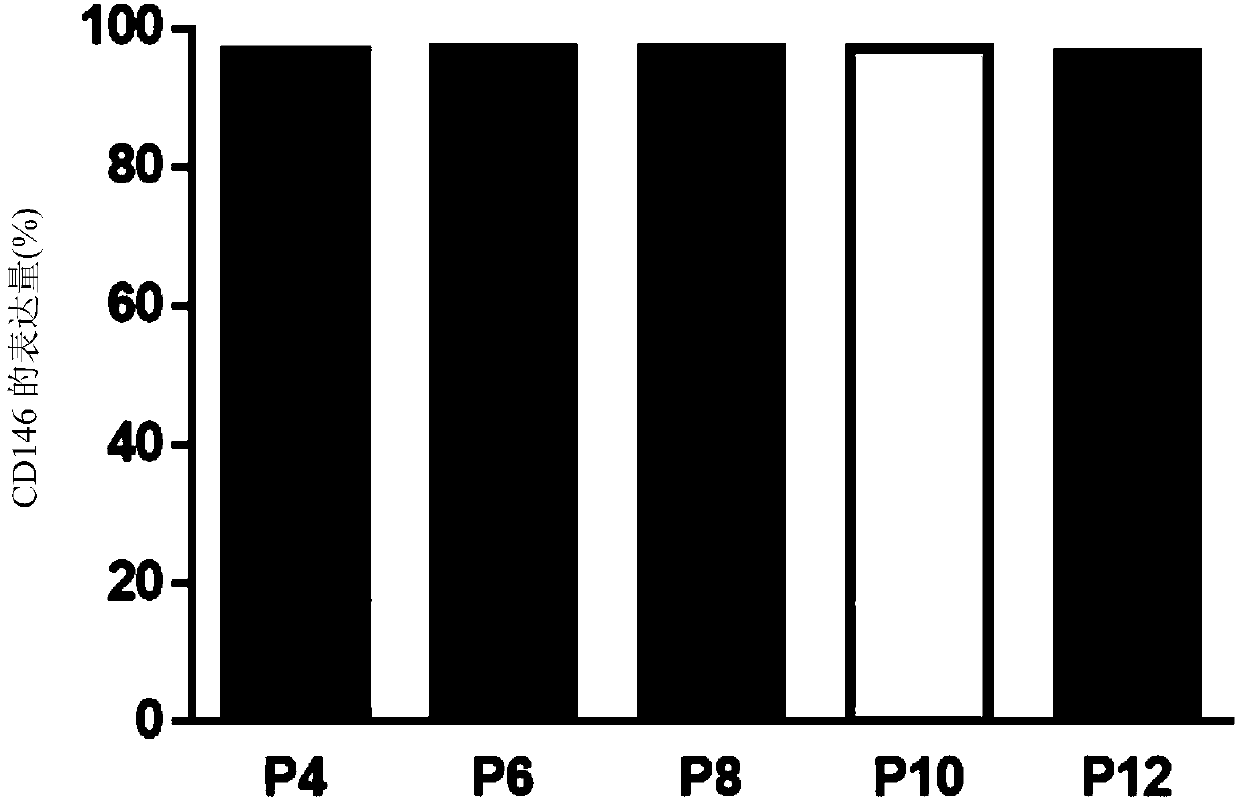
[0049] The MSCs derived from the umbilical cord were harvested at different passage numbers (passage numbers: 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12), and the expression of CD146 was analyzed by flow cytometry. The results showed that after subculture, the expression level of CD146 was still maintained ( figure 2 ).
example 3
[0050] Example 3: Assessment of the purity of MSCs
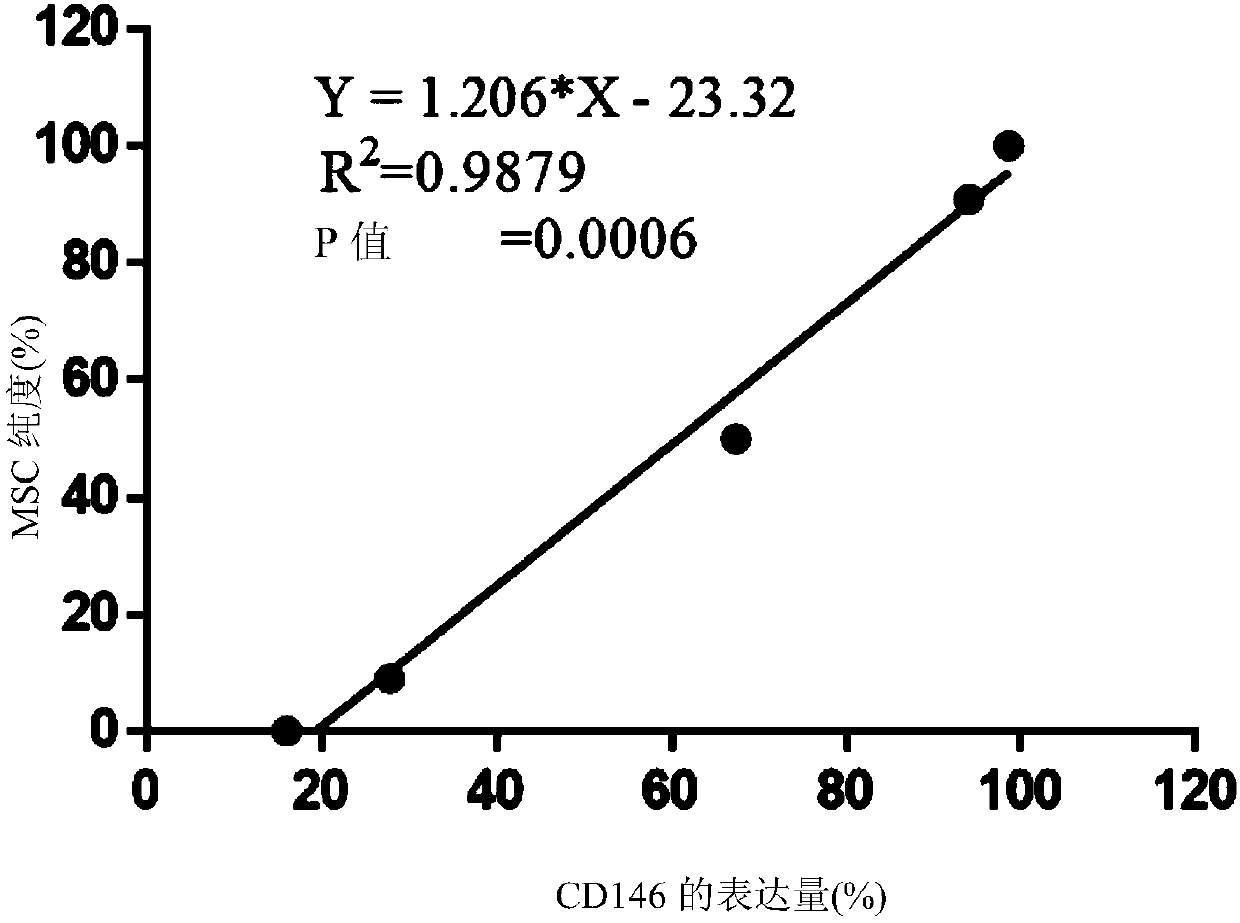
[0051] In a microcentrifuge tube, mix umbilical cord-derived MSCs with fibroblasts in the following ratio (MSC: cell number of fibroblasts): 2x10 5 : 0, 1.8x10 5 : 2x10 4 , 1x10 5 : 1x10 5 , 2x10 4 : 1.8x10 5 , or 0: 2x10 5 . CD146 in each microcentrifuge tube was then analyzed by flow cytometry + group. Subsequently, the relationship between the purity (%) of MSCs and the percentage of cells expressing CD146 was analyzed by simple linear regression, the results of which are shown in image 3 . The regression equation is Y=1.206X-23.32, where Y is the purity (%) of MSCs, and X is the percentage of cells expressing CD146. The results confirmed that there is a linear relationship between the expression level of CD146 and the purity of MSC.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap