Lubricating composition comprising a diester
A lubricating composition and composition technology, applied in the direction of lubricating compositions, base materials, additives, etc., can solve problems such as lubricant non-compliance, and achieve the effect of reducing fuel consumption and combustion consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
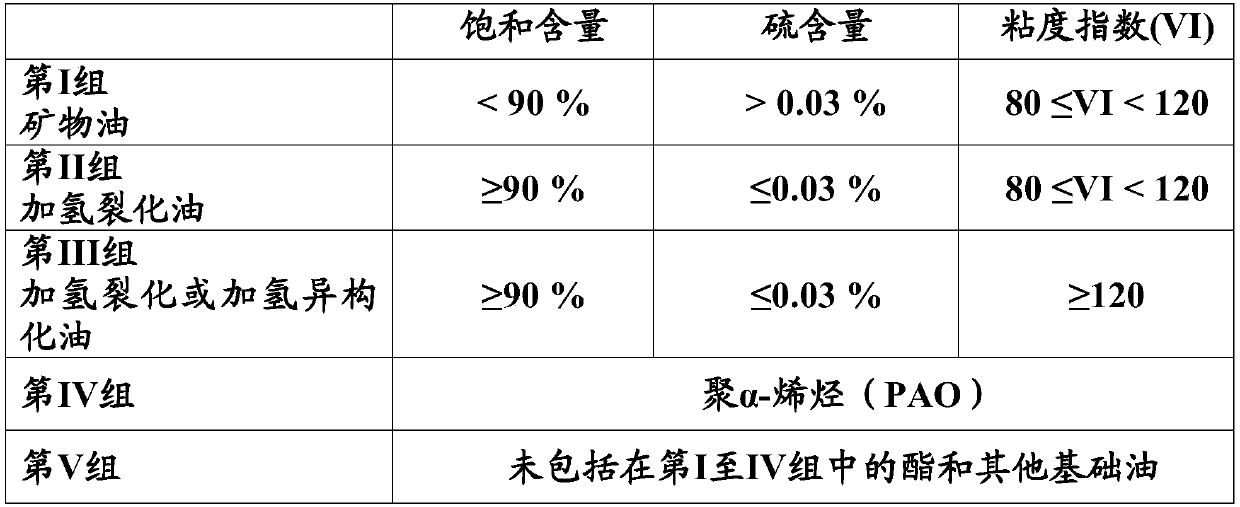
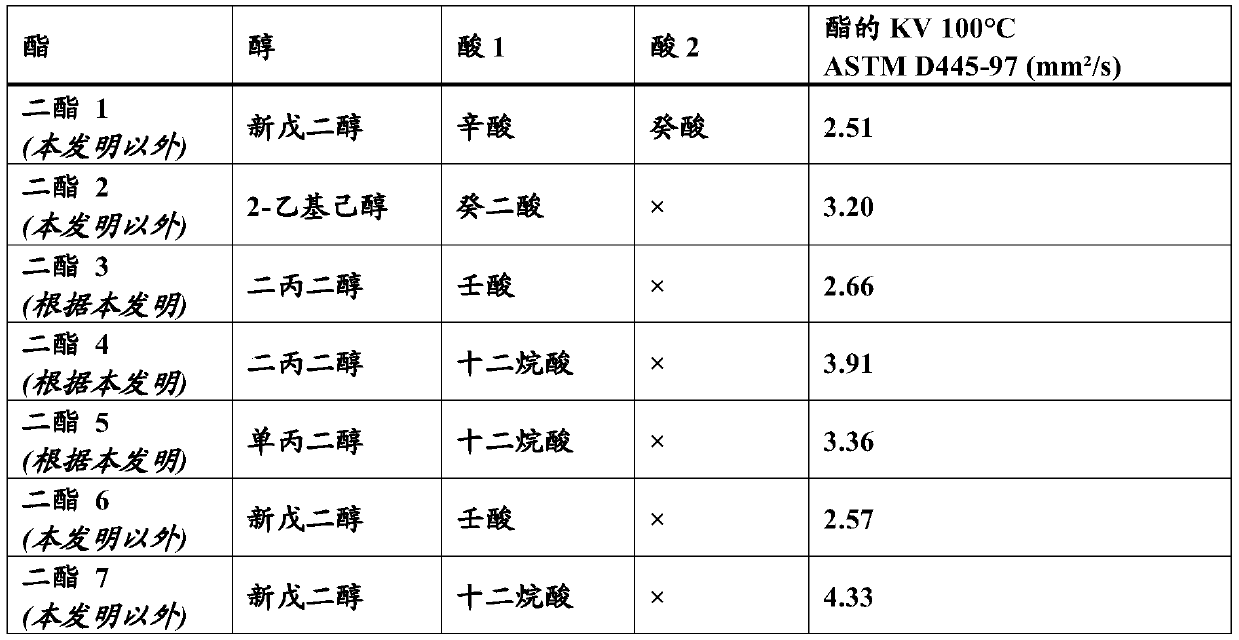
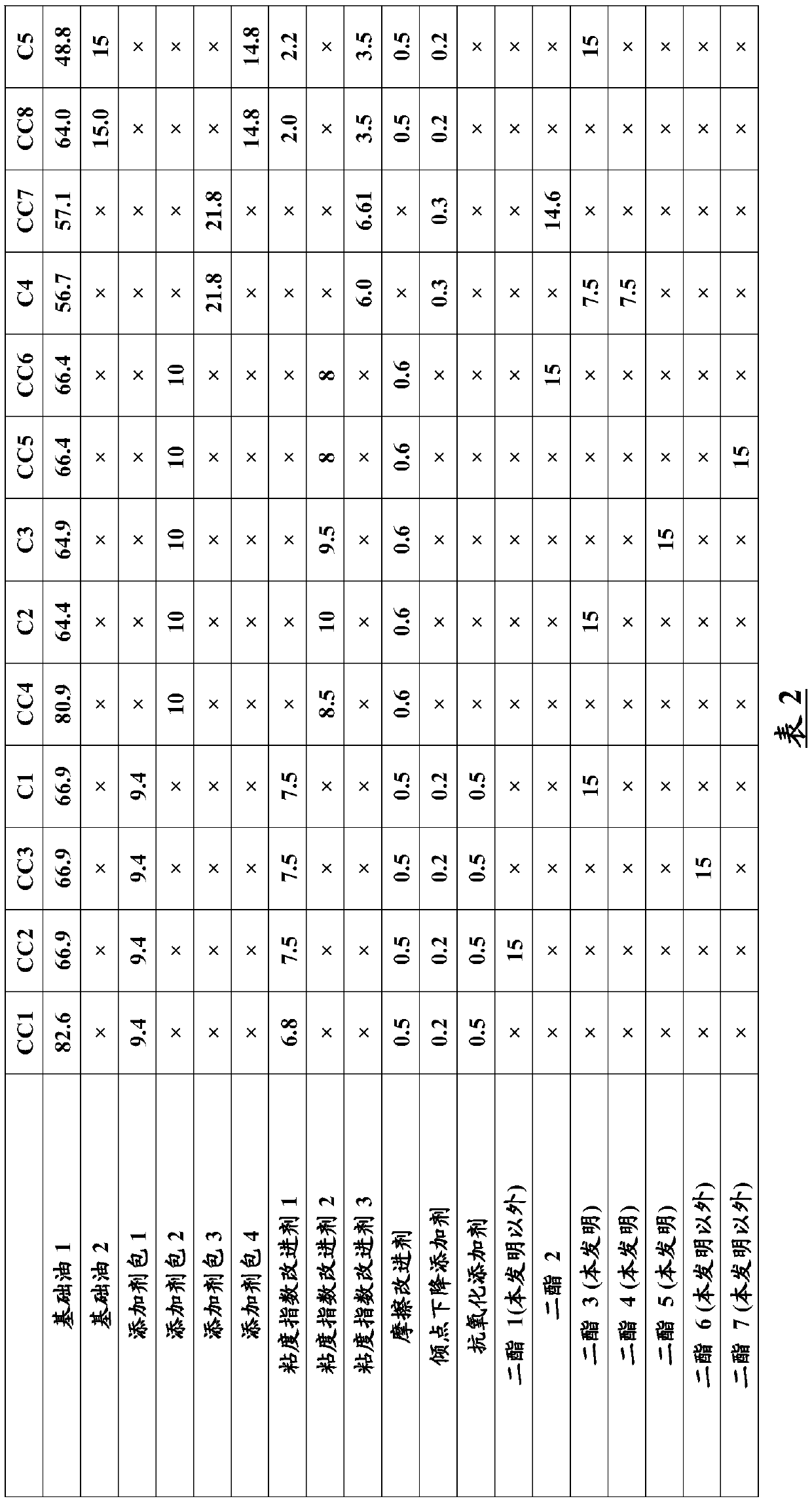
[0221] Physicochemical Characterization of Lubricating Compositions According to the Invention and Comparative Compositions
[0222] Tables 2 and 3 below show details of lubricating compositions according to the invention and comparative compositions and their physicochemical properties.
[0223] The lubricating composition is obtained by simply mixing the following ingredients at ambient temperature:
[0224] - Base oil 1 is a base oil of group III (kinematic viscosity at 100°C measured according to standard ASTM D-556 = 4.11 mm 2 / s), for example available from SK under the trade name "Yubase4+",
[0225] - Base oil 2 is a base oil of group III (kinematic viscosity at 100°C measured according to standard ASTM D-556 = 6mm 2 / s), for example commercially available from SK Corporation under the trade name "Yubase6",
[0226] - a conventional additive package (paquet) 1 comprising dispersants, detergents, antiwear additives,
[0227] - Regular Additive Pack 2,
[0228] - ...
Embodiment 2
[0241] Characterization of Compositions According to the Invention and Comparative Compositions in terms of Fuel Economy ("Fuel-Eco")
[0242] The test was carried out with the aid of an EB 1.2L Turbo engine with a power of 81kW at 5500rpm, driven by a generator which enables the application of a rotational speed of 900-4500rpm, and a torque sensor which enables the measurement of the movement by components in the engine resulting frictional torque. For each regime and each temperature, the frictional torque induced by the test lubricant was compared with the torque induced by the reference lubricant composition (SAE 0W30).
[0243] The conditions of this test are as follows.
[0244] The tests are carried out in the following order:
[0245] - flushing of the engine with a flushing oil containing detergent additives, followed by a reference lubricating composition;
[0246] - Measurement of frictional torque at four different temperatures indicated below on an engine usi...
Embodiment 3
[0262] Characterization of Compositions According to the Invention and Comparative Compositions in terms of Fuel Economy ("Fuel-Eco")
[0263] The test was carried out with the aid of a Nissan HR12DDR engine with a power of 180kW at 6500rpm, driven by a generator that enables the application of rotational speeds from 1000-4400rpm, and a torque sensor that enables the measurement of torque generated by the movement of components in the engine frictional torque. For each operating condition and each temperature, the friction torque induced by the test lubricant was compared to the average torque induced by the reference lubricant composition (SAE 0W16), which was evaluated before and after the test lubricant.
[0264] The conditions for this test are as follows.
[0265] The tests are carried out in the following order:
[0266] - flushing of the engine with a flushing oil containing detergent additives, followed by a reference lubricating composition;
[0267] - Measuremen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com