Hazard classification of barrier lakes and early warning methods of outburst debris flow and mountain torrents
A debris flow, dangerous technology, used in alarms, climate sustainability, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to accurately reflect the disaster process, single and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
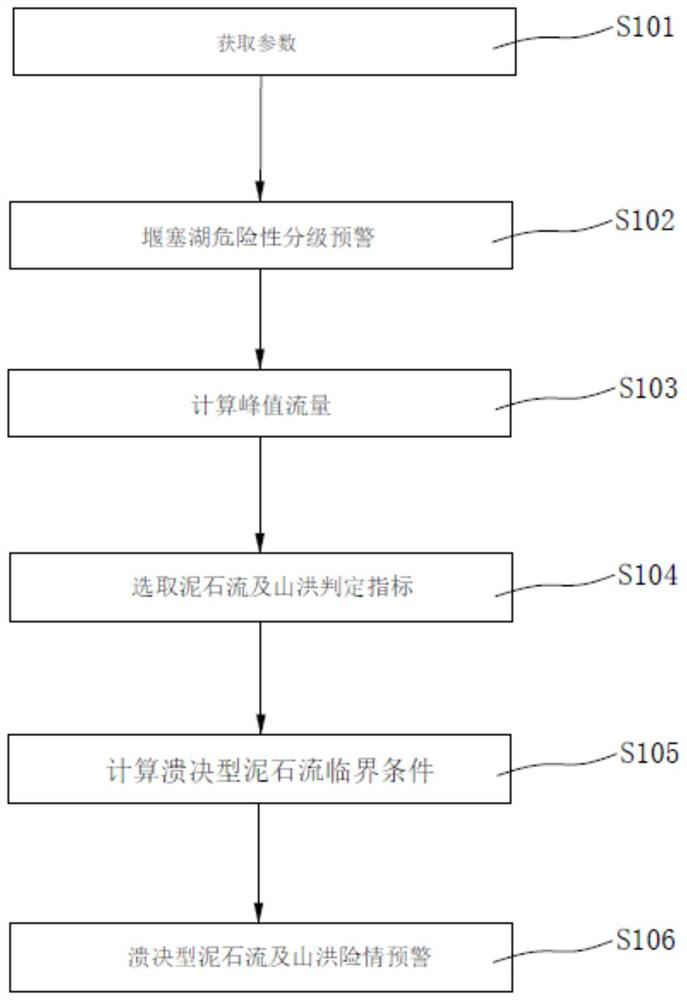
[0043] Embodiment 1, its barrier lake risk classification and burst type debris flow and mountain torrent dangerous situation early warning method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
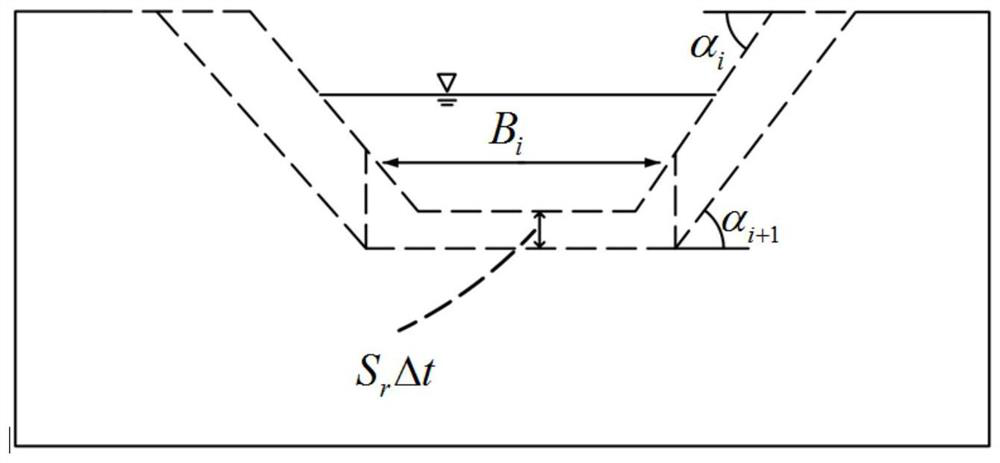
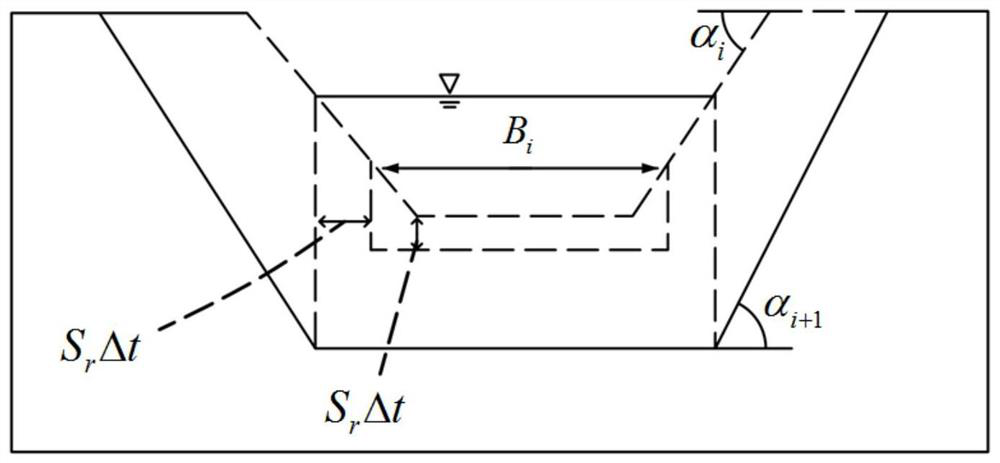
[0044] S101: Determine the top width of the initial breach of the barrier dam by means of on-site investigation, remote sensing, and hydrology B t0 , bottom width B b0 , height H 0 , breach slope angle α 0 , the initial water surface elevation H w0 , the initial elevation of the bottom of the breach Z 0 , initial water depth h 0 , initial storage capacity V 0 , median diameter d 50 And the slope J of the river course or ditch, etc.
[0045] S102: Early warning of barrier lake hazard classification, calculate the risk potential energy of the barrier lake, and use the risk potential energy classification as the index of barrier lake hazard classification.
[0046] alpha r The coefficient is calculated according to formula 1:
[0047]
[0048] where m r —coefficie...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Risk classification of Chayuangou dam and judgment of debris flow or flash flood after failure:
[0127] The Chayuangou barrier dam is a barrier dam formed after the 5.12 earthquake. Its scale is smaller than other barrier lakes formed in the earthquake. In the ditch, the debris flow ditch is a large low-frequency viscous ditch. The exposed strata in the Chayuangou watershed are composed of Triassic metamorphic sandstone, slate and phyllite. The rocks in the middle and lower reaches of the watershed are mainly phyllite; the upper reaches are mainly medium-grained plagiogranite. Due to the steep rocks on both sides of the valley, the rocks are weathered and broken, and there are a large number of collapsed rock piles of hundreds to thousands of cubic meters. The bottom of the ditch is mostly covered with slope alluvial gravel soil, with a thickness ranging from 1 to 3m, and a large amount of corundum and quartz sand mining wastes are piled up along both sides of the dit...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Judgment on formation of debris flow after Tangjiashan dam failure:
[0136] After the Wenchuan earthquake, a large number of landslides and collapses occurred in the earthquake area, which led to the appearance of a large number of barrier lakes, among which the Tangjiashan barrier lake is the most dangerous. Before the earthquake, the slopes on both sides of Tangjiashan were about 40°. From the structural point of view, they belonged to the slopes with medium and steep dip angles. The earthquake caused the slope on one side to become unstable, forming a high-speed landslide. Blocking the Tongkou River, forming a volume of 20.37 million m 3 The barrier dam is very likely to collapse and cause disasters downstream. The barrier dam is located in the alpine valley area, the terrain is high in the northwest and low in the southeast, with an altitude of 1500-2389m and a relative height difference of 400-1000m. There are differences in the slopes on both sides of the river...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com