Liquid crystal display device and driving method thereof
A technology of a liquid crystal display device and a driving method, which is applied to static indicators, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as high cost and affecting panel light transmittance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0077] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
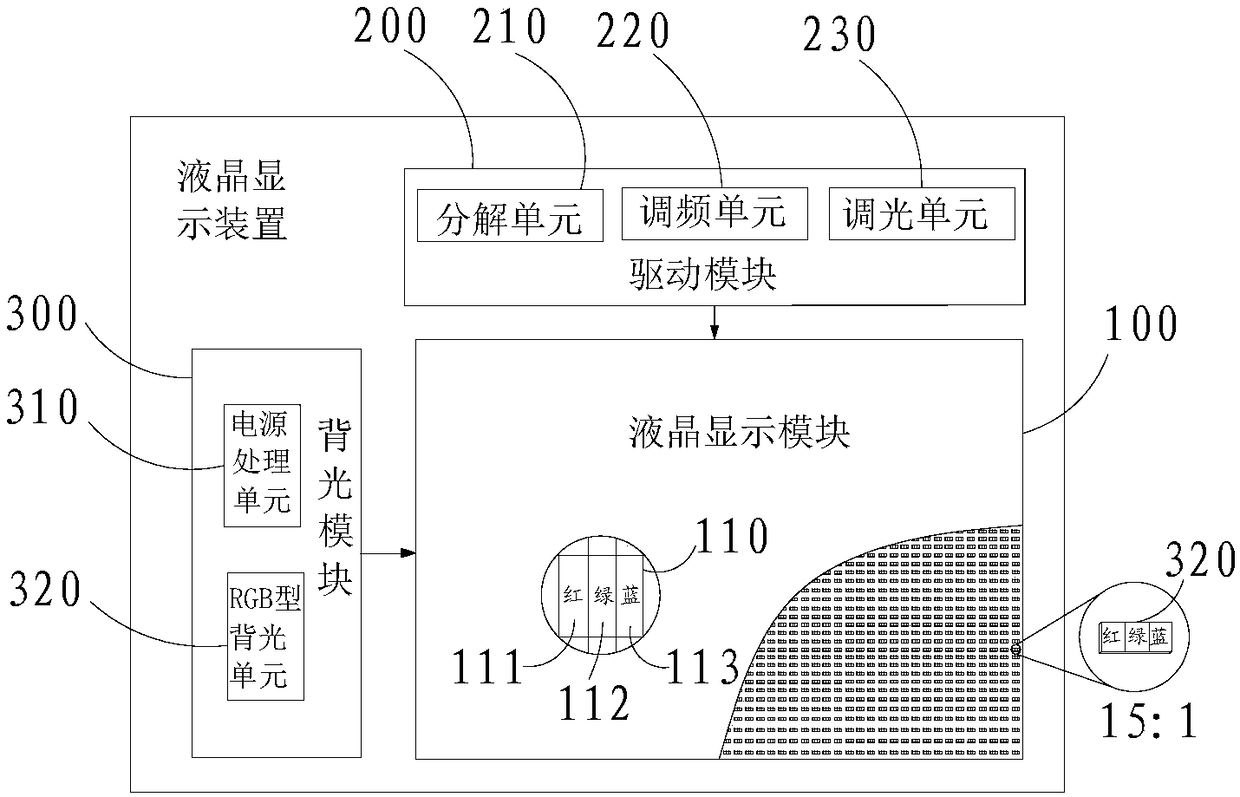
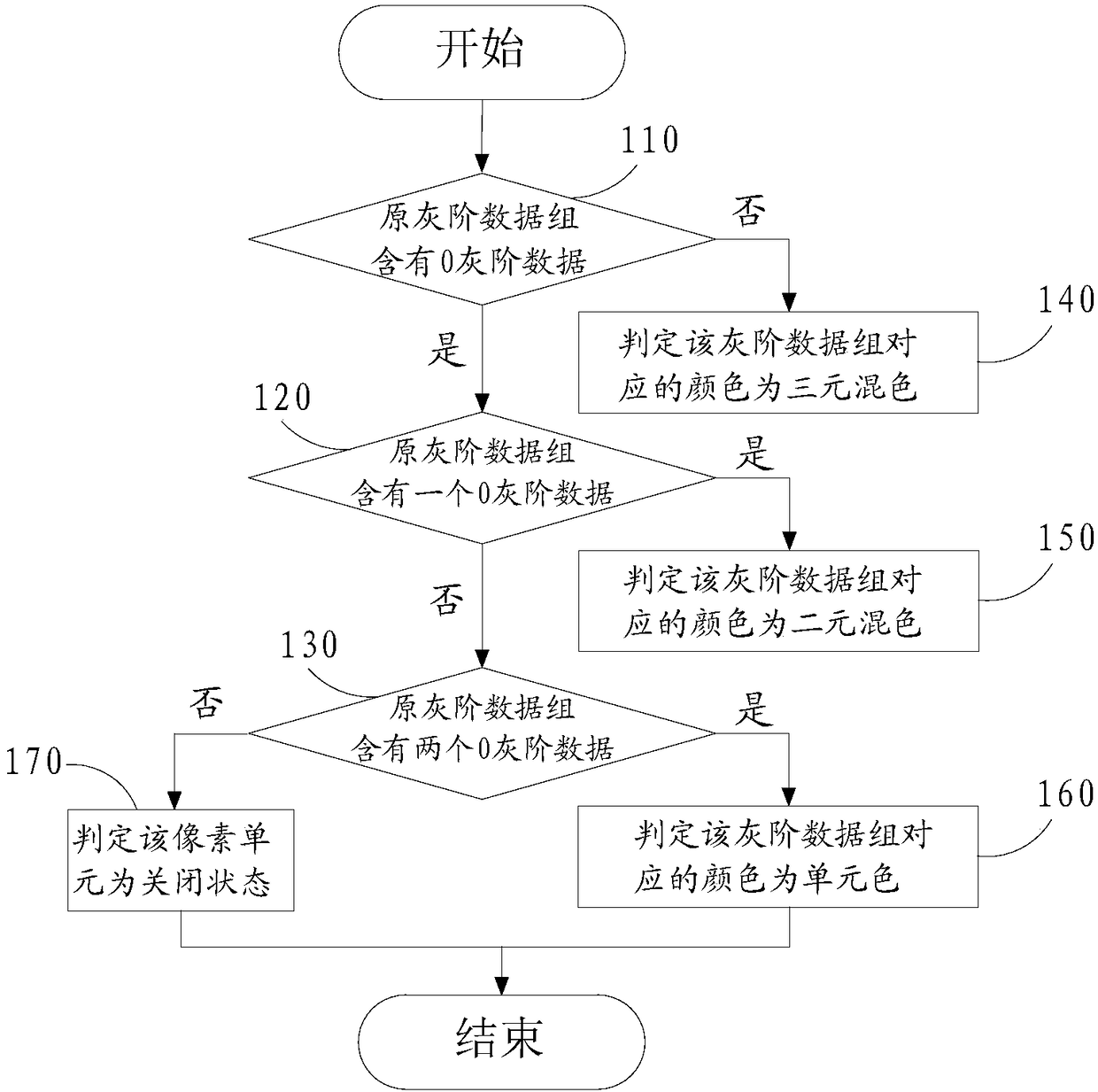
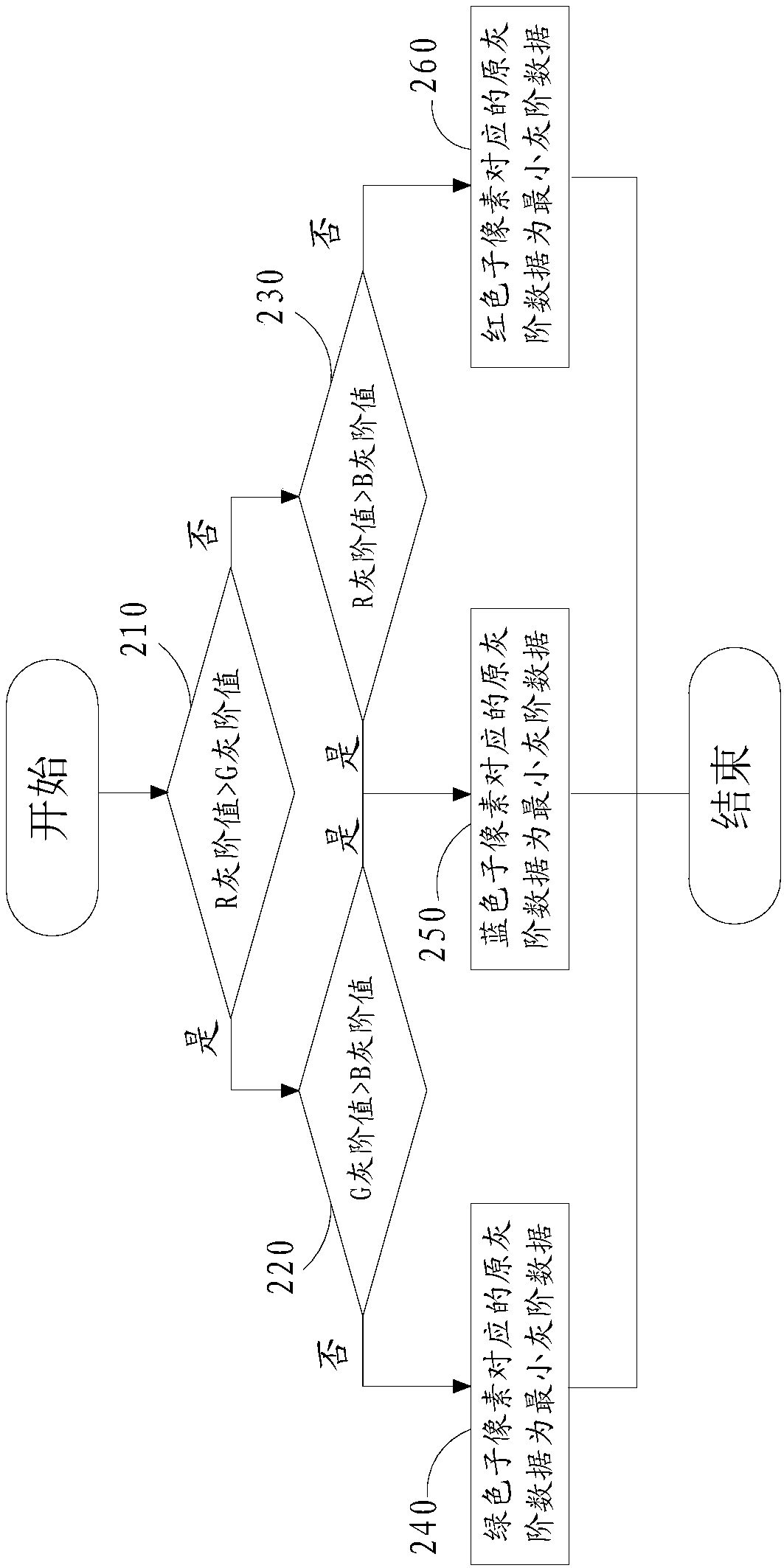
[0078] A method for driving a liquid crystal display device, such as figure 1 As shown, the liquid crystal display device includes: a display module 100 for displaying graphic information. The display module includes a plurality of pixel units 110 arranged in an array. The pixel unit 110 includes a red sub-pixel 111 , a green sub-pixel 112 and a blue sub-pixel 113 . The display module 100 is divided into at least two mutually independent display areas. And the backlight module 300 is provided with a plurality of backlight units 320 . The backlight unit includes a red light source, a green light...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com