Device for automatically locating railway vehicle
A technology of locomotives and phases, applied in the direction of vehicle control routing devices, transportation and packaging, railway car body parts, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
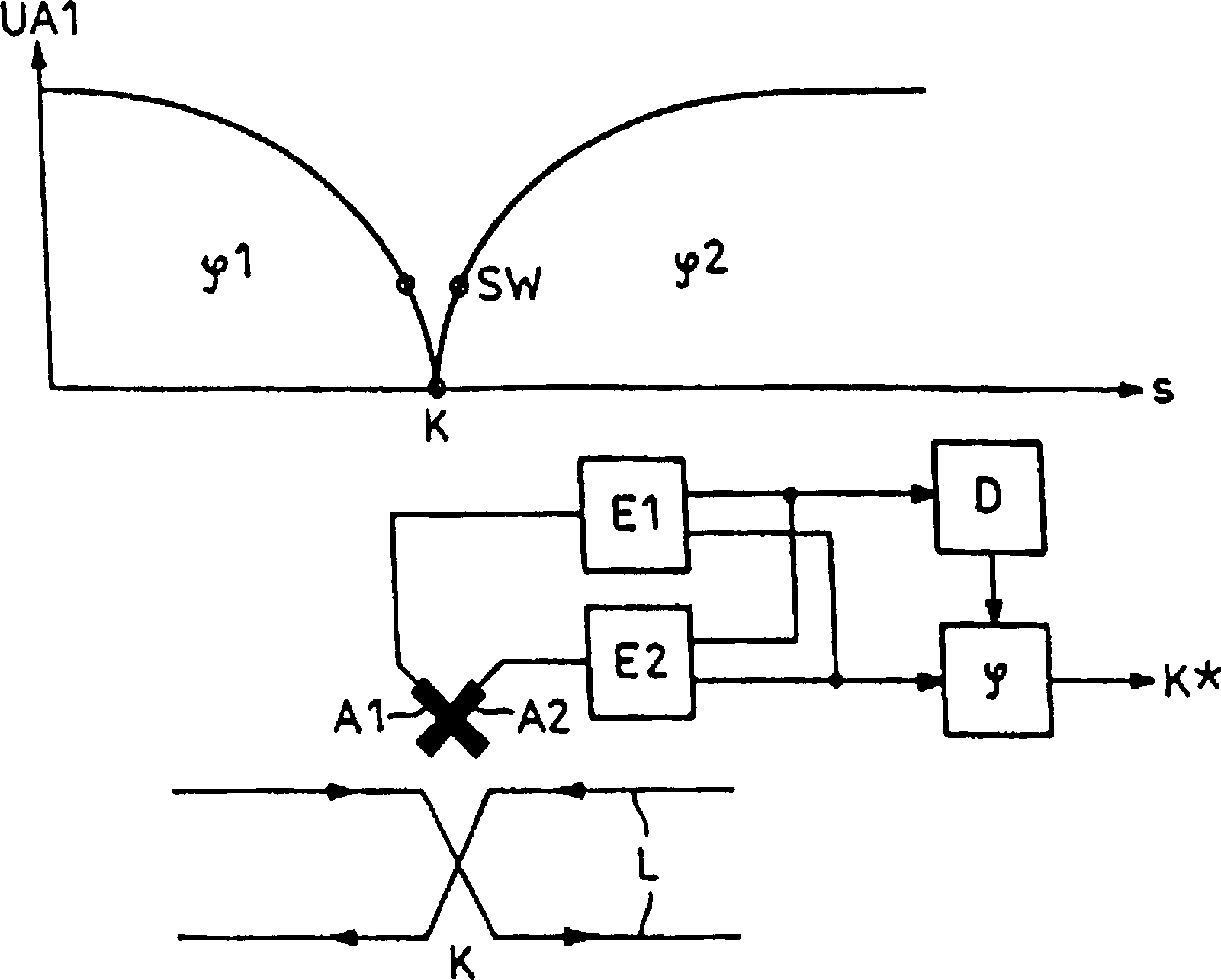
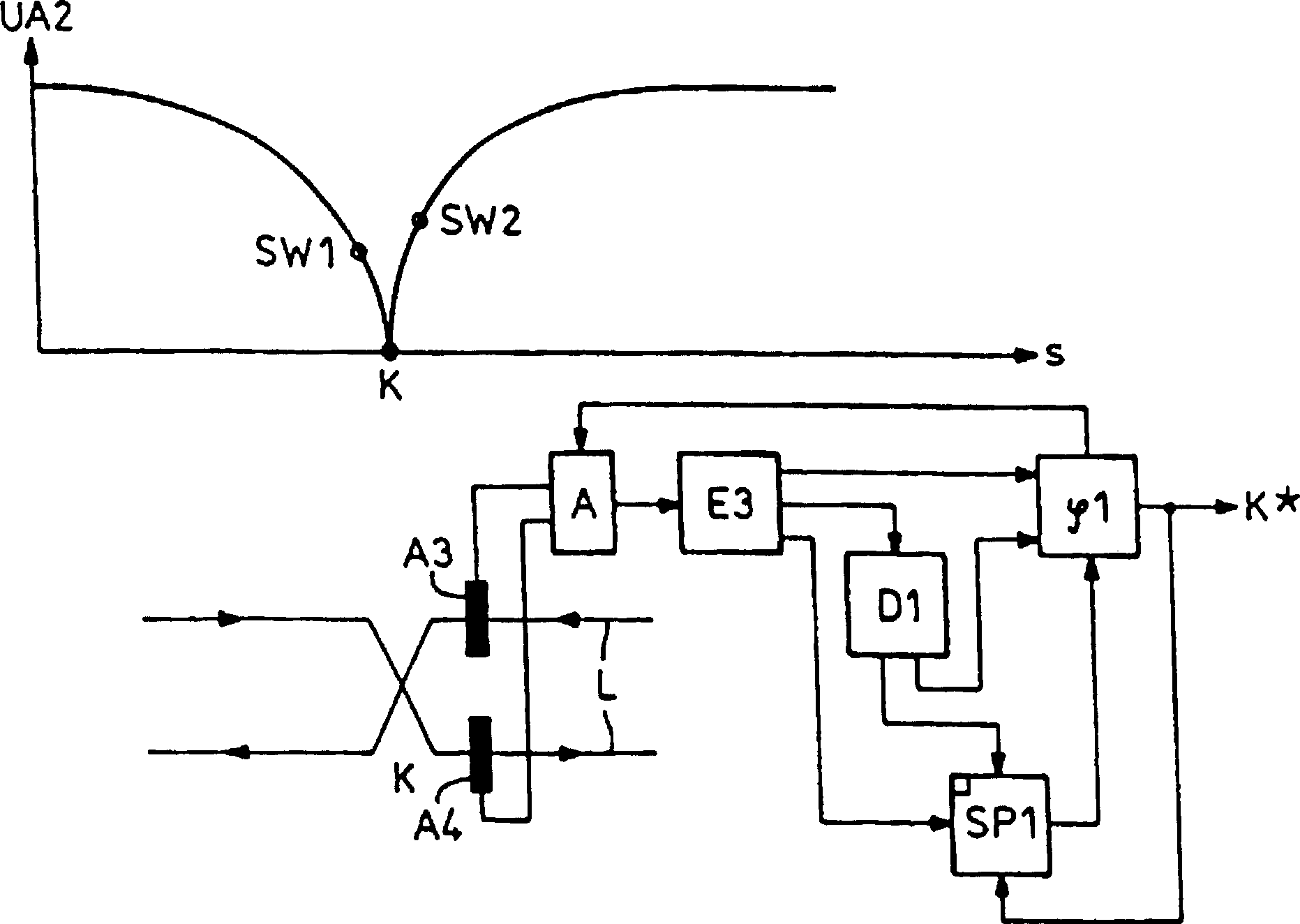
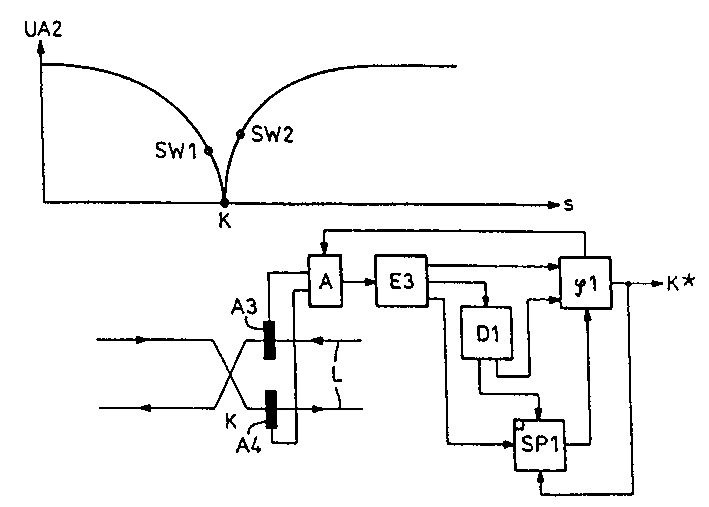
[0012] The figure shows a partial schematic diagram of a sensor wire L laid between the track rails (not shown), through which a signal current flows in the direction of the arrow. This signal current forms a magnetic field around the sensor wire which is picked up by the cross receiving antennas A1, A2 of the locomotive running on the track. At the line crossing point K, where a locomotive should be detected as it passes, the change in the geometry of the sensing conductors in the track towards the return conductors is significant. As can be seen from the illustrated variation of the receiving voltage UA1 of a receiving antenna on the locomotive side over the route S, the receiving voltage drops when the locomotive antenna approaches the line intersection in order to increase to the same value later. In this case, the phase of the received voltage changes by 180°, since the sensor line sections arranged at the bottom of the antenna have signal currents flowing in different di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com