Aorticorenal ganglion detection
A kidney and catheter technology, applied in the field of catheter components, devices for the treatment of hypertension and related conditions, can solve problems such as limited
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0167] consider Figure 22 As a schematic diagram of the setup to implement method 1 using unipolar selection. As previously discussed, the device may be configured to connect any electrode on the catheter distal assembly to the terminals (153 and 154) of the stimulation generator 63 . In this example, specific electrodes on the catheter distal assembly will be connected to terminals 153 . Throughout the described procedure, terminal 154 is connected to the dispersion pad. For this discussion, sensor element 58 measures blood flow velocity and is connected to monitoring unit 66 . The catheter distal assembly is positioned such that electrodes 42 - 49 are in good electrical contact with the upper side wall of renal artery 59 .
[0168] The following is an example of a search algorithm for searching for a target location. For a flowchart of the algorithm, see Figure 38 . It begins by stimulating the catheter electrode closest to the ostium, ie, electrode 42, and then sele...
Embodiment approach 2
[0195] consider Figure 23 and Figure 24 As a schematic diagram of the apparatus used to implement method 2.
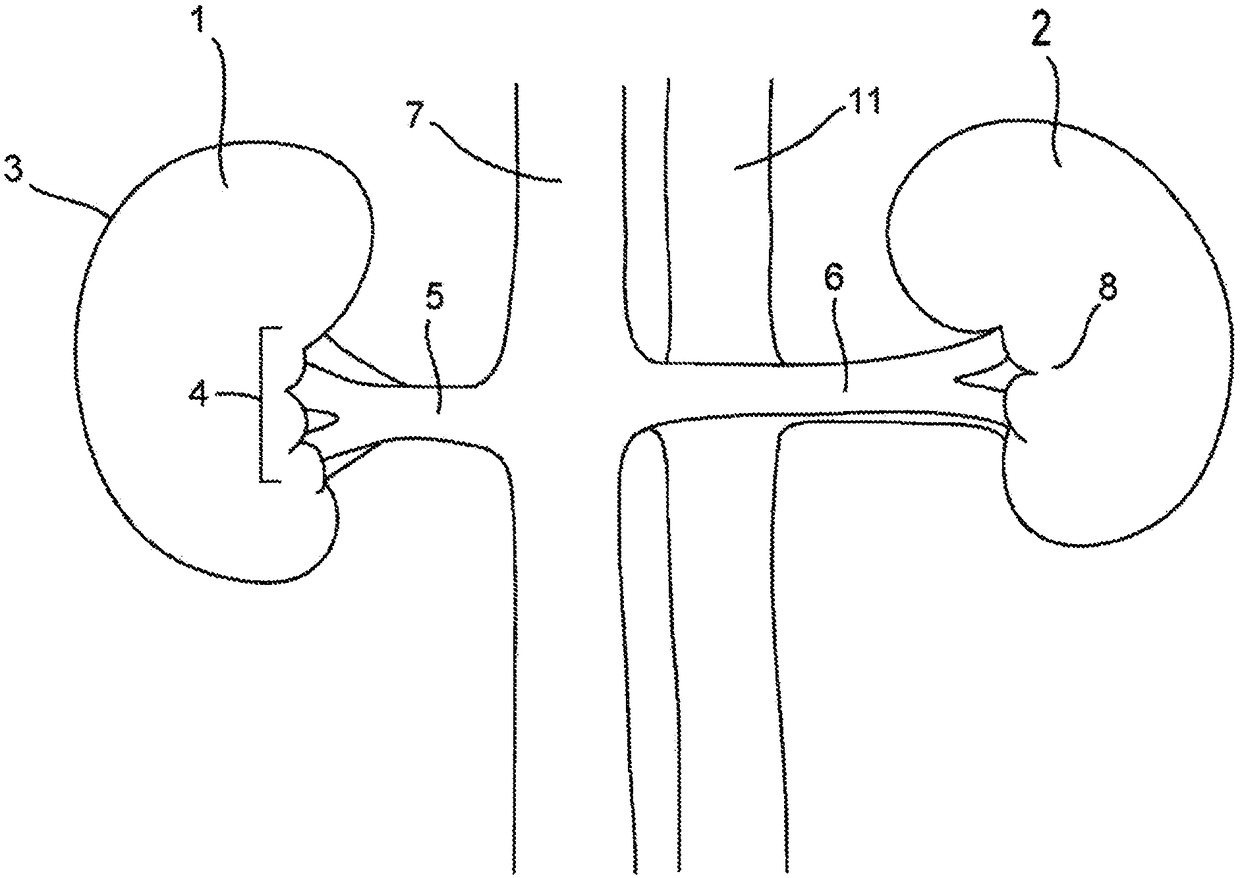
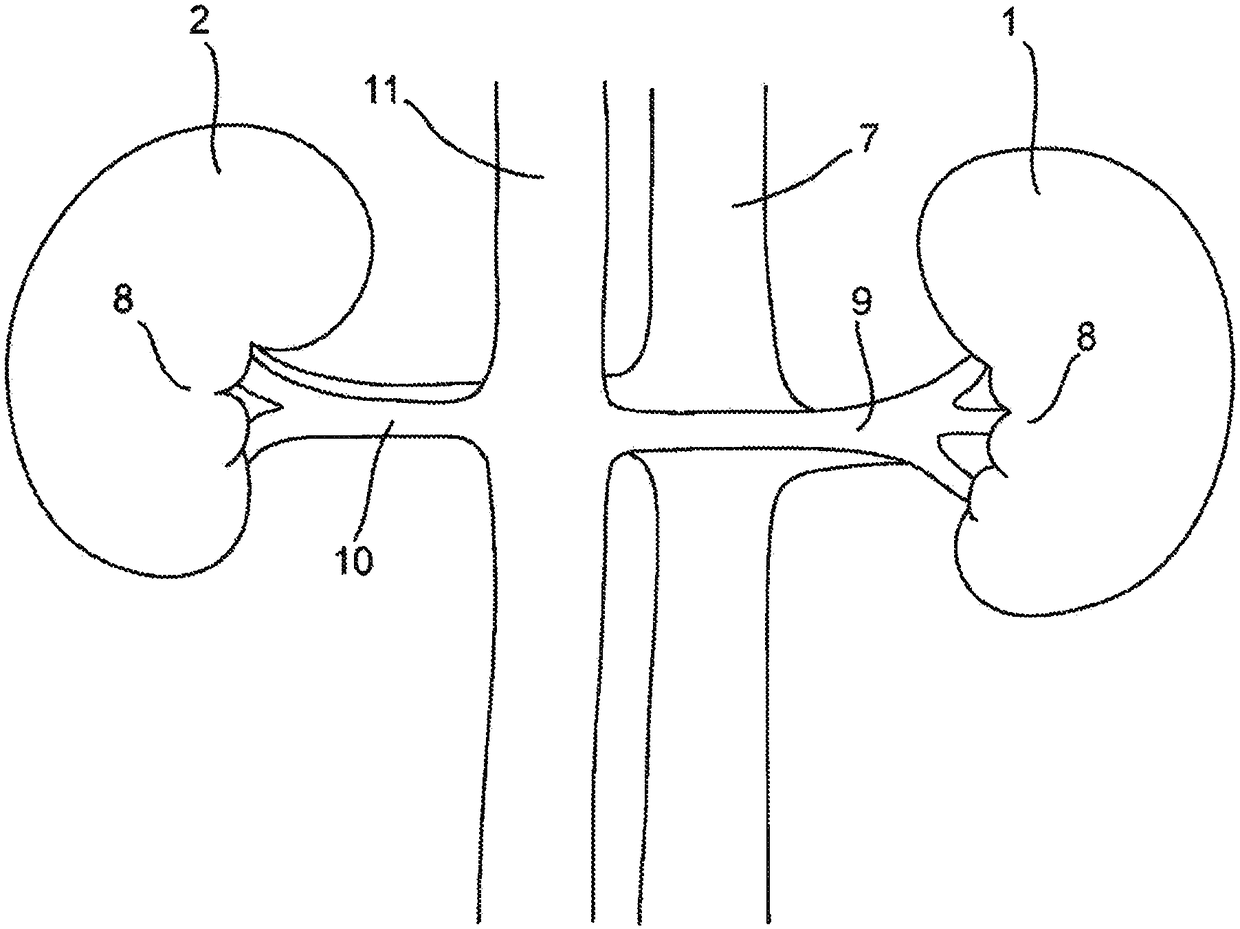
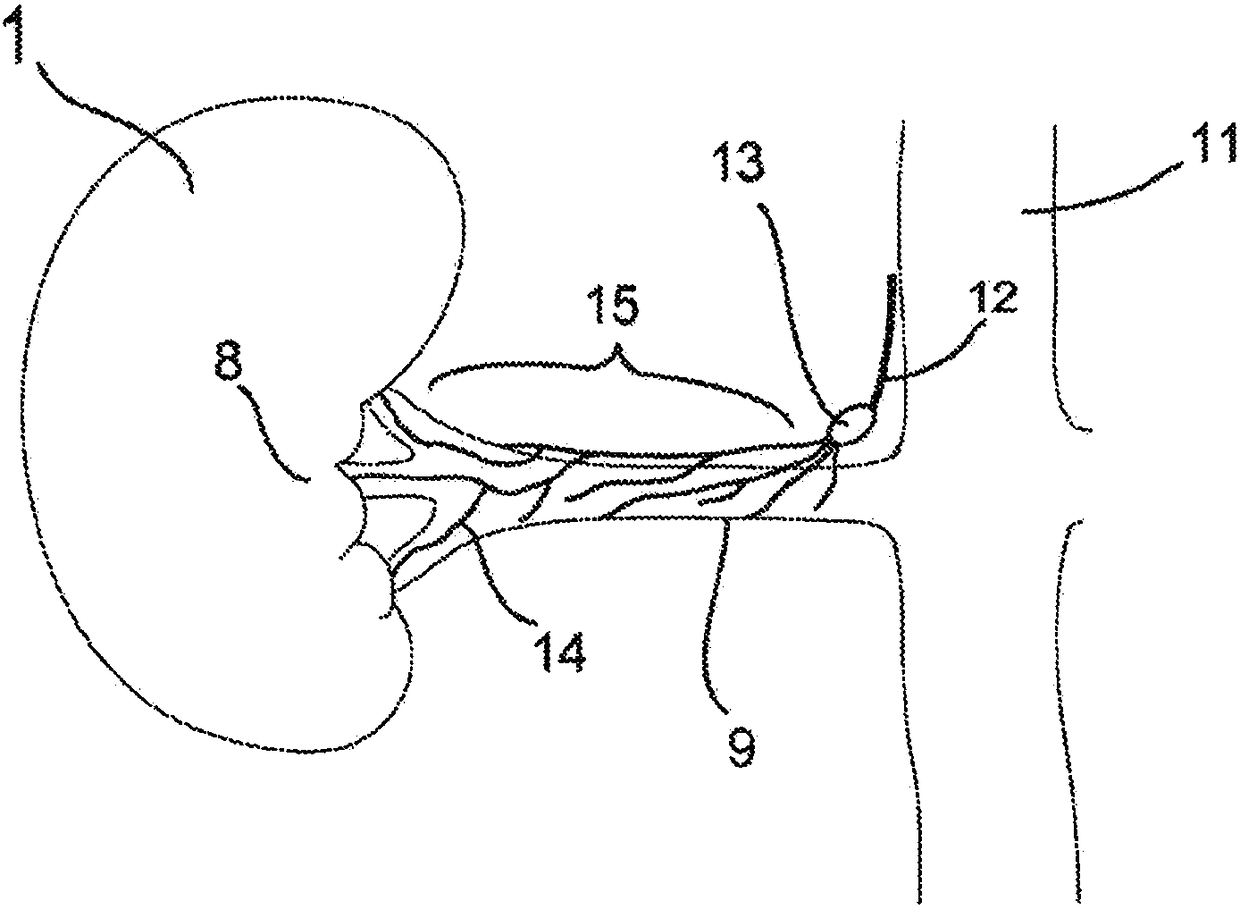
[0196] Measuring the RSNA at a location is done by selecting two electrodes adjacent to that location. If no significant RSNA is measured, there is no nerve within range of the receiver. Such as image 3 As shown, the ARG13 postganglionic nerve begins to innervate the renal artery just below the ARG. The segment of the superior renal artery between the target site and the ostium has little or no innervation; therefore, electrodes adjacent to this segment will detect little or no RSNA. Electrodes farther from the target location will detect RSNA, but as the nerve branches progressively toward the kidney, the amplitude decreases due to the dispersion of nerve activity. The example search algorithm shown below (for a flowchart of the algorithm, see Figure 40 ) to measure the RSNA of the two groups of electrodes located on the upper side to detect significant chan...
specific example
[0303] Renal artery spasm can be induced by applying mechanical pressure on the renal artery wall using a probe. Reduced responsiveness of the renal arteries to intravascular mechanical stimuli is a sign that renal afferents and / or ARGs have been damaged and are unable to transmit receptor signals to the CNS.
[0304] By applying electrical stimulation to afferent nerves surrounding the renal arteries, researchers (P. Gal et al., Journal of Hypertension 2014: 1-4) have reported changes in systemic blood pressure and / or heart rate. Reduced responsiveness of systemic blood pressure and / or heart rate to intravascular electrical stimulation along the renal arteries is a sign that renal afferents and / or ARGs have been damaged and are unable to transmit receptor signals to the CNS.
[0305] Depending on the nature of the stimulating signal (ie, pulse shape, pulse amplitude, pulse frequency, pulse duty cycle, monophasic versus biphasic), intravascular electrical stimulation of the AR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com