An Optical Modeling Method for Condenser Lens Construction in Concentrating and Heat Collecting System
A technology of concentrating heat and modeling methods, applied in the direction of concentrating mirrors, optics, optical components, etc., can solve problems such as large errors and difficulty in achieving theoretical concentrating effects, achieve high interception efficiency, realize structural optimization and efficiency improvement Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
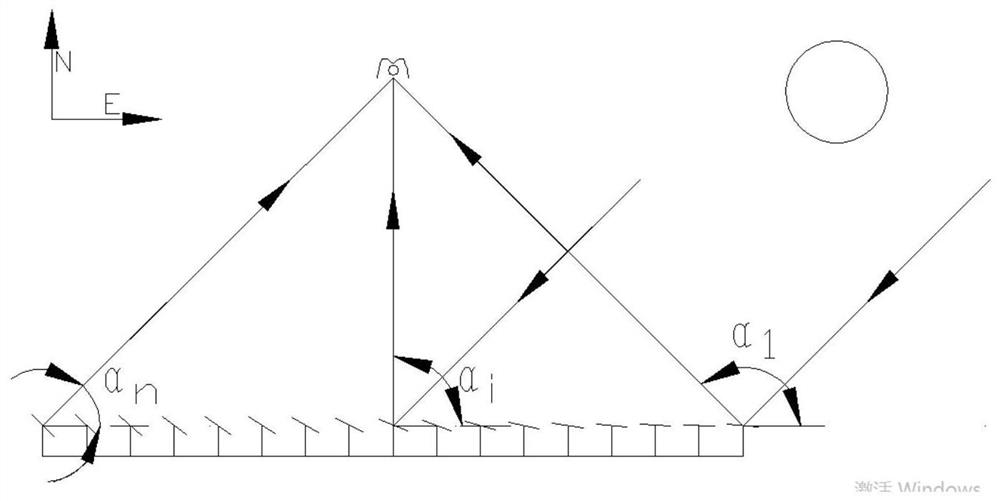
[0069] Taking the linear Fresnel concentrating system as an example, except for the secondary reflector, the other installation parameters of the system are shown in Table 1: take the east-west direction of the axis plane of the primary reflector as the x-axis, and take the line segment between the center points of the mirrors on the east and west edges The vertical line is the y-axis. (unit: mm)
[0070] Table 1
[0071]
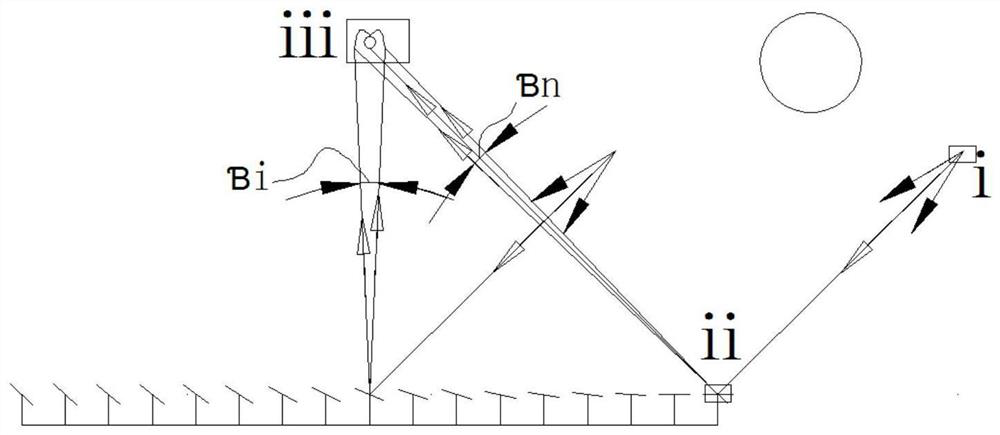
[0072] All primary mirror elements take the centerline of the opening plane of the secondary reflector as the aiming line.
[0073] The modeling of a secondary reflector consists of the following steps
[0074] Table 2
[0075]
[0076]
[0077] Calculating the Opening Size of the Secondary Mirror
[0078] Such as figure 1 As shown, use σ sun is the root mean square of the solar aperture angle, σ specularity is the root mean square error of the mirror surface shape, σ slope is the root mean square of the specular reflection error, σ trac...
Embodiment 2
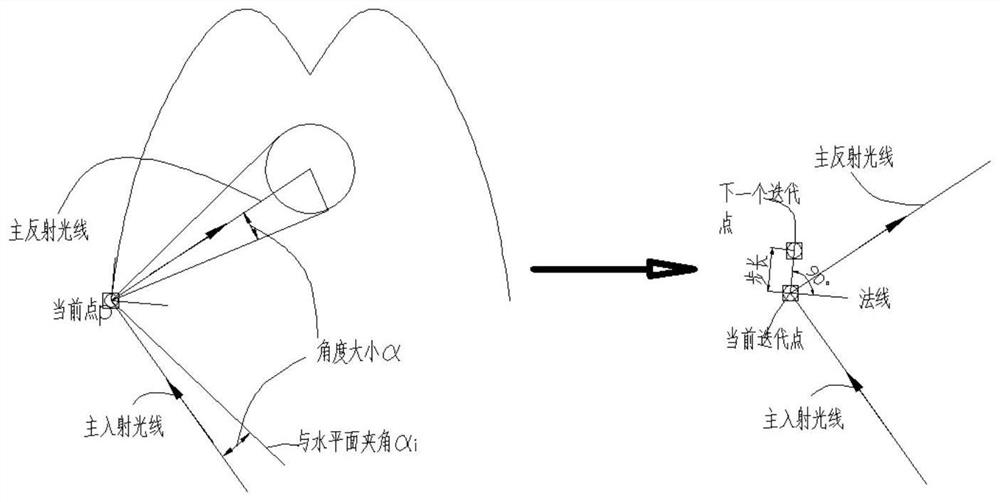
[0108] The traditional secondary reflector adopts the CPC structure of involute + parabola. The specific modeling method is as follows:
[0109] Involute part:
[0110] Taking the outer diameter of the metal inner tube of the vacuum heat collecting tube as the base circle and its center as the origin to establish a rectangular coordinate system, the parametric coordinate equation of the involute in the left half of the CPC can be obtained:
[0111] x=-R(sin t-tcost)
[0112] y=-R(cost+tsin t)
[0113] In the formula, R is the radius of the metal inner tube of the vacuum heat collector, and t is the parameter of the involute equation. Rotate the involute by α around the center of the circle so that the point t=t0 on the involute is on the CPC central axis, and t0 and α respectively satisfy the following
[0114] equation:
[0115]
[0116] x=-R(sin t 0 -t 0 cost 0 )
[0117] y=R(cost 0 +t 0 sin t 0 )
[0118] -(xcosα-ysinα)=0
[0119] In the formula, L is the su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com