Off-line analysis method of machining allowance for free-form surface parts
A technology of curved surface parts and machining allowance, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of low precision, reduce the number of tool passes and optimize the distribution of machining allowance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
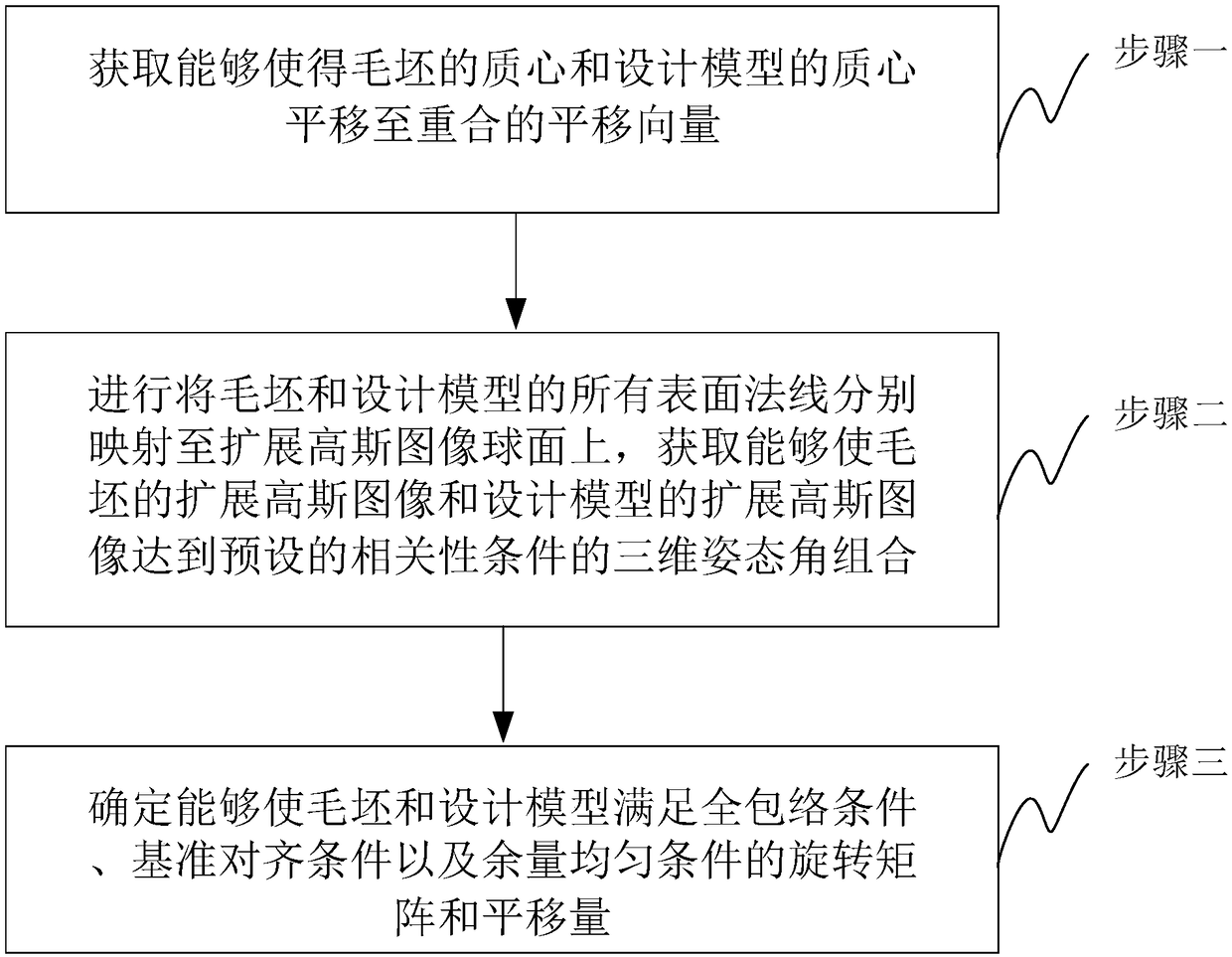
[0016] Specific implementation mode 1: The off-line analysis method of machining allowance for free-form surface parts in this implementation mode, such as figure 1 shown, including:
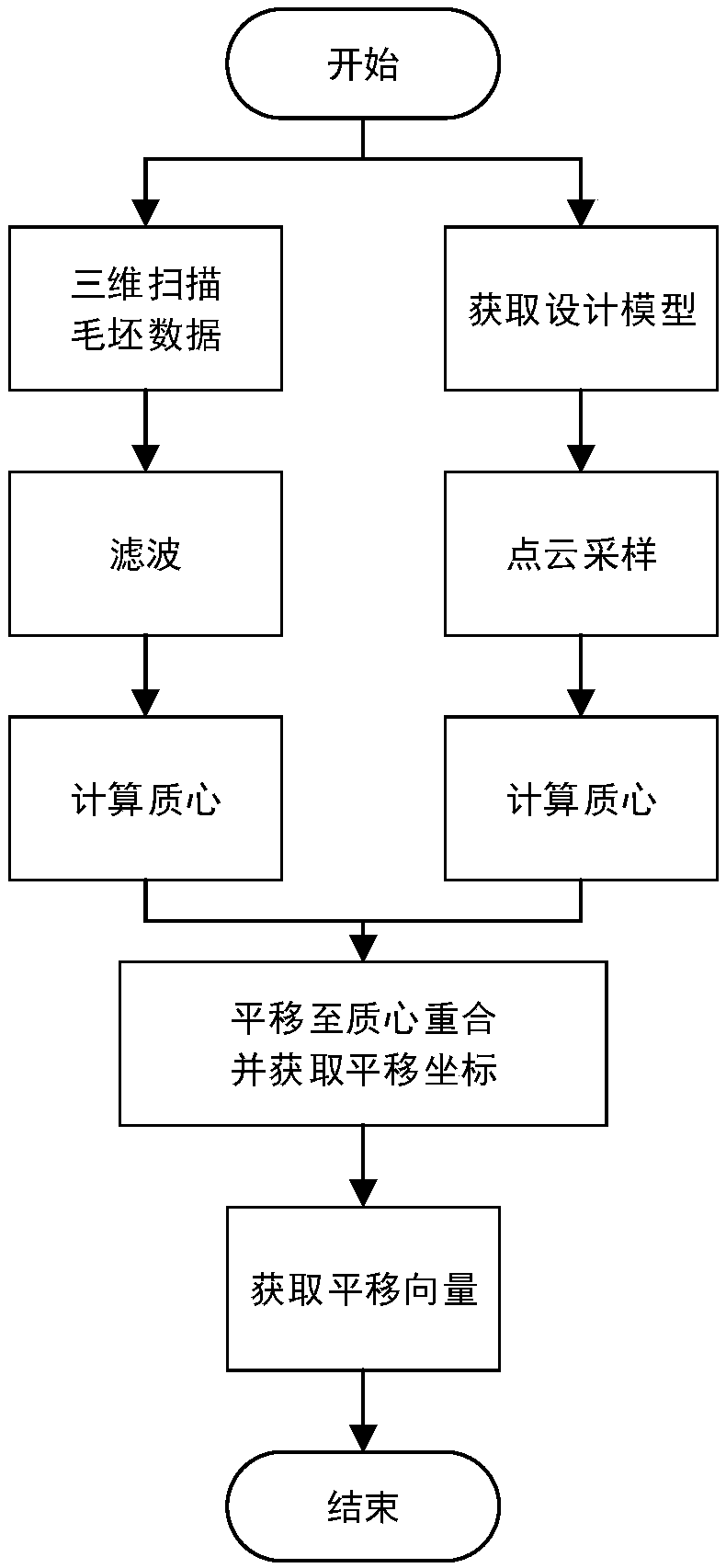
[0017] Step 1: Obtain a translation vector that can translate the center of mass of the blank and the center of mass of the design model to coincide.
[0018] This step is the process of obtaining the rough registration translation vector. The process of calculating the rough center of mass can be as follows: first, through the high-precision scanning and 3D reconstruction of the 3D scanner, and remove the outliers through filtering, to obtain the rough point cloud to be analyzed, and then Each point in the point cloud is regarded as a mass point, and the centroid of the entire point cloud is calculated as the centroid of the blank. The calculation process of the design model is similar. The design model can be used for point cloud sampling to obtain a model point cloud with the same volume as...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that step one includes:
[0035] The blank is scanned and 3D reconstructed, and filtered to remove outliers to obtain the blank point cloud.
[0036] Sampling the point cloud of the design model to obtain a model point cloud with the same volume as the blank point cloud.
[0037]Treat each point in the rough point cloud and model point cloud as a mass point, calculate the space position of the center of mass of the rough point cloud and the model point cloud, and make a difference between the rough point cloud and the centroid of the model point cloud to obtain the The centroid and design model's centroid are translated to coincident translation vectors.
[0038] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
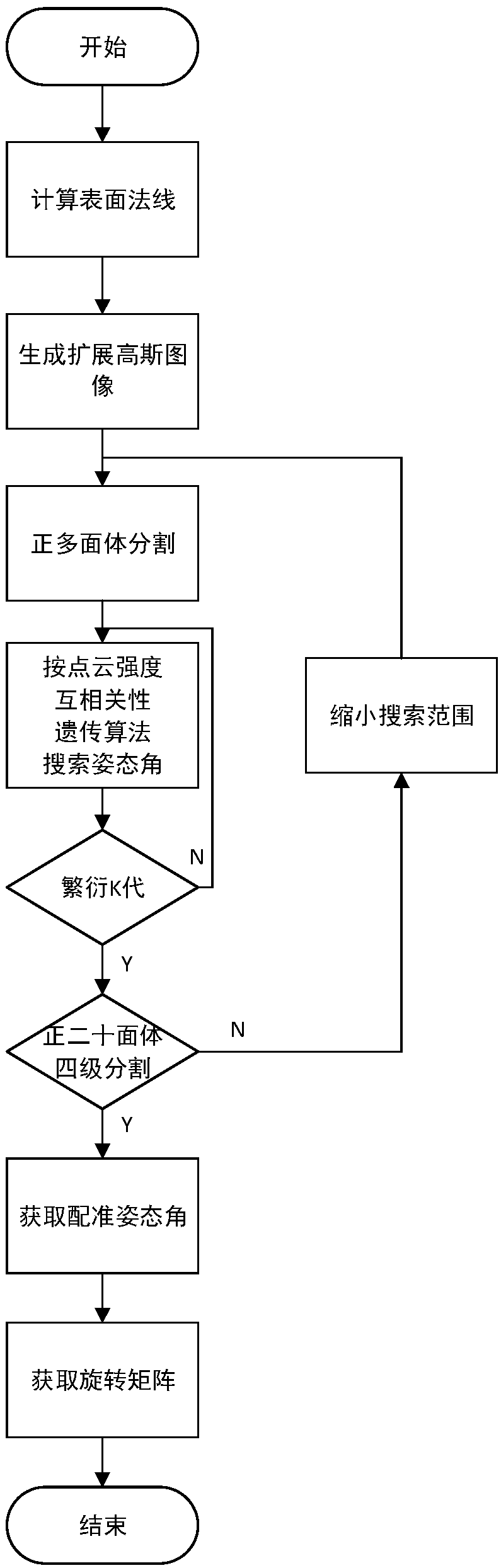
[0039] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is that step two is specifically:
[0040] Calculate all surface normals for blank and design model separately; generate extended Gaussian image sphere; map all surface normals for blank and design model to extended Gaussian image sphere, blank and design model on each face of the extended Gaussian image sphere The number of normals contained represents the characteristic strength of the blank and the characteristic strength of the design model, and the degree of correlation between the characteristic strength of the blank and the characteristic strength of the design model is calculated. The calculation formula is:
[0041]
[0042] Where Corr is the degree of correlation, is a vector consisting of the number of normals that the blank contains on each face of the extended Gaussian image sphere, A vector of the number of normals that the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com