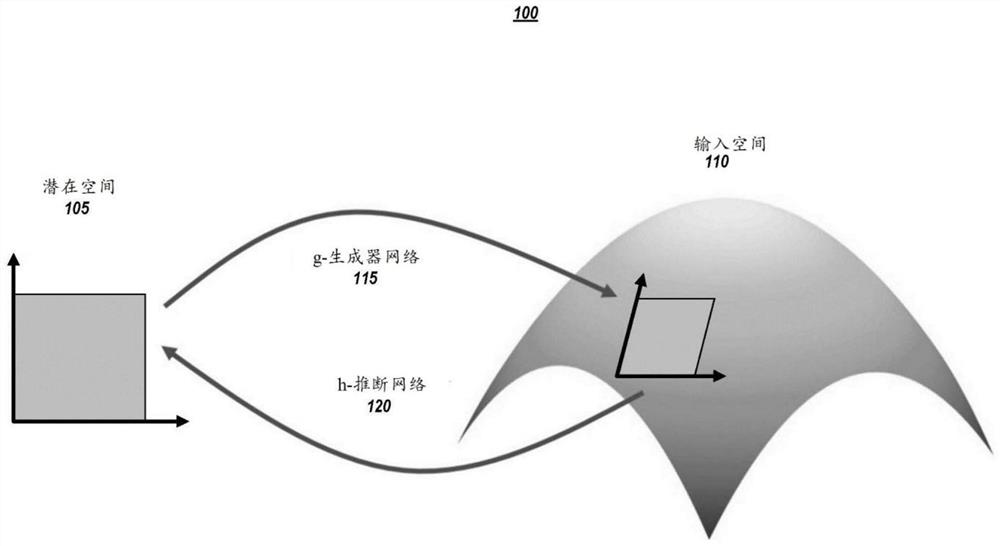
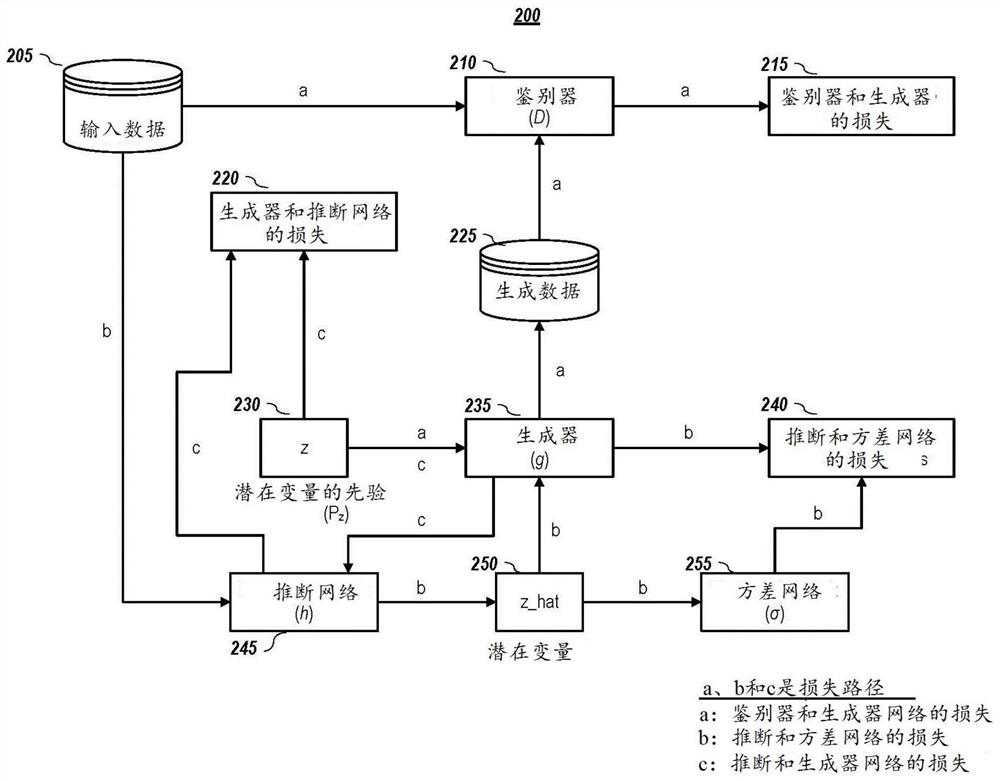
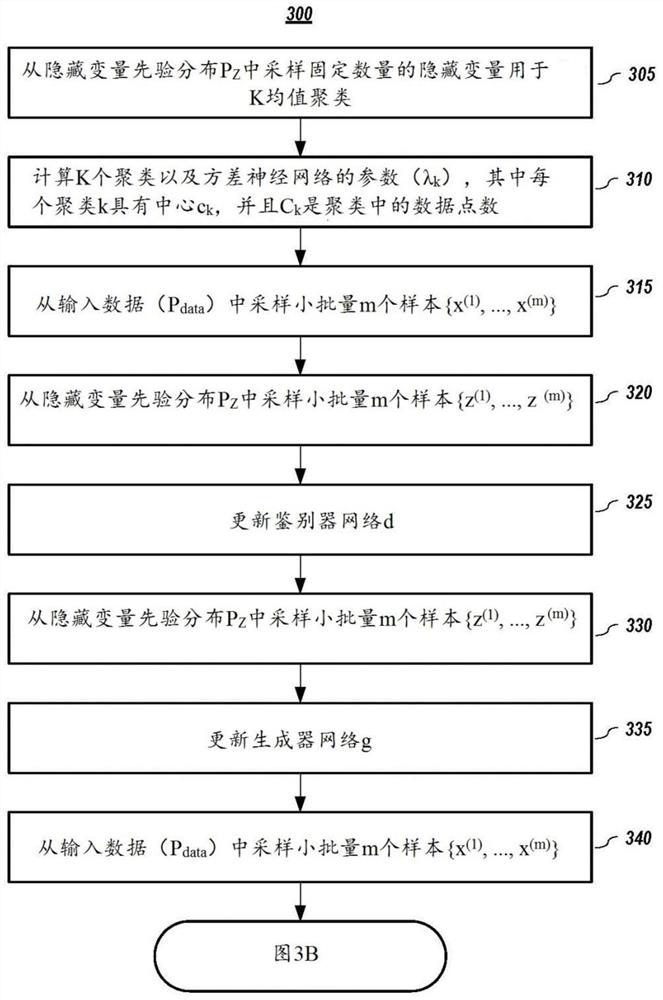
Estimation of the implicit likelihoods of generative adversarial networks
A network and generator technology, applied in the field of implicit likelihood embodiments, can solve problems such as not providing qualitative methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] In the following description, for purposes of explanation, specific details are set forth in order to provide an understanding of the present disclosure. It will be apparent, however, to one skilled in the art that the present disclosure may be practiced without these details. Furthermore, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the embodiments of the present disclosure described below can be implemented in various ways, such as a process, an apparatus, a system, a device, or a method on a tangible computer readable medium.
[0024] Components or modules shown in the figures are exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure for illustration and are intended to avoid obscuring the present disclosure. It should also be understood that throughout the discussion, components may be described as separate functional units, which may include subunits, but those skilled in the art will recognize that various components or portions thereof may be divided into separate com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com