Unmanned aerial vehicle internet of things system and method for balancing energy consumption and service life of sensor in unmanned aerial vehicle internet of things system
A networked system and sensor technology, applied in the direction of reducing energy consumption, network topology, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as unbalanced energy consumption, unbalanced energy consumption of sensors, and inability to effectively prolong the life of the system, so as to achieve energy consumption and The effect of longevity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
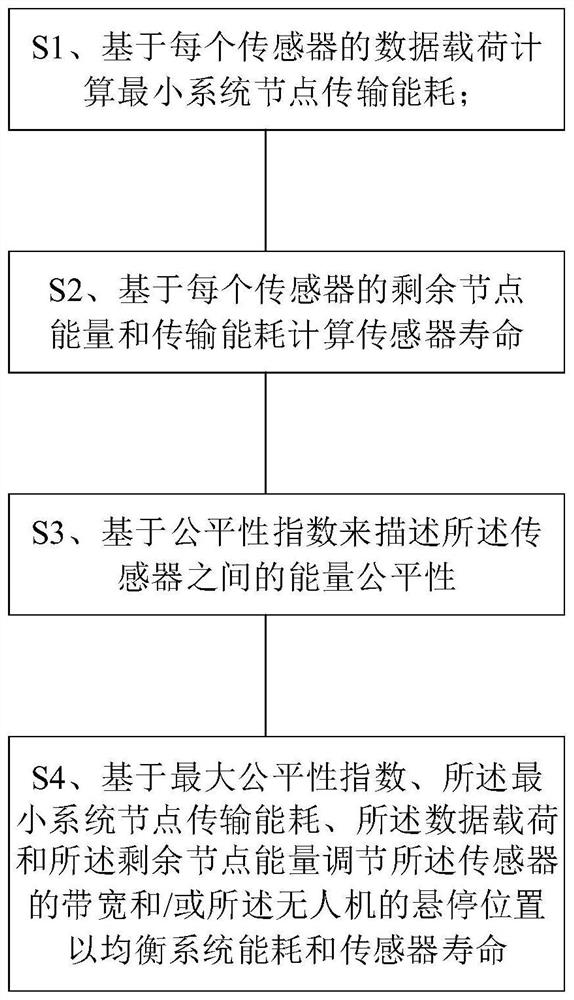
[0027] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
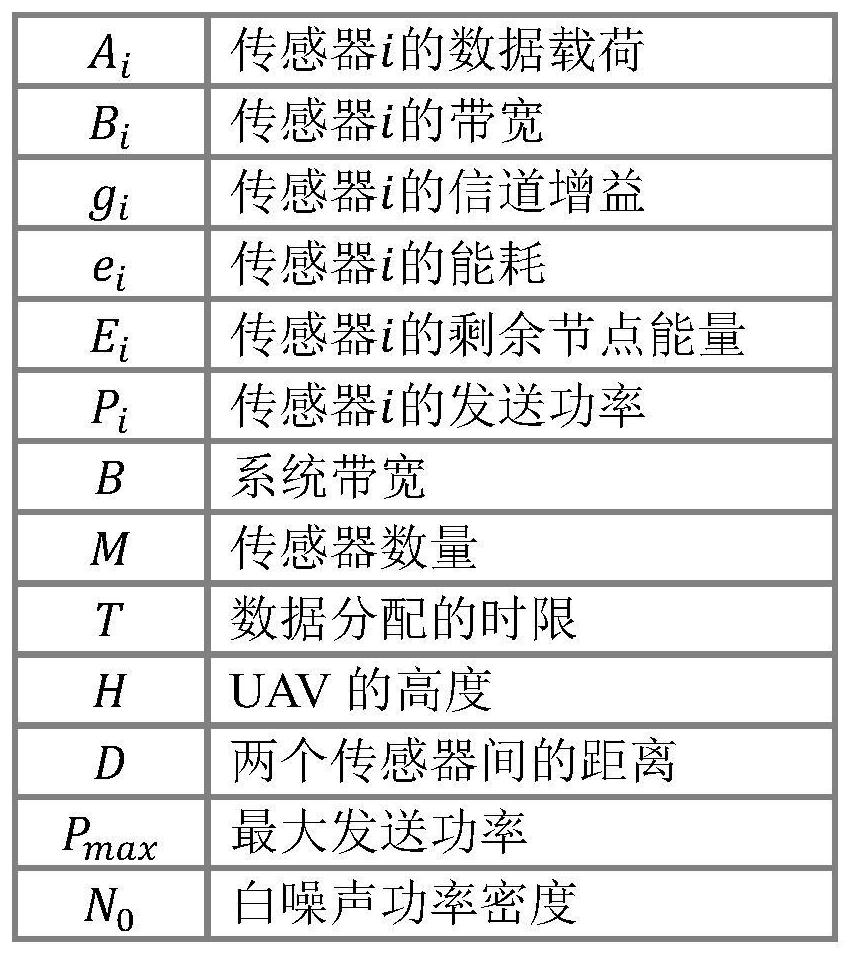
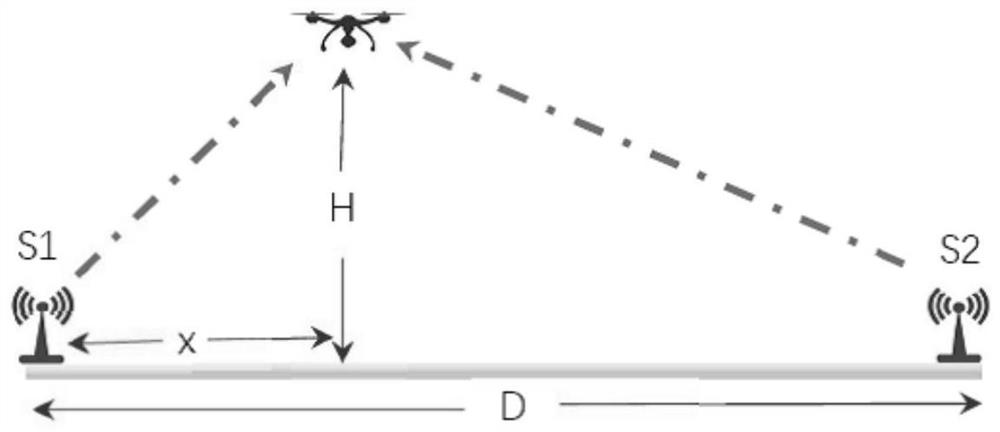
[0028] In this invention, we assume that M sensors are scattered on the ground, and the coordinates of sensor i are given by (x i ,y i ) represents, where 1≤i≤M. To gather ground information, an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is dispatched to collect data from multiple sensors. According to safety regulations, we assume that the drone is flying at a constant altitude H. The coordinates of the UAV projected on the ground are expressed as (Ux, Uy). Therefore, the distance between the drone and sensor i is:
[0029]
[0030] Due to the high altitude of the UAV, for the sake of illustration, we ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com