A robotic arm obstacle avoidance method based on proximity perception
A robotic arm and proximity sensor technology, applied in the field of robotic arm obstacle avoidance path planning, can solve the problems of large amount of visual information data, high price of visual sensors, and easy occlusion, so as to avoid easy occlusion, low cost, and meet real-time requirements. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
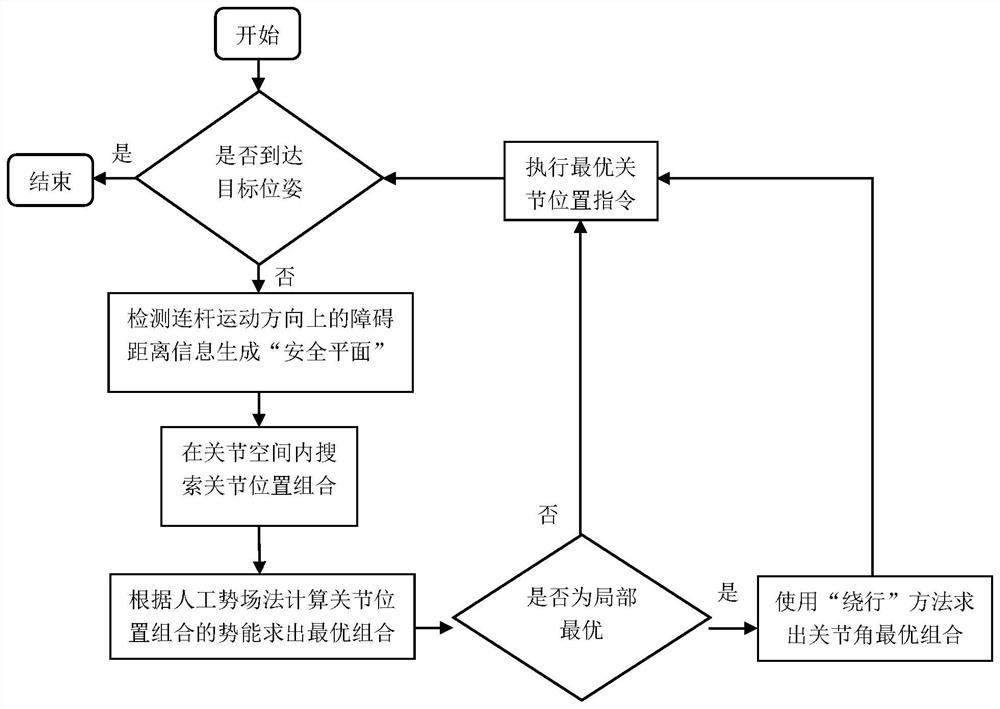
[0035] A method for avoiding obstacles of a mechanical arm based on proximity perception, the specific steps are as follows:
[0036] Step 1, lay out the proximity sensor array:
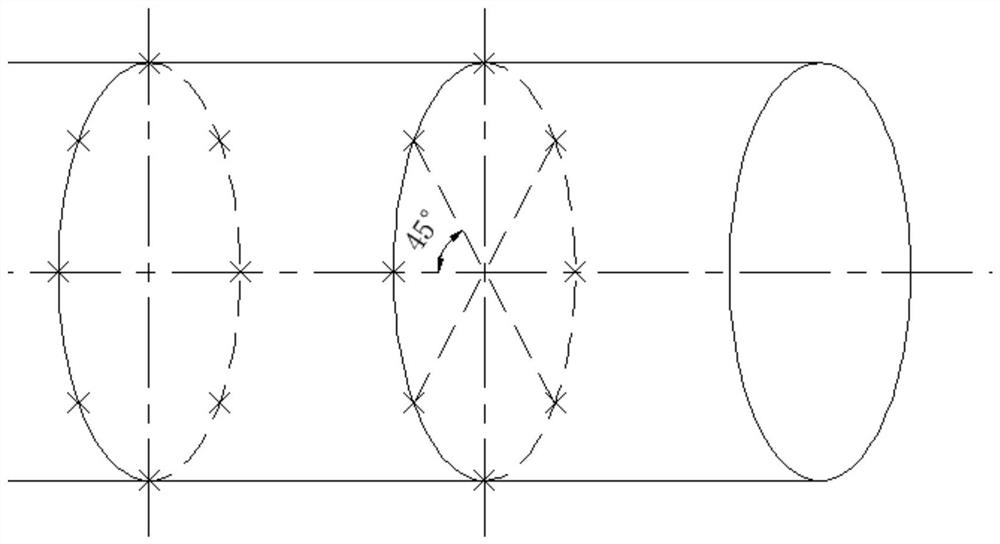
[0037] like figure 2 As shown, the proximity sensor array is arranged on the obstacle-avoiding link, and 8 (or 4, 6, etc.) are arranged equally on a circle, and each different circle is equally spaced from each other.
[0038] Step 2, determine the direction of movement of the connecting rod:
[0039] Calculate the expected pose of the connecting rod in the next control cycle through robot kinematics, combined with the current pose of the connecting rod, you can find the expected pose of the cycle under the center line of the connecting rod and determine its motion direction;
[0040] Step 3, collect sensor distance information:
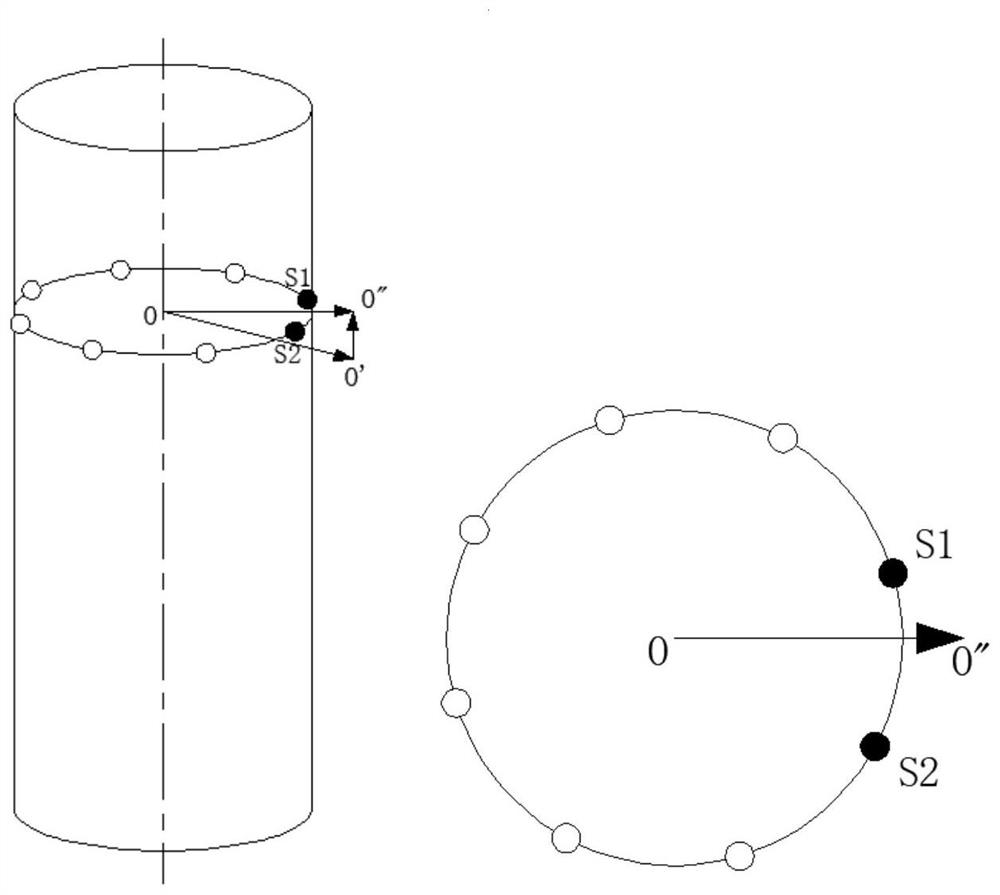
[0041] like image 3 As shown in the figure, the proximity sensor on a circle of the obstacle avoidance link is shown, O' is the desired spatial position of the center...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special feature is that in step 6, the artificial potential field method often falls into the local optimal trap, but the proposed algorithm can only perceive the safe plane, and the usual artificial potential field improvement method It is difficult to apply at this time, so an improved strategy based on detour is proposed, such as Figure 7 As shown, the obstacle avoidance link escapes from the local optimal trap after using the detour strategy. In this method, when the obstacle avoidance link falls into the local optimal trap, the potential function of the gravitational field changes, making the The connected previous joint rotates in one direction, and the gravitational potential field of the other joints is still determined according to the target pose, resulting in circumvention behavior until the safe plane changes, the algorithm escapes from the local optimal trap, and finally the robot reaches the ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com