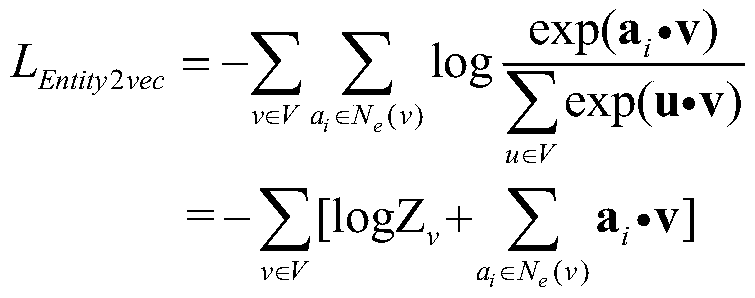Graph completeness method based on knowledge graph neighborhood structure
A knowledge map and neighborhood technology, applied in the field of knowledge map representation and reasoning, can solve problems such as inability to effectively use entity and relation neighborhood information, poor interpretability, and high computational complexity of the model, and achieve high model convergence rate and prediction The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] The implementation of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings and examples.
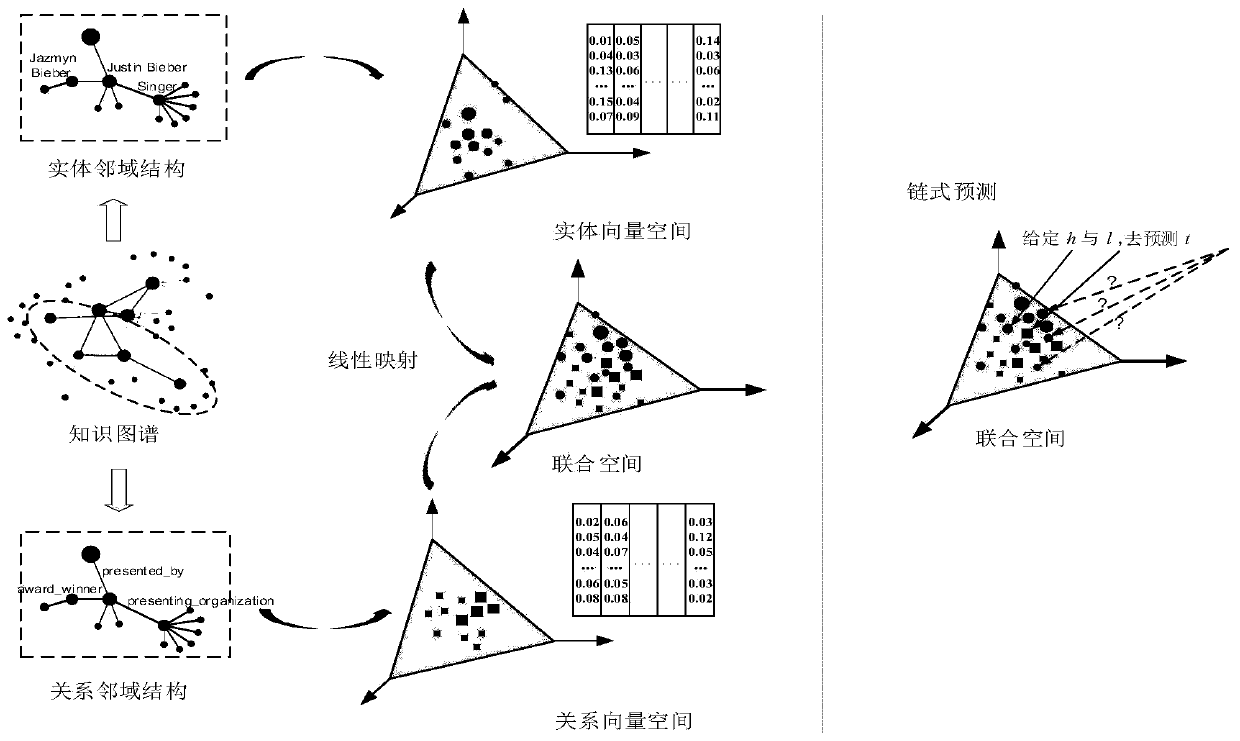
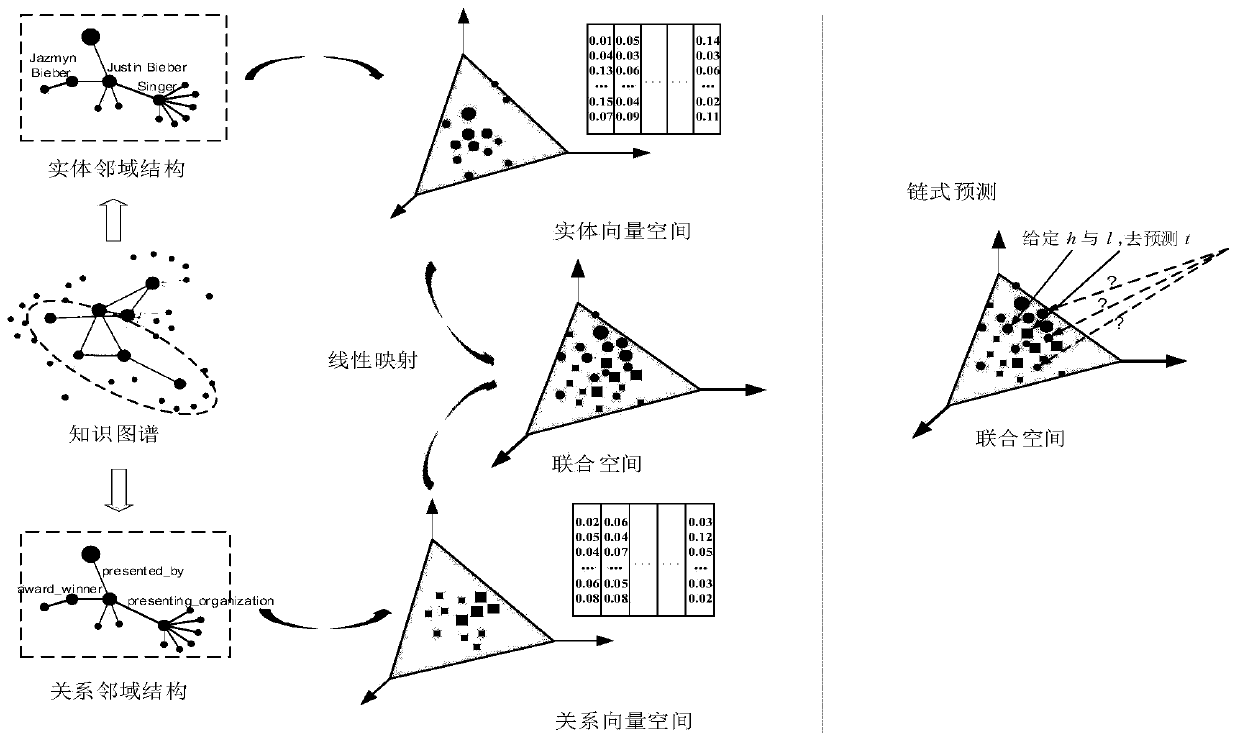
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention is a map completion method based on the knowledge map neighborhood structure, including the following steps:
[0039] Step 1. Select each entity v in the knowledge map as the source entity in turn. Starting from the source entity, perform a random walk with a fixed number of steps η to obtain an entity sequence matrix with a scale of |E|×η, where |E | is the number of entities in the map. The entity sequence matrix can be regarded as a corpus using entities as vocabulary. Specify the window size to intercept the neighborhood of entity v, and use N to obtain the neighborhood of entity v e (v) said. Based on the neighborhood information, the Entity2vec model is established as follows:
[0040]
[0041] Including:
[0042]
[0043] Therefore, formula (1) can be further expressed as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com