Herpes simplex virus and application thereof
A technology of herpes simplex virus and virus strain, applied in the direction of virus, virus/bacteriophage, double-stranded DNA virus, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing replication and killing ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0106] Example 1 Obtaining of HL-1 strain virus with oncolytic effect
[0107] a) Virus collection
[0108] 63 healthy volunteers with recurrent herpes labialis were recruited, and the herpes fluid was aseptically collected.
[0109] b) Virus screening
[0110] The purpose of this section is to test and screen primary clinical isolates of HSV-1 and select the virus strain with the strongest oncolytic ability.
[0111] Experiments were performed simultaneously using 5 to 8 virus strains each time. Using 17 strains of HSV-1 virus as a control, the virus strains were infected with the same MOI in cells in a six-well plate, and parallel experiments were performed, and the CPE (cytopathic effect) phenomenon caused by the virus was observed after 48 hours of infection and evaluated after crystal violet staining. number of plaques. CPE should be caused by typical HSV-1 infection. The cells become round and gradually fall off from the center of infection to form plaques. Strains ...
Embodiment 2
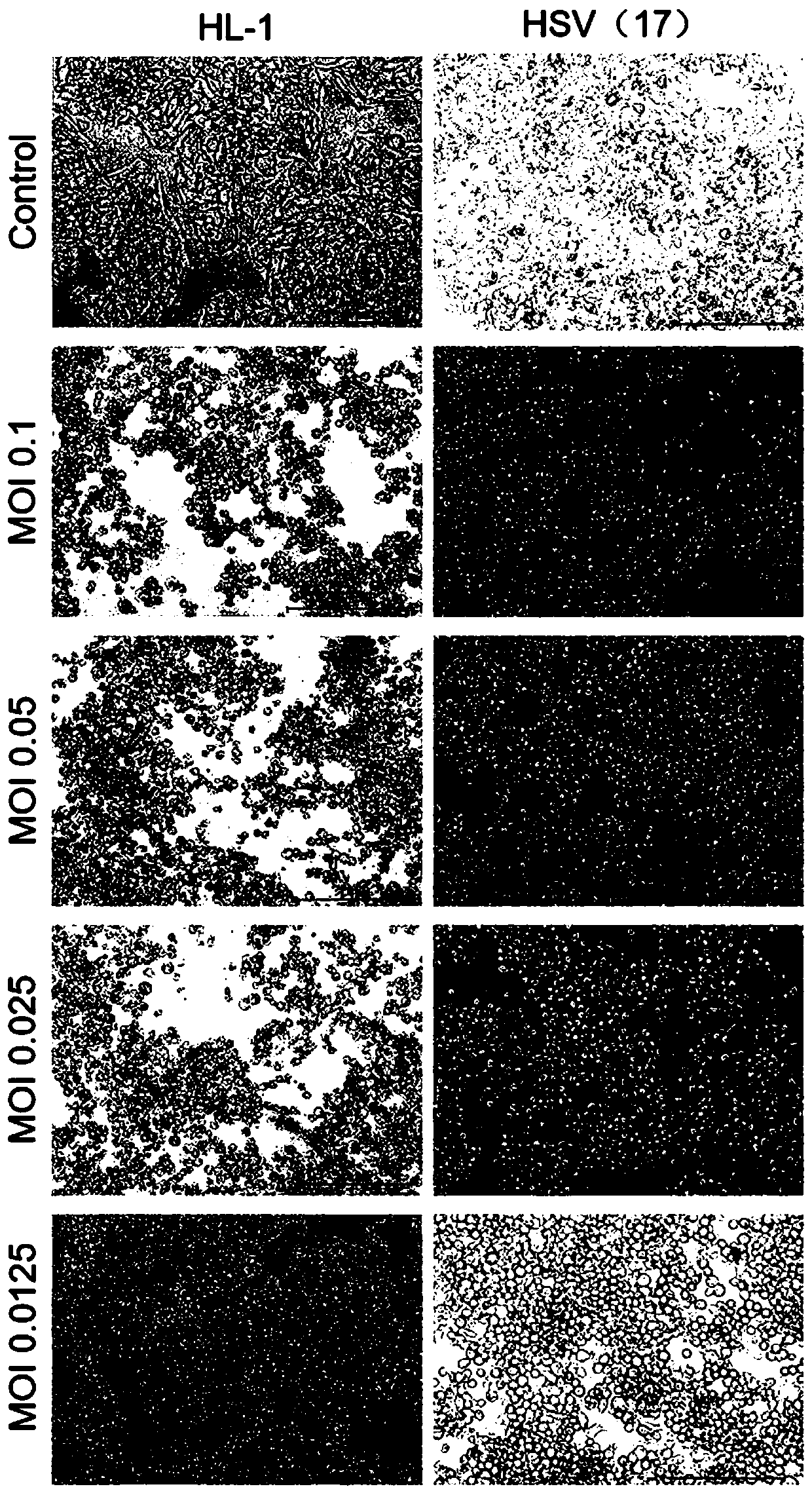
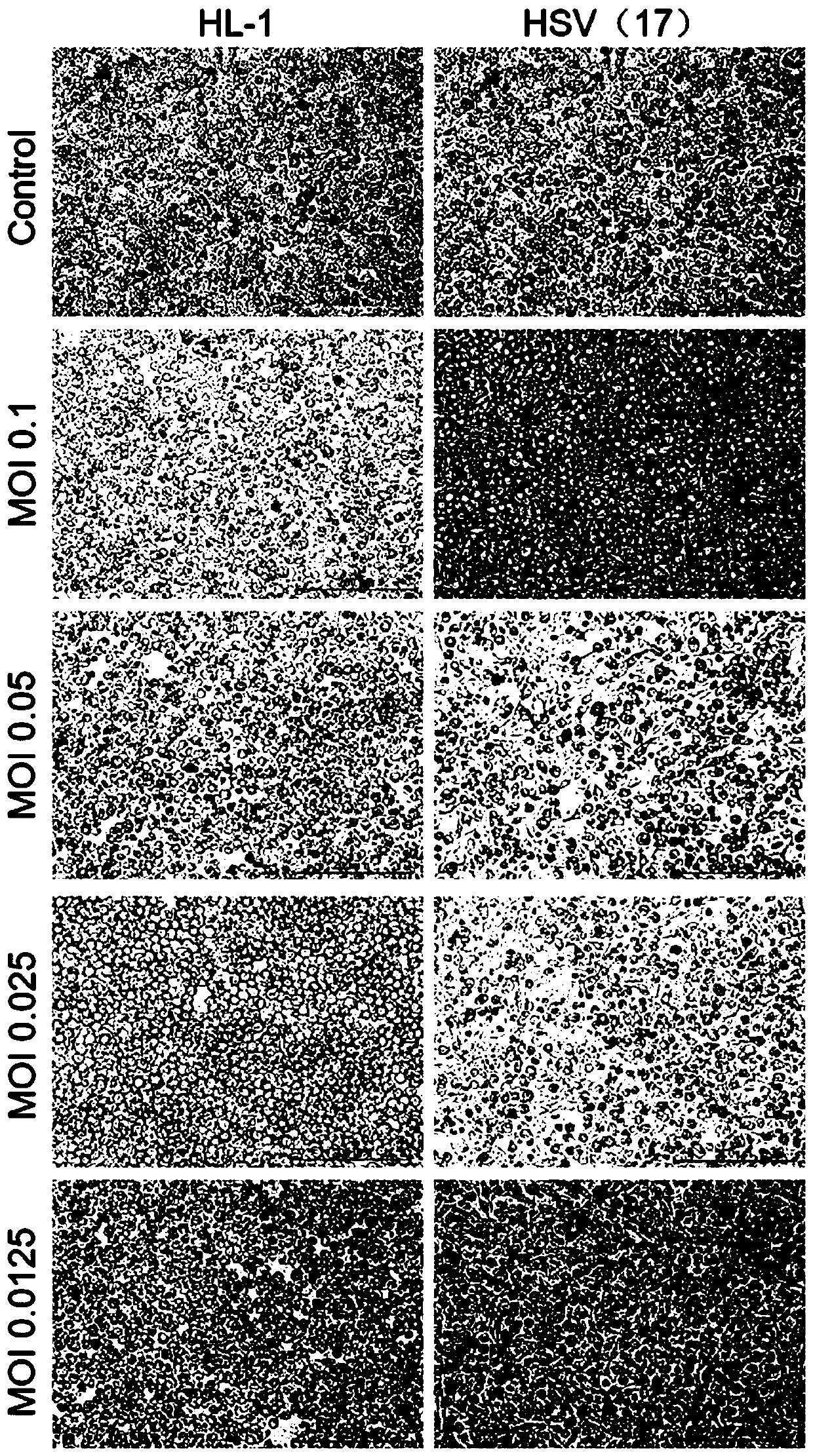
[0126] Example 2 Comparison of oncolytic effects between HL-1 wild strain and 17 strains
[0127] This example provides the comparative experiments and results of replication of HL-1 and 17 strains on different cells and their ability to transfect tumor cells. Experimental cells include: Hep G2 human liver cancer cells, A375 human skin cancer cells, A549 human lung cancer cells, MCF7 human breast cancer cells, HeLa human cervical cancer cells, U251 human glioma cells, and Vero monkey kidney cells.
[0128] The experimental method is as follows:
[0129] 1. Microscopic observation after HL-1 and HSV (17) transfected different cells respectively
[0130] The above-mentioned cells in the logarithmic growth phase were taken, digested and subcultured into a six-well plate for culture. After 24 hours, the old medium was discarded, and 2ml of medium was added to each well. The transfection was carried out according to the number of viruses at different MOIs. After the virus was a...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Example 3 Comparison of Oncolytic Effects of HSV (HL-1) Recombinant Virus and HSV (17) Recombinant Virus
[0155] The ICP34.5 gene and ICP47 gene of the virus strain with the CCTCC preservation number V201810 (CCTCC: 201810) of the present invention and the control virus 17 virus strain were knocked out by genetic engineering methods, and the recombinant virus HL1-△34.5- after gene knockout was compared. △47 and 17-△34.5-△47 have different transfection ability to tumor cells. Experimental cells include Hep G2 human liver cancer cells, A375 human skin cancer cells, A549 human lung cancer cells, MCF7 human breast cancer cells, HeLa human cervical cancer cells, U251 human glioma cells, and Vero monkey kidney cells.
[0156] Cells in the logarithmic growth phase were taken, digested and passaged to 96-well plates. After 24 hours, the old medium was discarded, and 9 different virus dilutions were added, 100 μl / well, so that the MOI was 20, 5, 1.25, 0.3125, 0.0781, 0.0195, 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com