Systems and methods for evaluating a loss function or a gradient of a loss function via dual decomposition
A loss function and gradient technique, applied in the field of computer systems for evaluating loss functions and/or their gradients, capable of solving a large number of operations, requiring linear running time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
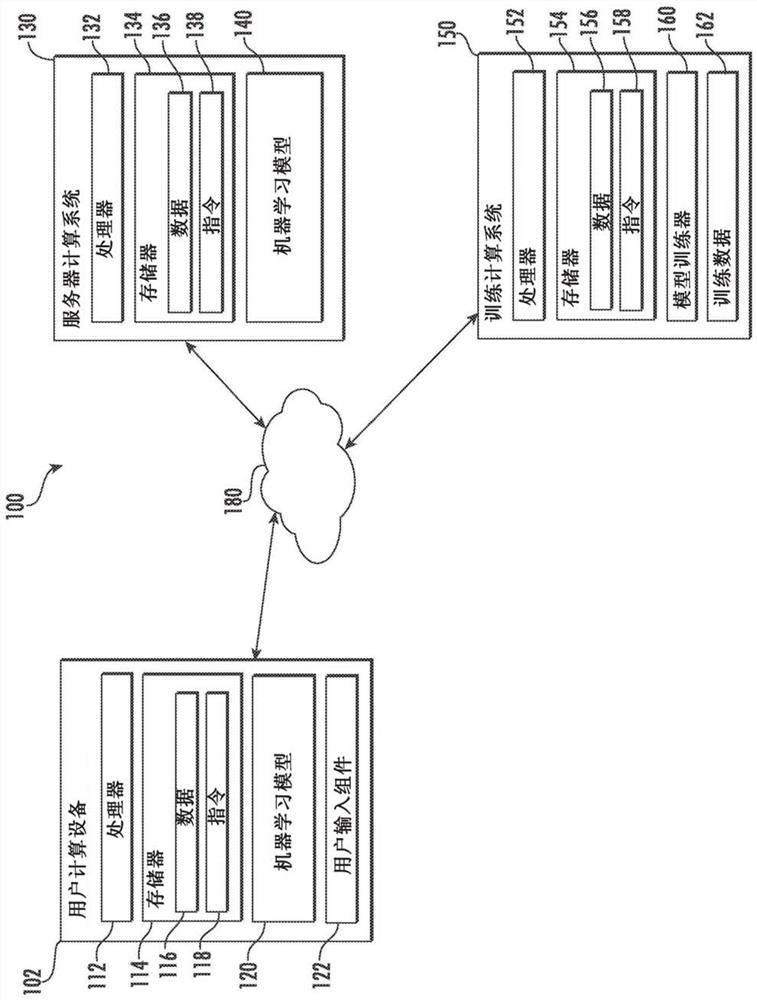
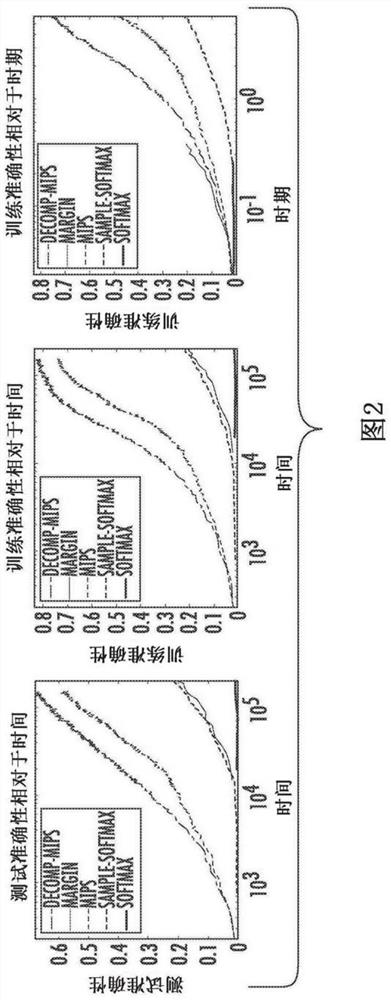
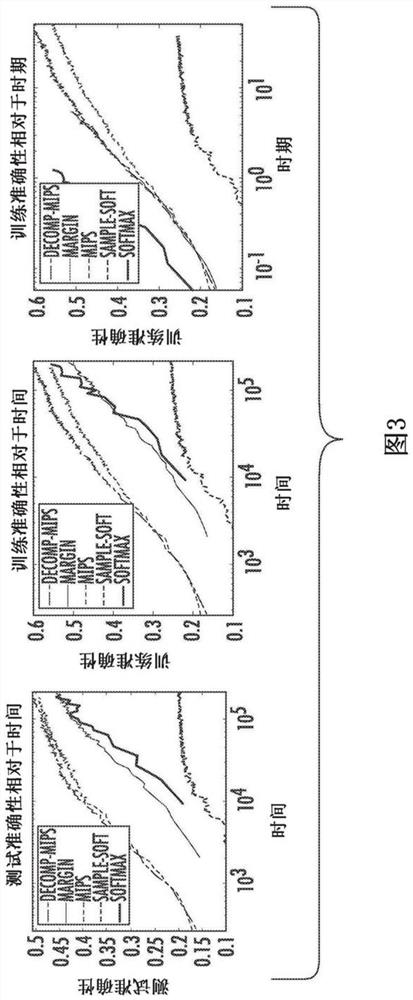
[0028] In general, the present disclosure relates to systems and methods for evaluating loss functions or gradients of loss functions. For problems with large output spaces, evaluating the loss function and its gradients can be computationally expensive, typically taking linear time in the size of the output space. Recently, methods to accelerate learning via efficient data structures for nearest neighbor search (NNS) or maximum inner product search (MIPS) have been developed. However, the performance of such data structures usually degrades in high dimensions. The present disclosure provides systems and methods for reducing an intractable high-dimensional search problem to several much easier to solve lower-dimensional search problems via a dual decomposition of a loss function. The present disclosure further provides a greedy message passing technique that guarantees the convergence of the original loss. In this manner, the disclosed systems and methods can substantially i...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap