Q-learning optical network-on-chip adaptive routing planning method based on Dijkstra algorithm
An optical-on-chip network and self-adaptive technology, which is applied in data switching networks, multiplexing system selection devices, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as low convergence speed, high time complexity, and inability to provide the shortest path. Achieve fast speed, expand the scope of application, and have universal effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
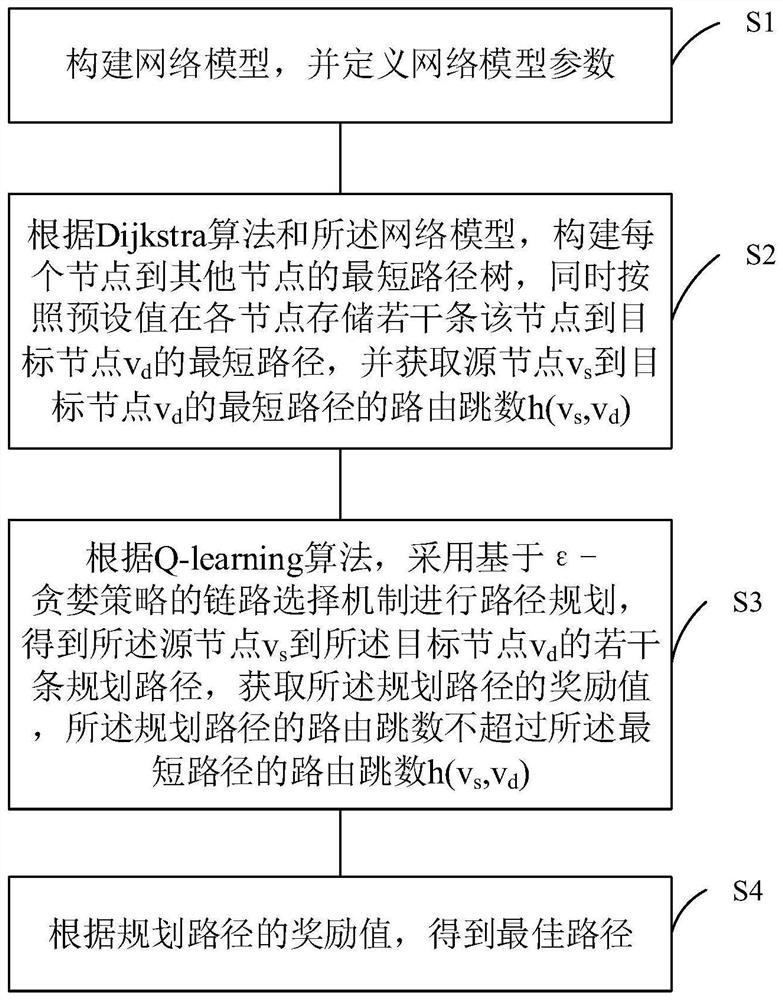
[0052] Based on the N×N mesh network and the Cygnus router, the Q-learning optical on-chip network adaptive routing planning method based on the Dijkstra algorithm in this embodiment is specifically described. Please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flowchart of a Q-learning optical on-chip network adaptive routing planning method based on the Dijkstra algorithm provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the method of the present invention includes:
[0053] S1: Construct a network model and define network model parameters;
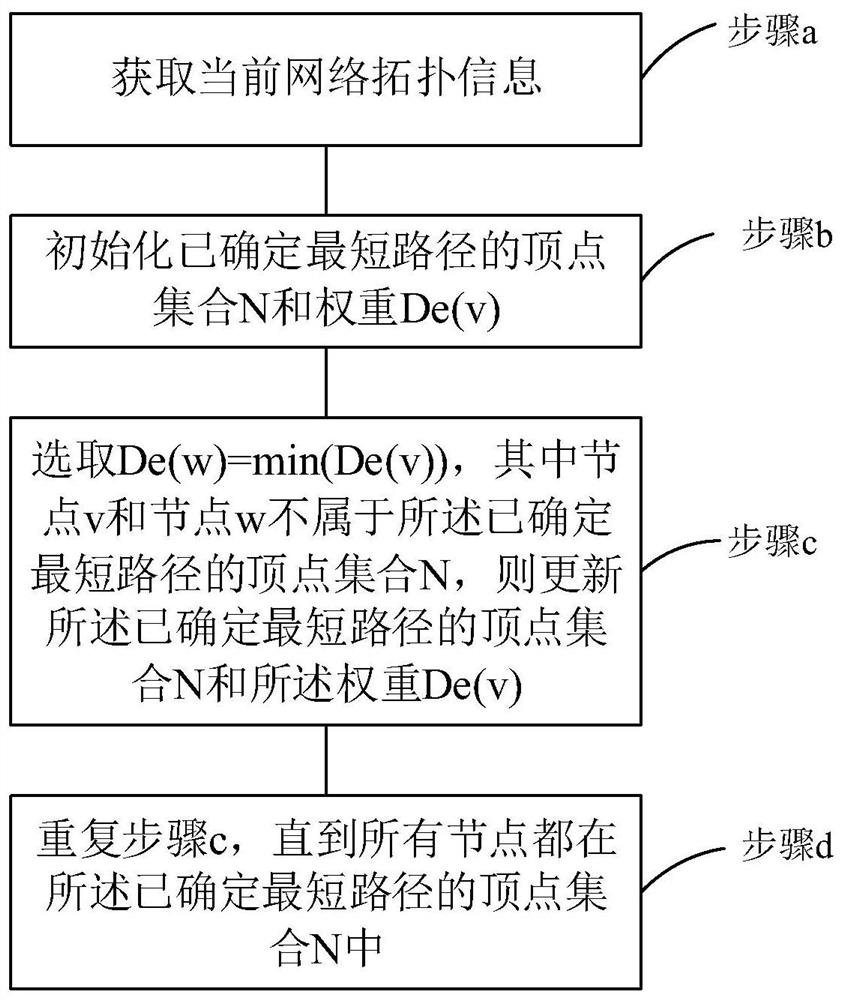
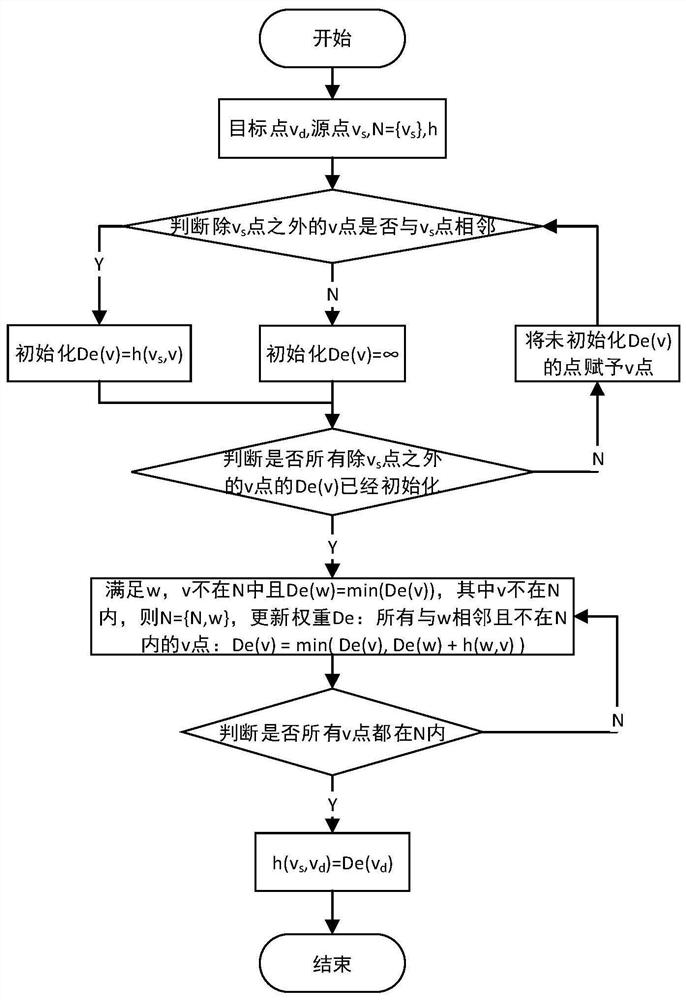
[0054] Specifically, in this embodiment, the network is represented by a weighted directed graph G(V, E), where V represents a router node set, and E represents a router node bidirectional data link set. Based on the N×N mesh network to construct a coordinate system and a Cygnus router with five inputs and five outputs, each node can be identified by coordinates (x, y). A path is defined as an ordered set of points ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com