Highly stable optical frequency atomic clock based on dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser
A semiconductor and laser technology, applied in the field of atomic clocks, can solve the problems of poor frequency stability of laser atomic clocks, difficult to achieve, and harsh working conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
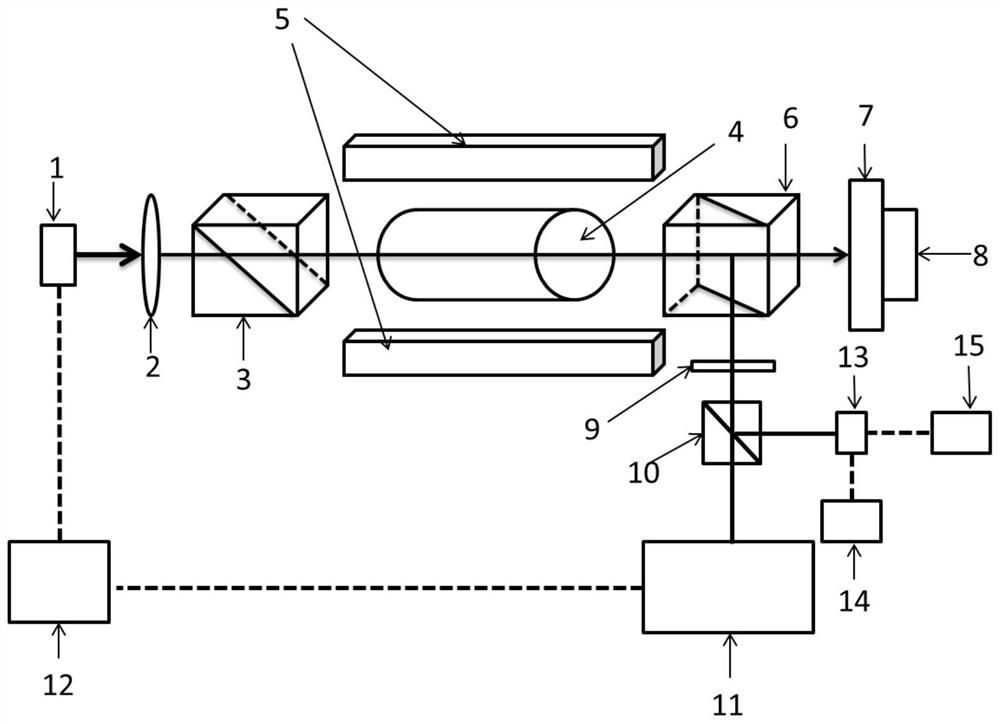
[0039] A high-temperature optical-frequency atomic clock based on a cesium atom 852nm dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser figure 1 As shown, it includes a dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser, a half-wave plate 9 and a third polarization beam splitter 10 arranged on the optical path at the output end of the dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser, a modulation transfer spectrum frequency stabilization module 11, a servo feedback circuit 12, a high frequency detector 13 spectrum analyzer 14 and frequency counter 15. Wherein, the dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser comprises a laser diode 1, a collimator lens 2, a first polarization beam splitter 3, a cylindrical cesium atom gas cell 4 with a length of 3 cm and a diameter of 1.5 cm, and a second laser diode 1 arranged on the optical path in sequence. Polarizing beam splitter prism 6, laser cavity mirror 7 and piezoelectric ceramics 8 arranged on laser cavity mirror 7, wherein, permanent magnet 5 is arrange...
Embodiment 2
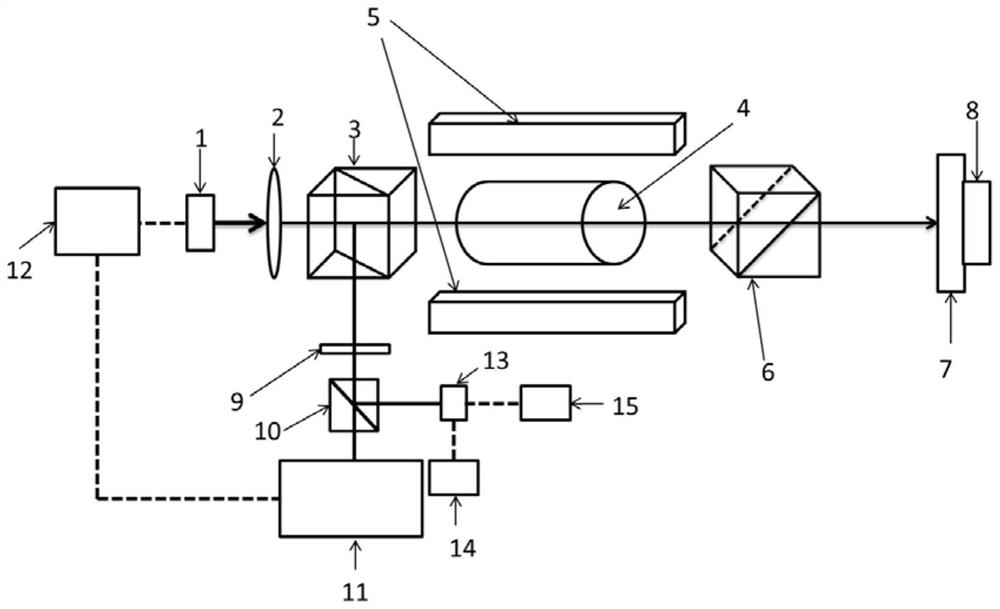
[0053] Such as figure 2 The high-temperature optical-frequency atomic clock based on a cesium atom 852nm dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser shown is used to illustrate another positional relationship between the first and second polarization beam splitters.
[0054] What is different from Embodiment 1 is that the setting direction of the laser diode has been changed so that its output light is a vertically polarized coherent light beam, and the setting direction of the first polarization beam splitter is changed with the second laser diode (in order to keep the second polarization beam splitter and the second polarization beam splitter simultaneously) Orthogonality, the placement angle of the second polarization beam splitter also changes accordingly).
[0055]In this way, the vertically polarized coherent beam emitted by the laser diode 1 coated with anti-reflection film becomes vertically polarized light after being collimated by the collimator lens, so that after t...
Embodiment 3
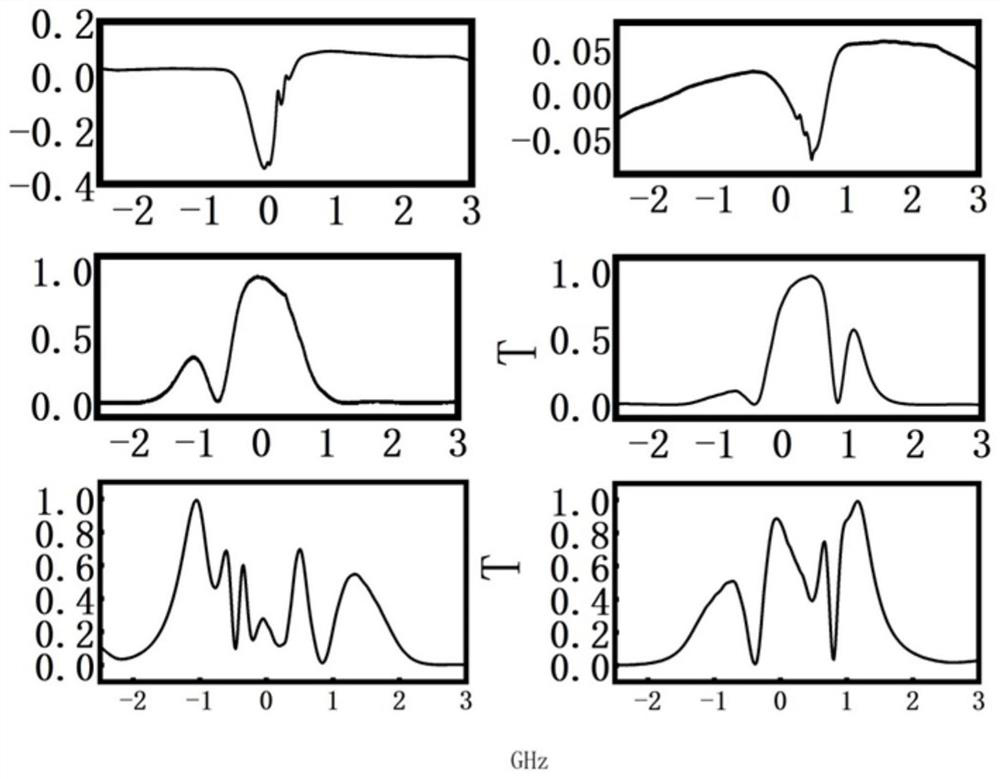
[0057] A high-temperature optical-frequency atomic clock with the same structure and positional relationship as in Example 1, the difference is that the cesium atom gas chamber is filled with 5 Torr argon as a buffer gas, and its transmission spectrum is verified under the conditions of a magnetic field of 500-700 Gauss and a temperature of 43-55 ° C. Figure 7 As shown, it is confirmed that a stable dual-frequency laser output can also be obtained.
[0058] The above embodiment shows that the frequency control unit used in the cesium atom 852nm dual-frequency Faraday semiconductor laser is a cesium atom 852nm Faraday atom filter comprising two transmission peaks at the ground state F=3 transition and the ground state F=4 transition place, and the present invention is the first Using this innovative structure and principle to realize a dual-wavelength semiconductor laser is fundamentally different from existing dual-wavelength laser wavelengths.
[0059] It should be noted tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com