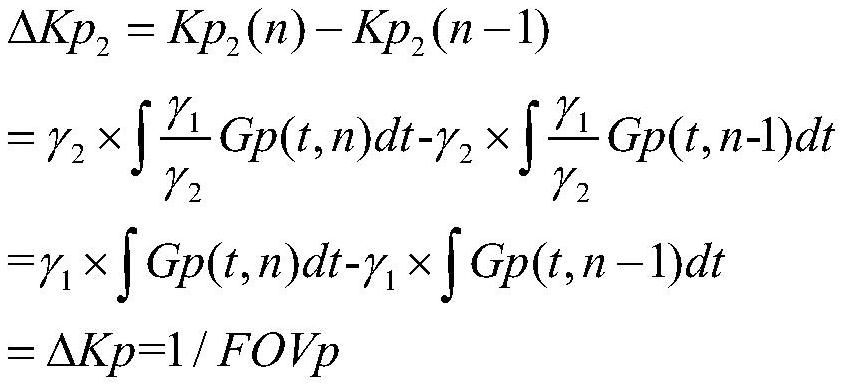A Segmented Coding Dual-Core Synchronous Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and segmentation coding, which is applied in the direction of using nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system for measurement, magnetic resonance measurement, and measurement of magnetic variables. It can solve the problem of different image sizes and resolutions, large differences, and unfavorable nuclide image registration , comparison and other issues, to achieve the same effect of image resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] In order to facilitate those of ordinary skill in the art to understand and implement the present invention, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the implementation examples described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
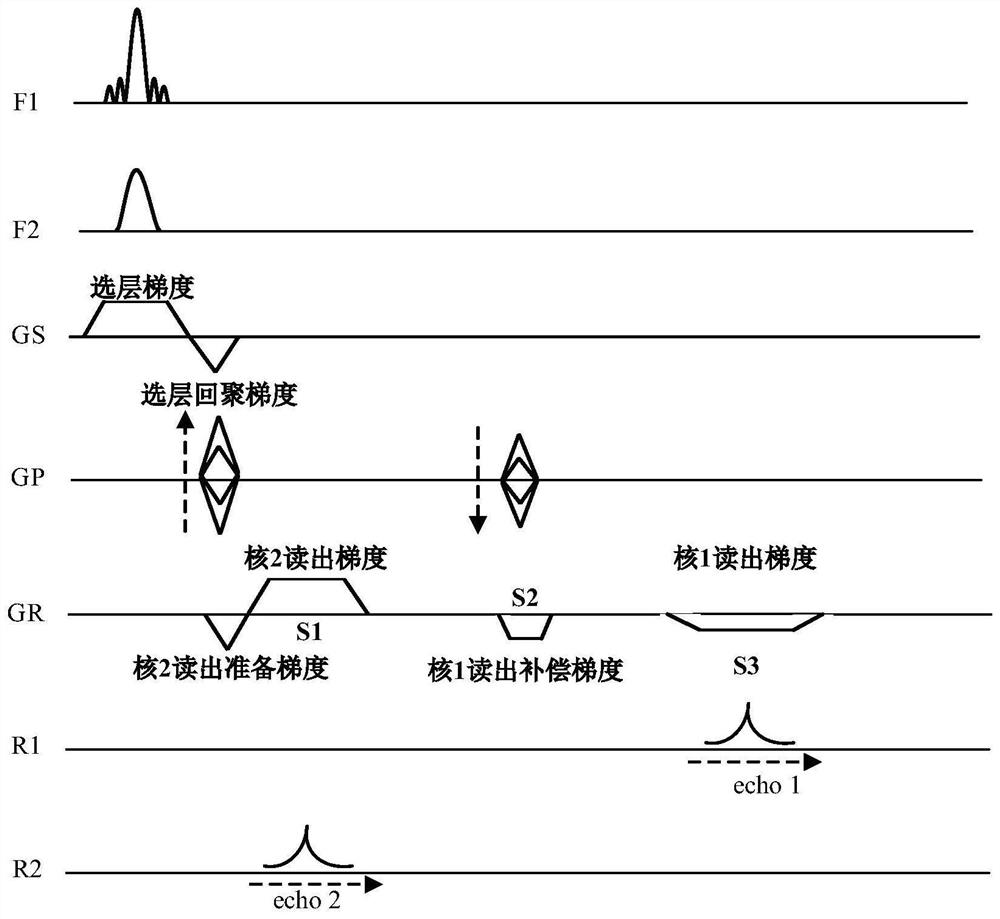
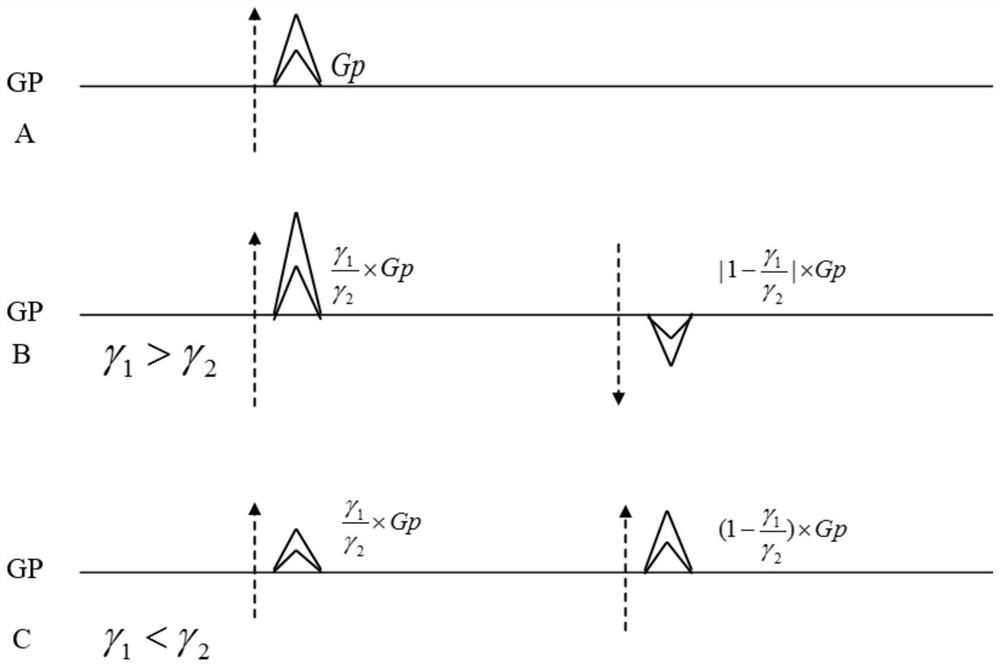
[0056] Loaded on the console of an MRI system that supports two or more channels of simultaneous transmission and reception such as figure 1 The pulse sequence shown; where the two transmit channels and the two receive channels correspond to core 1 and core 2, respectively.
[0057] A dual-nuclear synchronous magnetic resonance imaging method for segment encoding, comprising the following steps:
[0058] Step 1. Set the inspection area FOV (Field of View), layer thickness Th, and sampling matrix [M N];
[0059] Among them, M is the number of sampling points, N is the number of en...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com