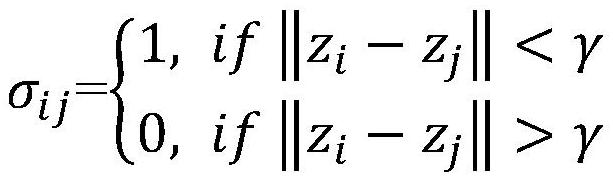Group target clustering method based on algebraic graph theory
A technology of algebraic graph theory and group objectives, applied in complex mathematical operations, instruments, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve problems such as confusion of grouping results, errors in grouping results, and unsuitability for practical application scenarios without prior knowledge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
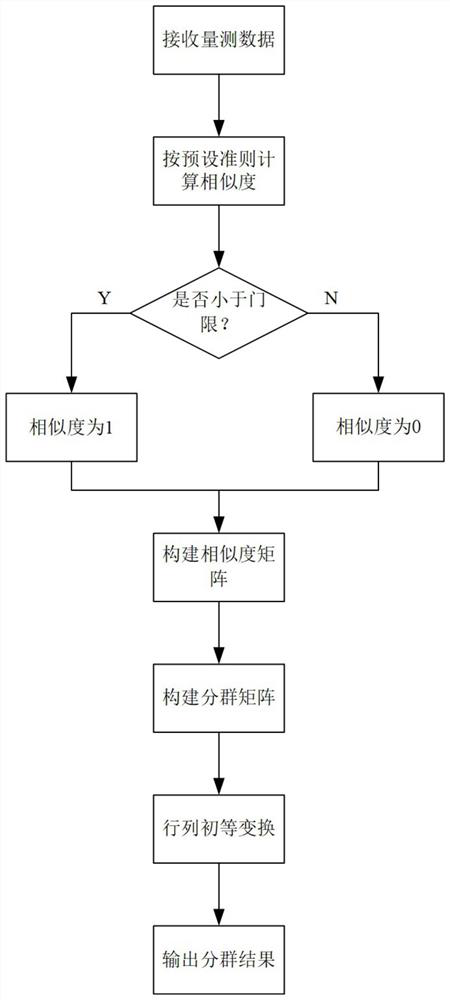
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, a group target grouping method based on algebraic graph theory includes the following steps:
[0033] Step 1. It is assumed that the radar performs pulse compression and constant false alarm detection on the echo during a scanning process to obtain a set of effective measurement sets Z in the scanning space at the tth moment t ={z i}={z 1 ,z 2 ,…,z k}, where z i is the state vector of the i-th target, and the state vector includes the position, velocity and acceleration of the target, i=1, 2,..., k, k is the number of targets in the t-th scanning moment;
[0034] Step 2. Calculate the similarity σ between the i-th element and the j-th element in the set Zt ij , wherein, j=1, 2, ..., k; similarity can be defined according to actual needs, and the distance between commonly used targets is used as the discrimination criterion; the present invention adopts the following preferred definitions:
[0035]
[0036] Among them, γ is the preset...
Embodiment 2
[0057] In this embodiment, taking the group target as a flock of birds as an example, a method for grouping group targets based on algebraic graph theory is described in detail.
[0058] Step 1. Use a high-resolution radar containing only distance information to observe multiple flocks of birds; high-resolution radar bandwidth B=785MHz, distance resolution △=c / 2B=0.19m, where c is the speed of light; for the data after a certain scan After performing pulse compression and constant false alarm detection, a total of 6 effective echoes were detected, and the distances to the radar were 300m, 315m, 320m, 298m, 305m, and 318m; mark the targets as No. 1 to No. 6 in the above order;
[0059] Step 2. Calculate the similarity between objects. According to the bird habits and flight characteristics, the threshold is set to 6m; when the distance between two birds is less than 6m, it is judged to be similar; when the distance between two birds is greater than 6m, it is judged to be dissim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com