A Dynamic Task Impact Estimation Method Based on Adaptive Switching Bayesian Networks
A Bayesian network and adaptive switching technology, applied in the field of information systems, can solve the problems of SKRM lack of quantitative task impact analysis, no strict regulations on cross-layer interconnection, accuracy of impact assessment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
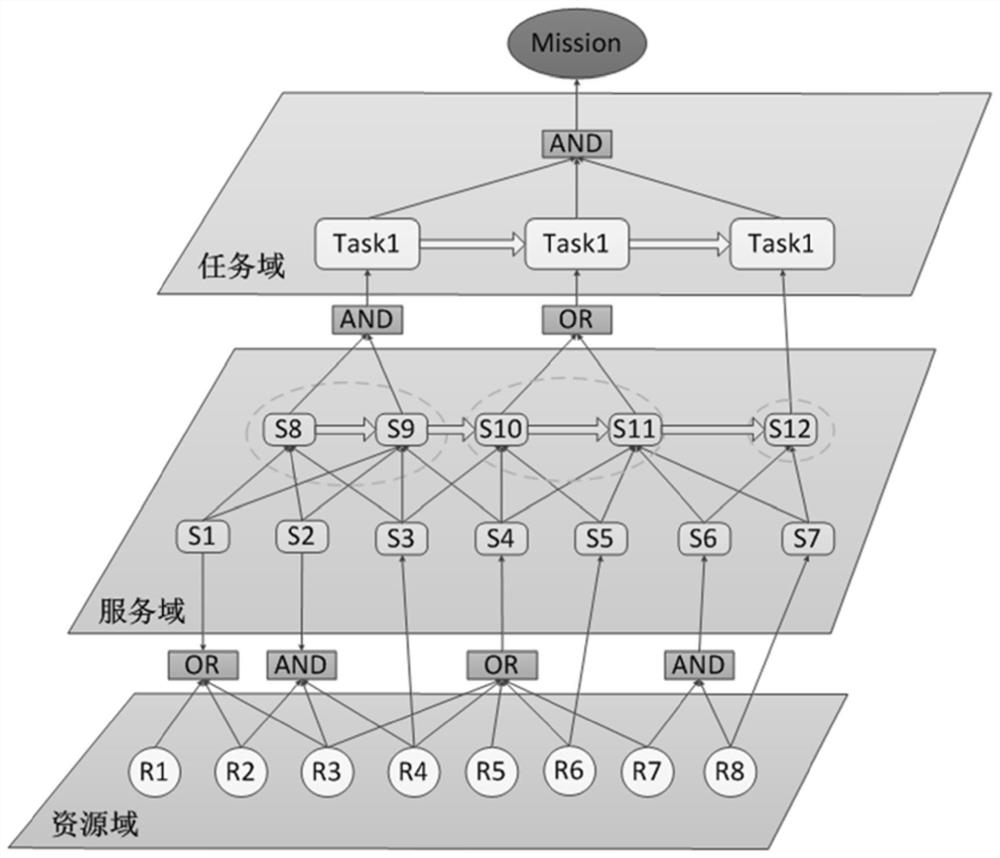
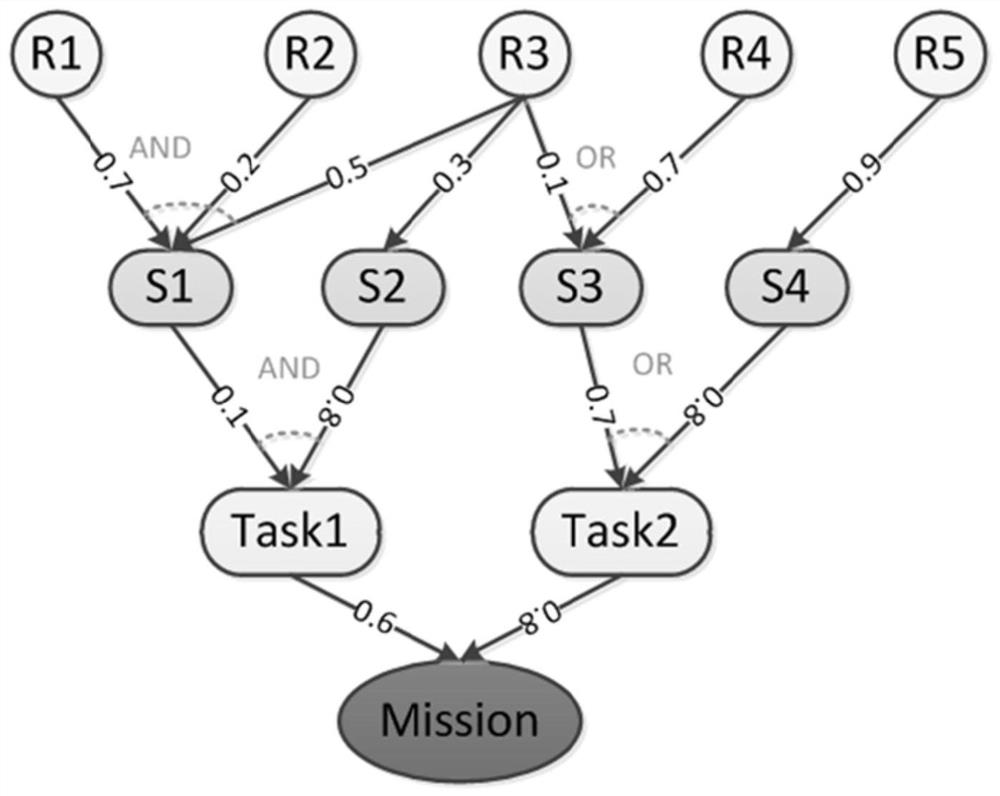
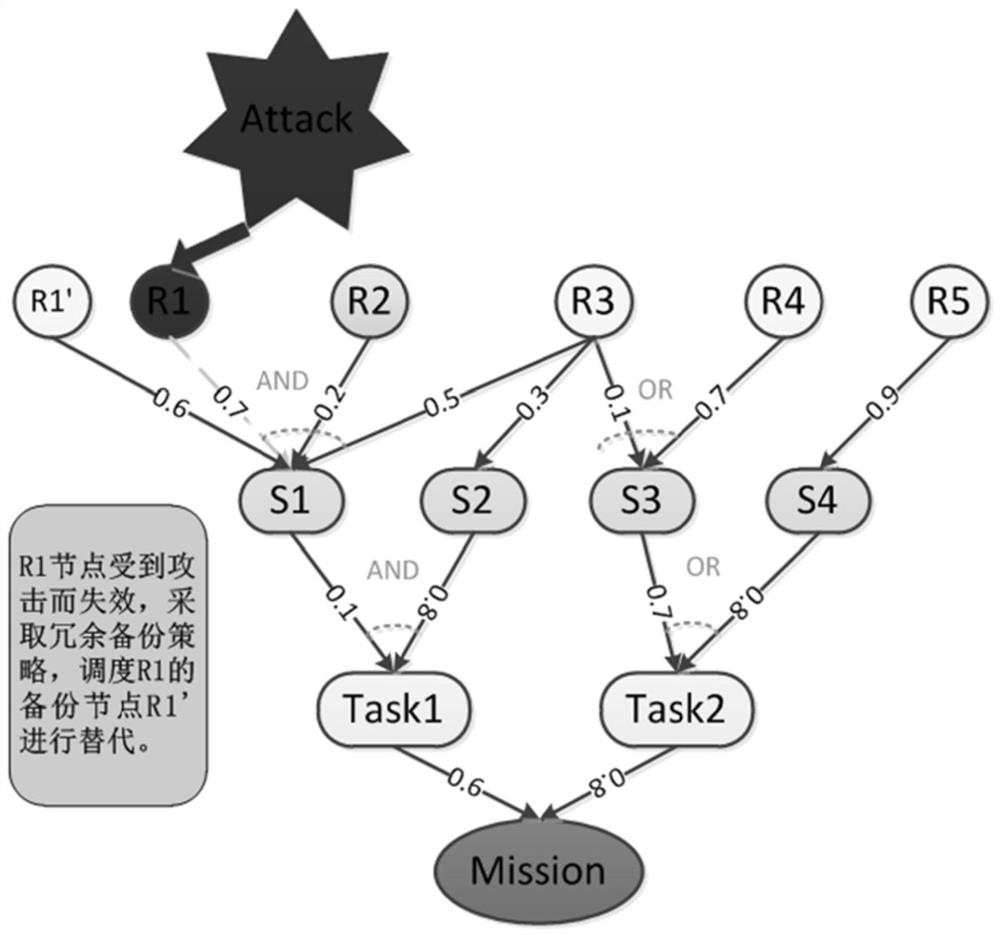
[0094] Figure 5 Shown is a concrete case of a Bayesian network built on the task-resource model, in this case a task consists of several task functions. In order for each task to be normal, all of its constituent tasks should be normal. Also, all task functions should be submitted in the correct order. Likewise, each task function is also composed of several service components.
[0095] Table 1 shows the conditional probability table corresponding to the Bayesian network in the above figure. In this table, tasks, task function 1, and task function 2 have two states of failure and normal, and are assigned to system nodes according to actual conditions.
[0096] Table 1
[0097]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com