Group b meningococcal vaccine and its preparation method and application
A meningococcal and vaccine technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as sensitivity, and achieve the effect of broad antigen spectrum and high bactericidal activity titer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] The preparation method of the fusion protein of the present invention is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0039] Constructing a recombinant plasmid comprising the coding gene as described above;
[0040] Transforming the recombinant plasmid into host cells, identifying, screening and identifying correct positive strains, and transforming the correctly identified positive strains into expression cells; culturing.
[0041] Preferably, the recombinant plasmid containing the above-mentioned coding gene is obtained by inserting the sequence of the coding gene into a plasmid vector by double restriction digestion. More preferably, the vector is pET32a(+).
[0042] Preferably, the expression strain is E. coli BL21(DE3).
[0043] The group B meningococcal vaccine of the present invention includes the fusion protein as described in any one of the above.
[0044] Preferably, the fusion protein includes: chimeric protein I and chimeric protein II; the ami...
Embodiment 1
[0064] 1. Design of group B meningococcal fHBP chimeric protein
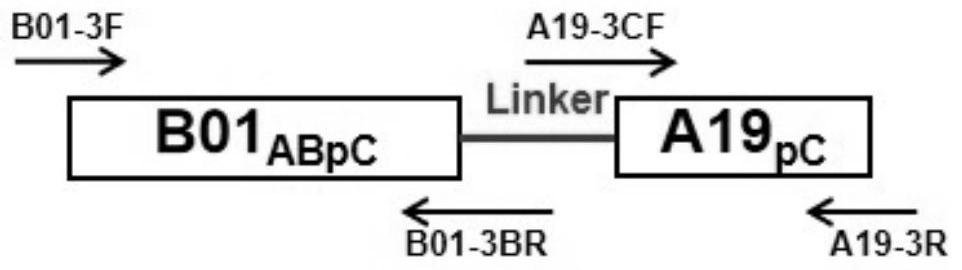
[0065] The N-terminal partial sequence of V1 (including structural domain A, B and partial structural domain C, B01 ABpC ) and the partial sequence of domain C of V2 (partial domain C, A19 pC ) for fusion, and the Linker between them is a small peptide segment (GEHT) in the amino acid sequence of fHBP, namely B01 ABpC -A19 pC . Since there is no similarity sequence between these two fragments, they can be connected by overlapping PCR method (such as figure 1 shown).
[0066] then B01 ABpC -A19 pC As templates, two chimeric proteins (chimeric protein I: Cp-1 and chimeric protein II: Cp-2) were constructed by gene site-directed mutagenesis, as shown in Table 1 below.
[0067] Table 1 Site-directed mutation information of two chimeric proteins
[0068]
[0069] 2. Technical methods
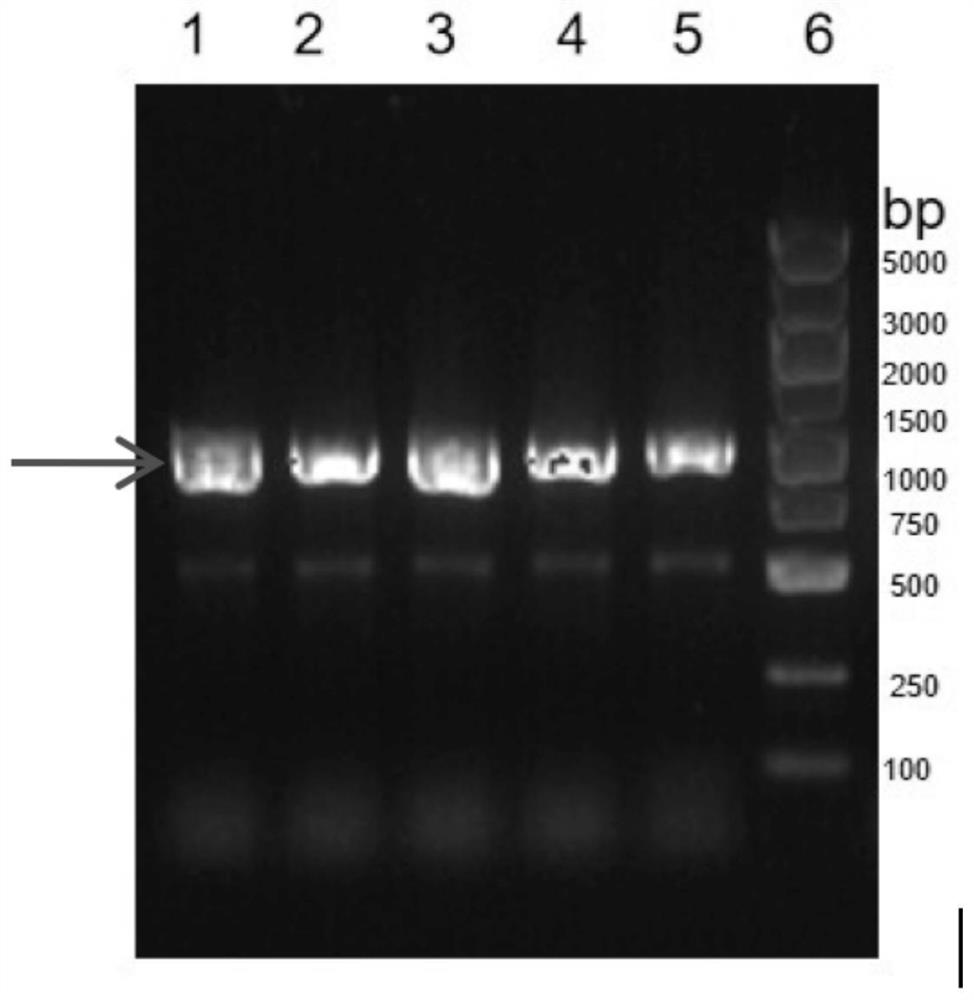
[0070] 1) PCR amplifies three variant genes respectively:
[0071] The N-terminal partial sequence of V1 variant B01 (B0...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Example 2 Vaccine preparation and immune effect test
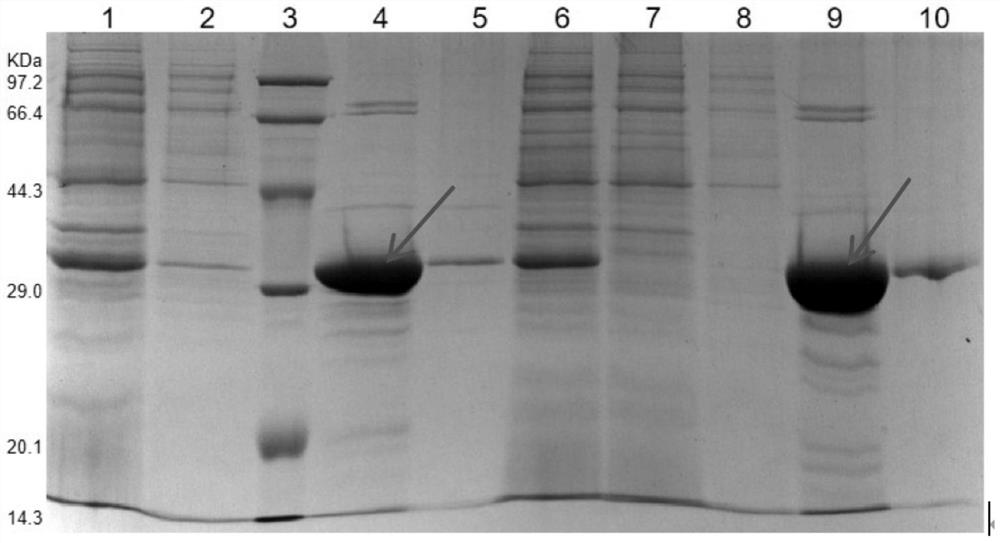
[0148] Vaccine preparation: under sterile conditions, the chimeric protein I (Cp-1) and chimeric protein II (Cp-2) described in Example 1 were mixed with equimolar mass, and then mixed with Freund's adjuvant ( Complete Freund's adjuvant for the first immunization and incomplete Freund's adjuvant for the second immunization) were mixed at a volume ratio of 1:1.
[0149] Contrast vaccine: equal amounts of variant V1 protein and variant V2 protein (amino acid sequences are respectively SEQ ID NO.26-27) were mixed with Freund's adjuvant at a volume ratio of 1:1, and two equal amounts of variable The total molar mass of the bulk protein was equal to the total molar mass of chimeric protein I and chimeric protein II, and the ultrasonic emulsification was carried out under ice bath conditions.
[0150] SEQ ID NO.26[V1, B01, mature peptide]
[0151] MSSGGGGSGGGGVTADIGTGLADALTAPLDHKDKGLKSLTLEDSISQNGTLTLSAQGAEKTYGNGDSLNTGKL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com