Rope skipping counting method and device, wearable equipment and storage medium
A counting method and technology of wearable equipment, which can be applied to rope skipping, sports accessories, etc., can solve the problems of large manpower consumption, poor precision of transmission mechanism and technical device, and easy damage of transmission structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
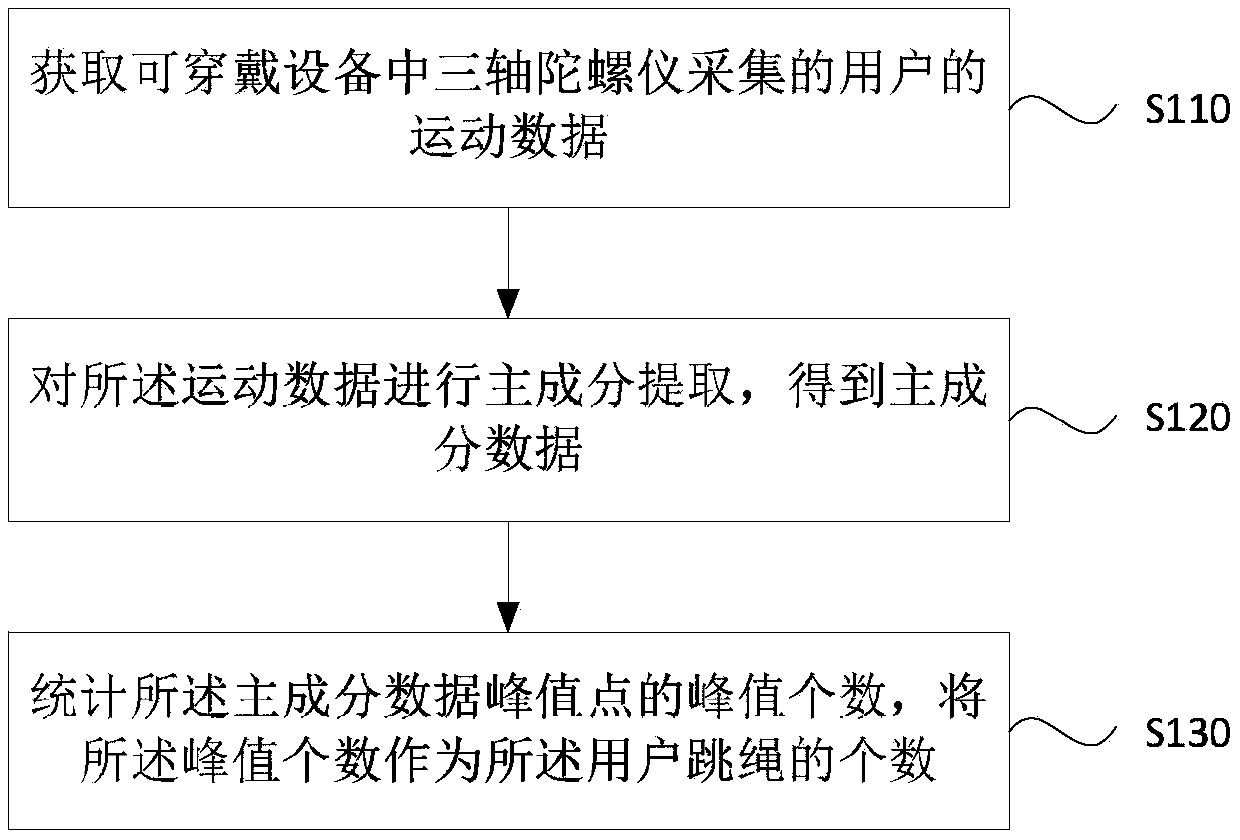
[0054] figure 1 This is a flowchart of a rope skipping counting method provided in the first embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to a situation where a wearable device is used to count the number of skipping ropes. The method can be executed by a rope skipping counting device, which is integrated in the wearable device. Among them, the wearable device may be a smart wearable device such as a bracelet or a watch. Specifically, the method includes the following steps:
[0055] S110. Obtain the user's motion data collected by the three-axis gyroscope in the wearable device.
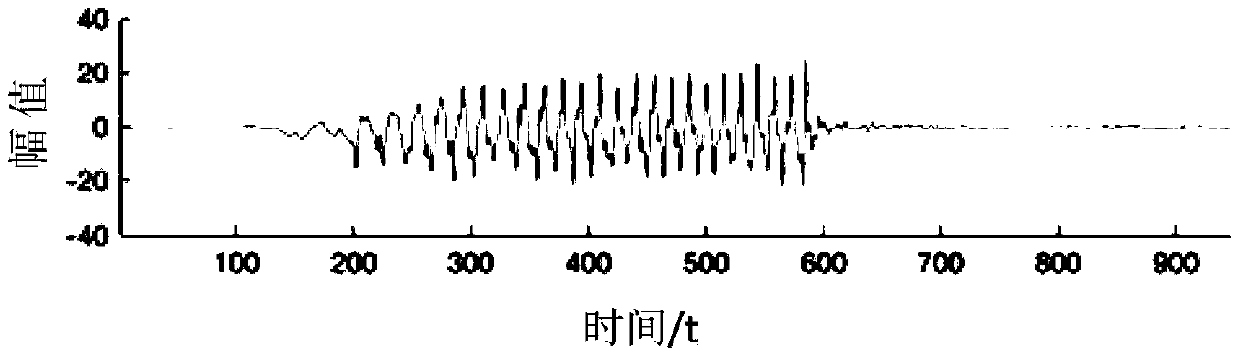
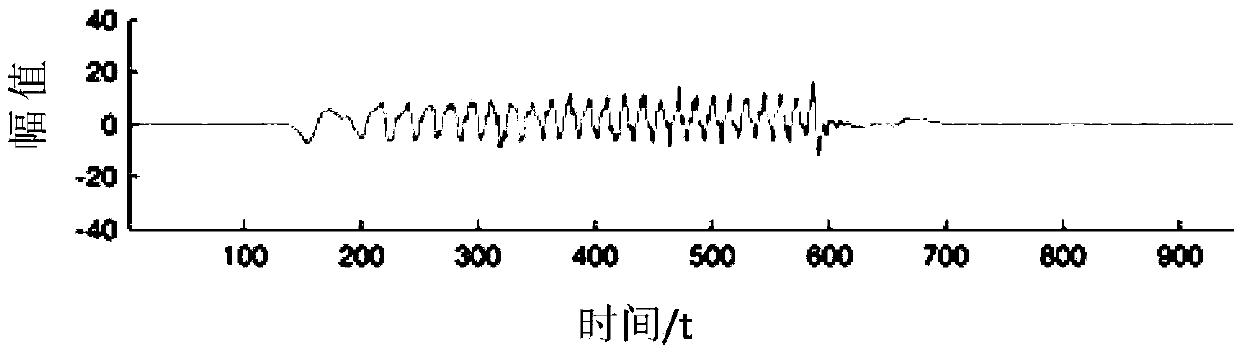
[0056] A gyroscope is a device for measuring angular velocity. In the embodiment, a three-axis gyroscope is used to collect movement data when the user skips rope. The three-axis gyroscope is installed in a wearable device. When the user wears the wearable device to jump rope, The three-axis gyroscope can simultaneously measure the motion data of the X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis. The d...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Figure 5 This is a flowchart of a method for counting skipping ropes provided in the second embodiment of the present invention. The method is embodied on the basis of the foregoing embodiment. Specifically, the method includes the following steps:
[0066] S210. Obtain the user's motion data collected by the three-axis gyroscope in the wearable device.
[0067] S220: Generate a first matrix according to the motion data.
[0068] The embodiment uses the principal component analysis method to extract the principal component data of the motion data. Specifically, it is assumed that the motion data in the X-axis direction is x=(a 11 , A 12 ,..., a 1n ), the movement data in the Y-axis direction is y=(a 21 , A 22 ,..., a 2n ), the movement data in the Z-axis direction is z=(a 31 , A 32 ,..., a 3n ), where n is the number of motion data, the first matrix A=[x, y, z] generated based on the motion data in the X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis directions T , The first matrix A is a 3×n matrix...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Picture 10 This is a structural diagram of a rope skipping counting device provided in the third embodiment of the present invention. The device can execute the skipping rope counting method described in the foregoing embodiment. For details, refer to Picture 10 , The device includes:
[0087] The obtaining module 310 is used to obtain the user's motion data collected by the three-axis gyroscope in the wearable device;
[0088] The principal component extraction module 320 is configured to perform principal component extraction on the motion data to obtain principal component data;
[0089] The statistics module 330 is configured to count the number of peaks of the principal component data peak points, and use the number of peaks as the number of skipping ropes of the user.
[0090] The third embodiment of the present invention provides a structural diagram of a rope skipping counting device. By acquiring the user's motion data collected by a three-axis gyroscope in a wearable...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com