Degrees of freedom for diffraction elements in wave expander
A diffraction pattern, light wave technology, used in optical components, instruments, light guides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] In this specification, reference to "an embodiment," "one embodiment," etc. means that the particular feature, function, structure, or characteristic being described is included in at least one embodiment of the technology presented herein. The appearances of such phrases in this specification are not necessarily all referring to the same embodiment. On the other hand, the further mentioned embodiments are not necessarily mutually exclusive.
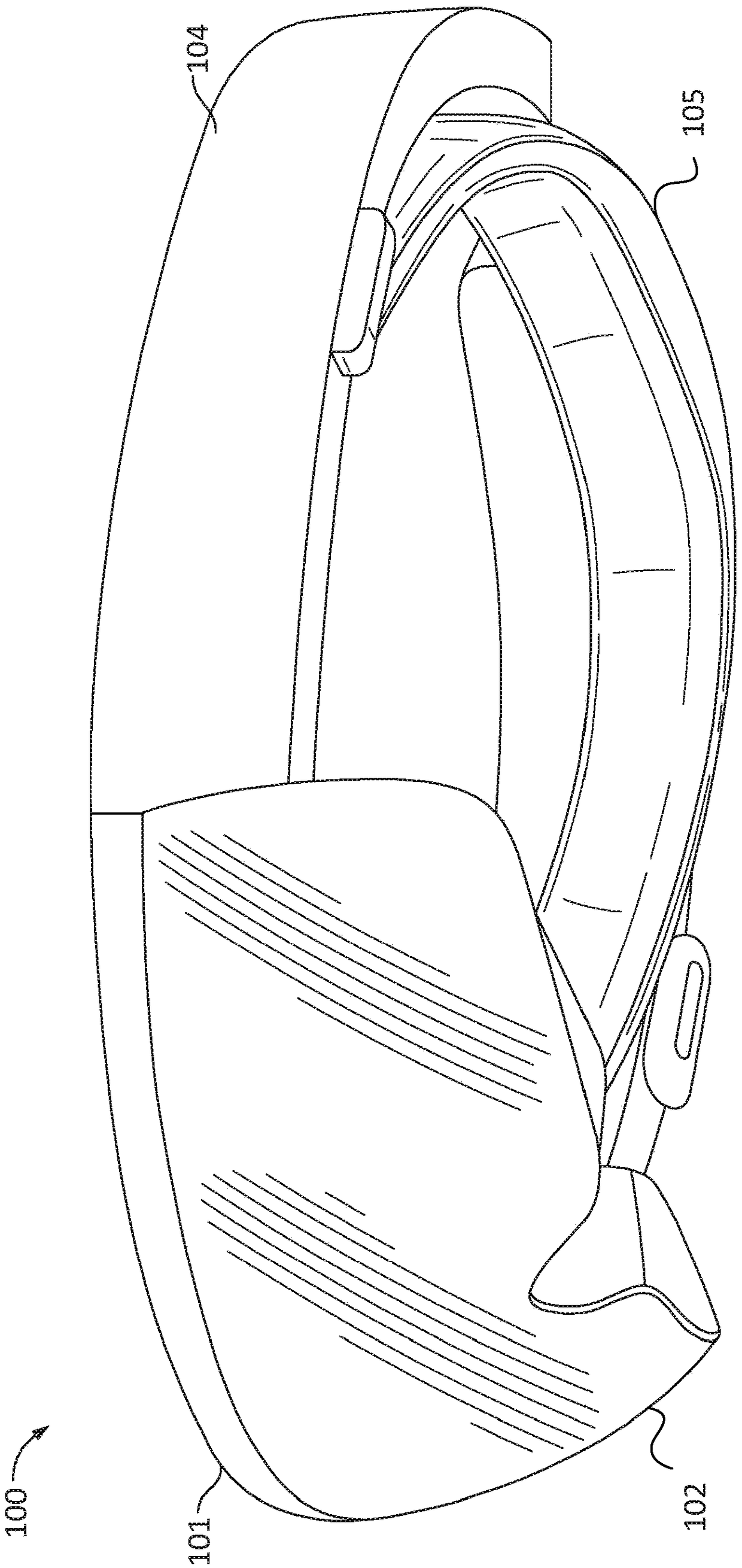
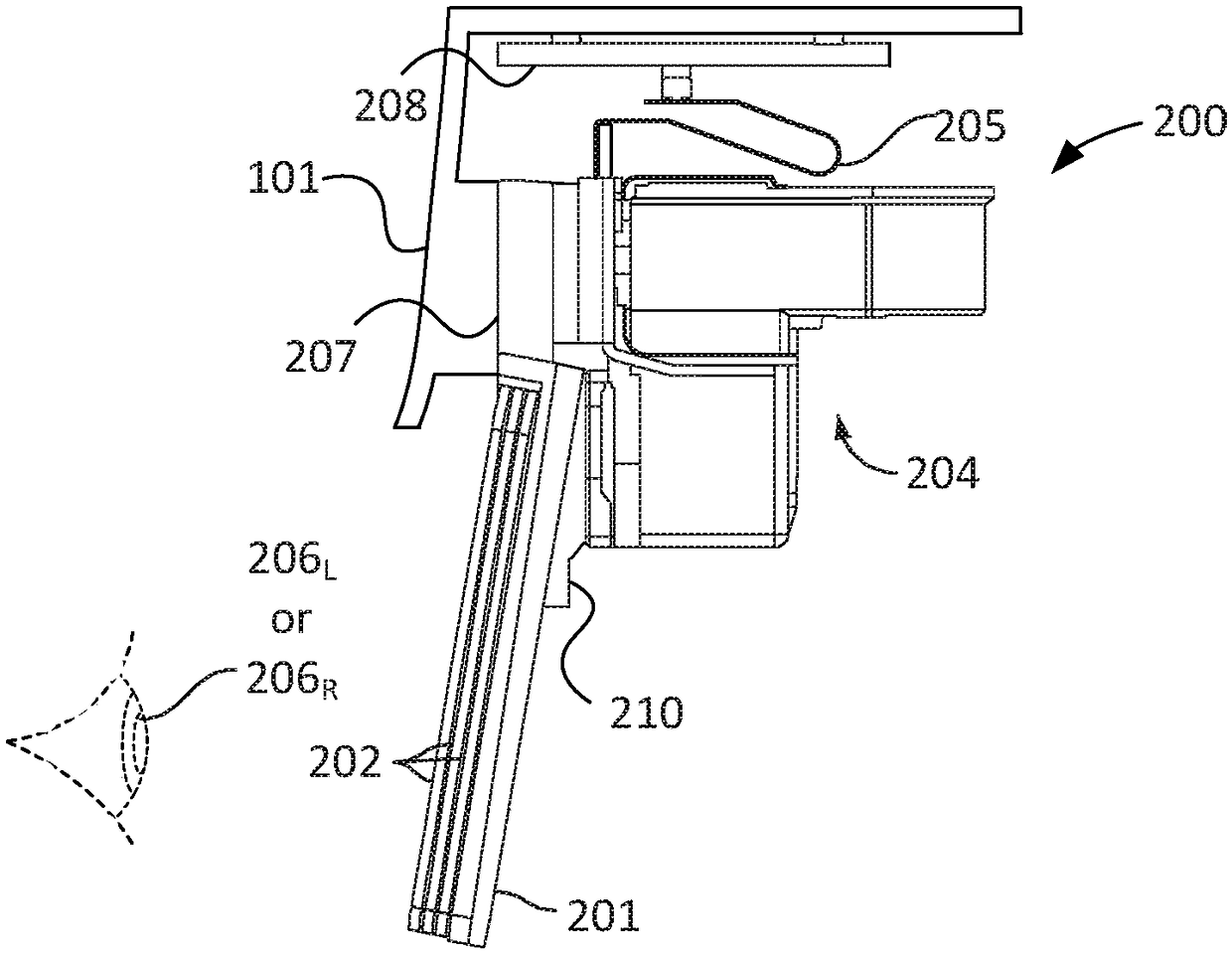
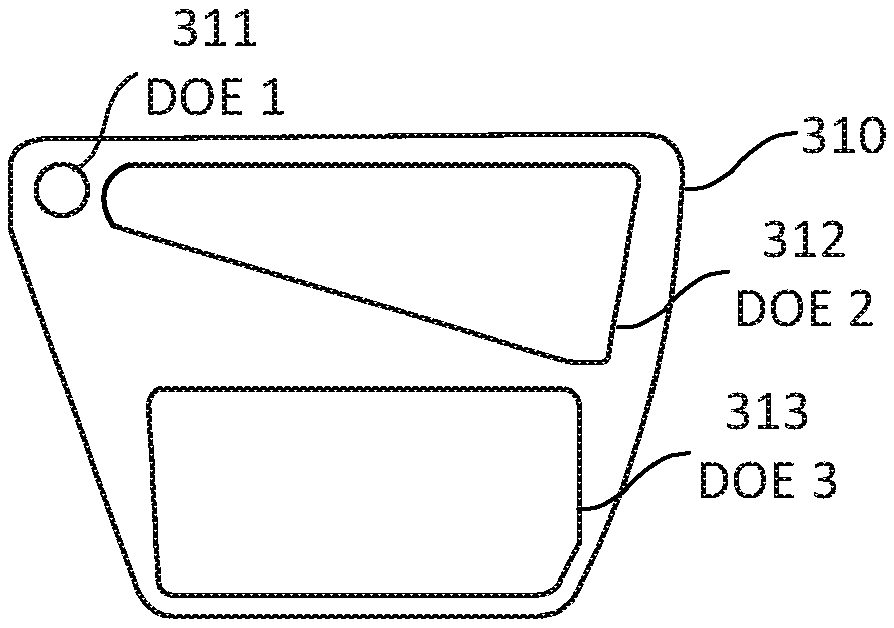
[0020] Some near-eye AR display devices include one or more waveguides positioned in front of one or more light receptors of a user (eg, a human eye). The output waveguide can propagate and expand the light waves provided by the imager and direct the light waves towards the light receptors of the user of the near-eye AR display device using a diffractive optical element (DOE). For example, an output waveguide can spread light waves in a particular direction. Expansion in this context means that a light wave is divided into multi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com