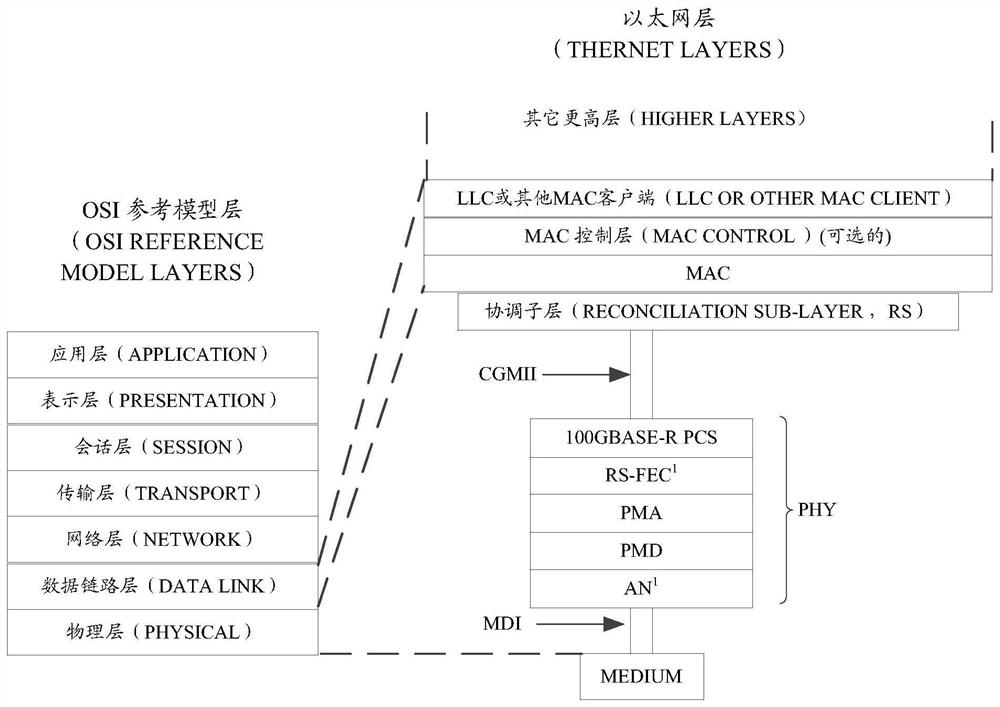
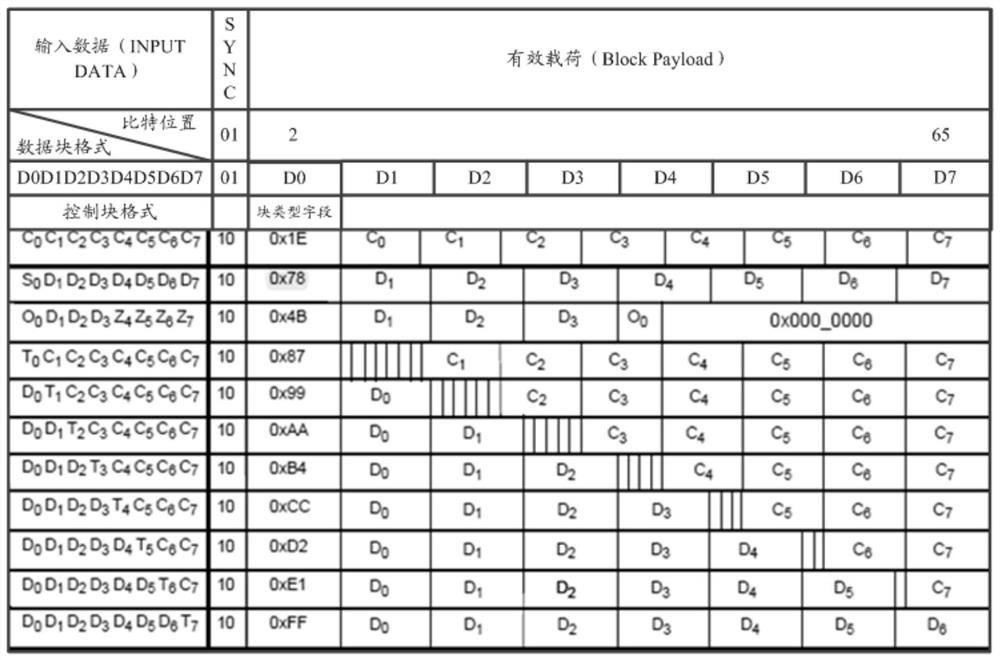
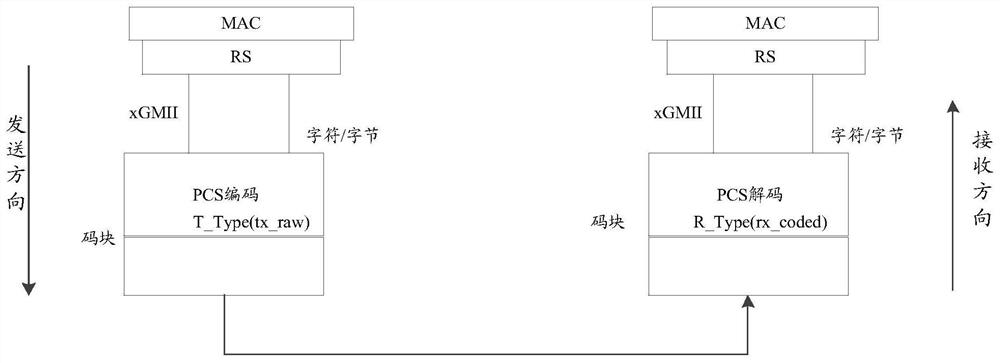
Rate adaptation method and device
A rate adaptation and code block technology, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as low reliability, misinterpretation of messages at the sink end, and influence on the correctness of message interpretation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0177]Example 1, T code blocks and errors caused by T code blocks.
[0178] (1) Errors caused by improper insertion position of IDLE:
[0179] like Figure 10A As shown, the original code block stream sent by the sender is the first line of code block stream. If the rate adaptation IDLE is not added or deleted in the middle, the sink will check the sequence of code blocks according to the receiving state machine, and the decoded code block stream is the first row. Two-line code block stream. Because there is an E code block, the first packet is wrong and will be discarded by the MAC when the FCS check fails.
[0180] like Figure 10B As shown, if IDLE is inserted between the T code block and the T code block in the original code block stream sent by the sender, because it is inserted between the T code block and the T code block, the original code block stream is changed. The relationship between error code blocks, such as Figure 10B As shown in the first line of , this ...
example 2
[0184] Example 2, errors caused by T code blocks and E code blocks.
[0185] (1) Errors caused by improper insertion position of IDLE:
[0186] like Figure 10E As shown, the original code block stream sent by the sender is the first line of code block stream. In the case of no rate-adapted IDLE code block insertion, the status of the message received and interpreted by the sink is shown in the second line , that is, both packets are error-prone.
[0187] like Figure 10F As shown, because the IDLE code block is inserted between the T and E code blocks of the original code block stream during rate adaptation, the state after the code block is inserted is as follows Figure 10F As shown in the first line, the packet received by the sink end is interpreted as Figure 10F The status in the second line, that is, the second message has an error, does not match the actual situation where both messages have errors.
[0188] (2) IDLE deletes errors caused by improper location:
...
example 3
[0191] Example 3, errors caused by T code blocks and D code blocks.
[0192] (1) Errors caused by improper insertion position of IDLE:
[0193] like Figure 10I As shown in , the original code block stream sent by the sender is the first line of code block stream. In the case of no IDLE code block insertion for rate adaptation, the status of the message interpreted by the sink end is shown in the second line, that is, two All messages are wrong.
[0194] like Figure 10J As shown, in the case of IDLE code block insertion for rate adaptation, the sender inserts IDLE code blocks between the original code block stream T code block and D code block, as shown in Figure 10J As shown in the first line, the message status interpreted by the sink is as follows Figure 10J As shown in the second line, that is, the second packet has an error, which is inconsistent with the actual situation that both packets have errors.
[0195] (2) IDLE deletes errors caused by improper location: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com