A Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing Filter
A wavelength division multiplexing and filter technology, applied in the field of silicon-based photonic integrated chips, can solve the problems of increasing insertion loss and device size, increasing the size of the device, and reducing the athermal characteristics of the filter, so as to reduce the size and avoid the Effects of extra loss and phase deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
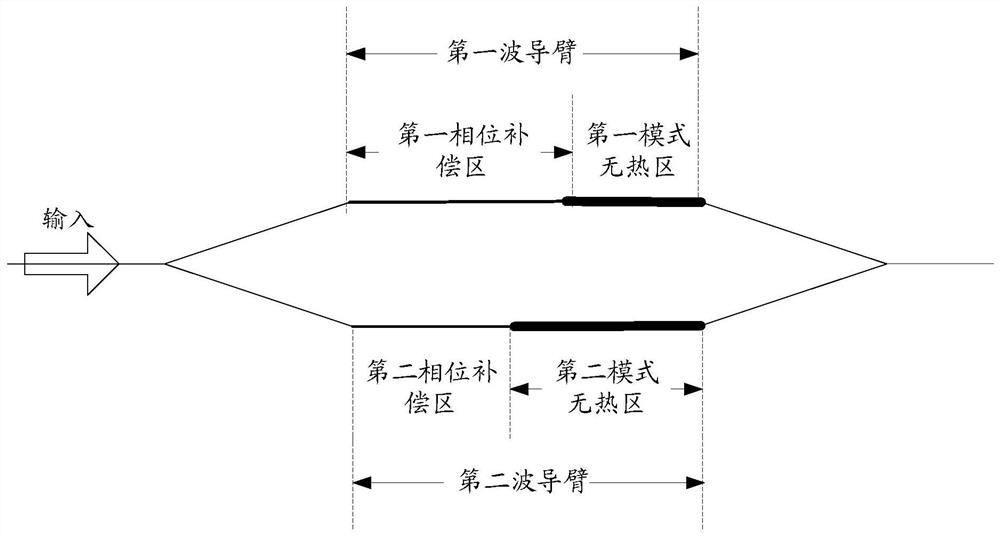
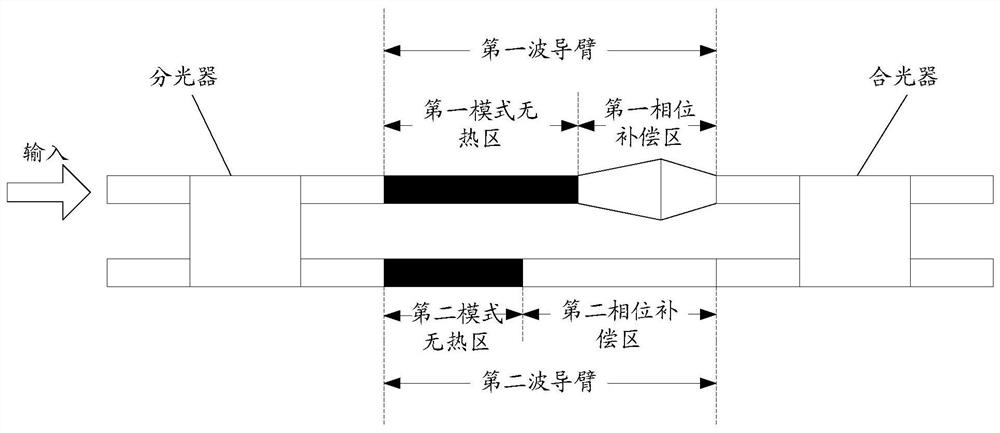
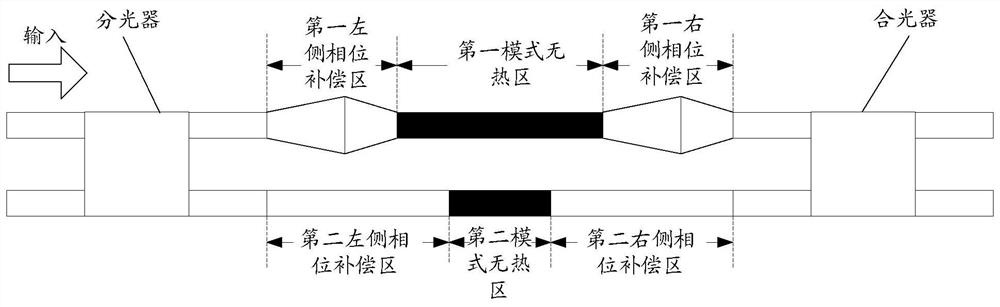
[0032] In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments in the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined arbitrarily with each other.
[0033] In an ordinary athermal filter, since the athermal design will make the waveguide lengths of the two arms of the MZI different, it is inevitable to use Bend for phase and length compensation for the waveguide wiring. However, Bend itself will produce a large phase error in actual processing. In addition, for TE 1 Mode, the loss of Bend is strong; it needs to be converted into the mode before entering the Bend, otherwise a curved waveguide with a large radius will be required. However, the size of the filter will be significantly increased after mode conversion, and a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com