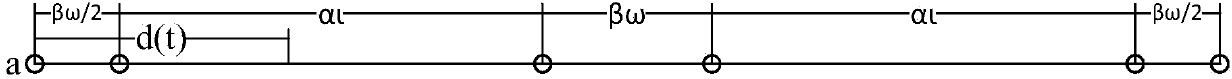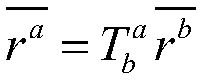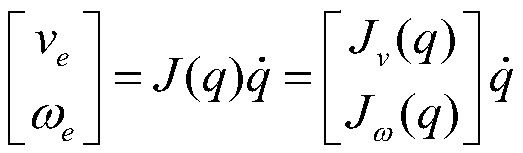Patents
Literature
157 results about "Stagnation point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
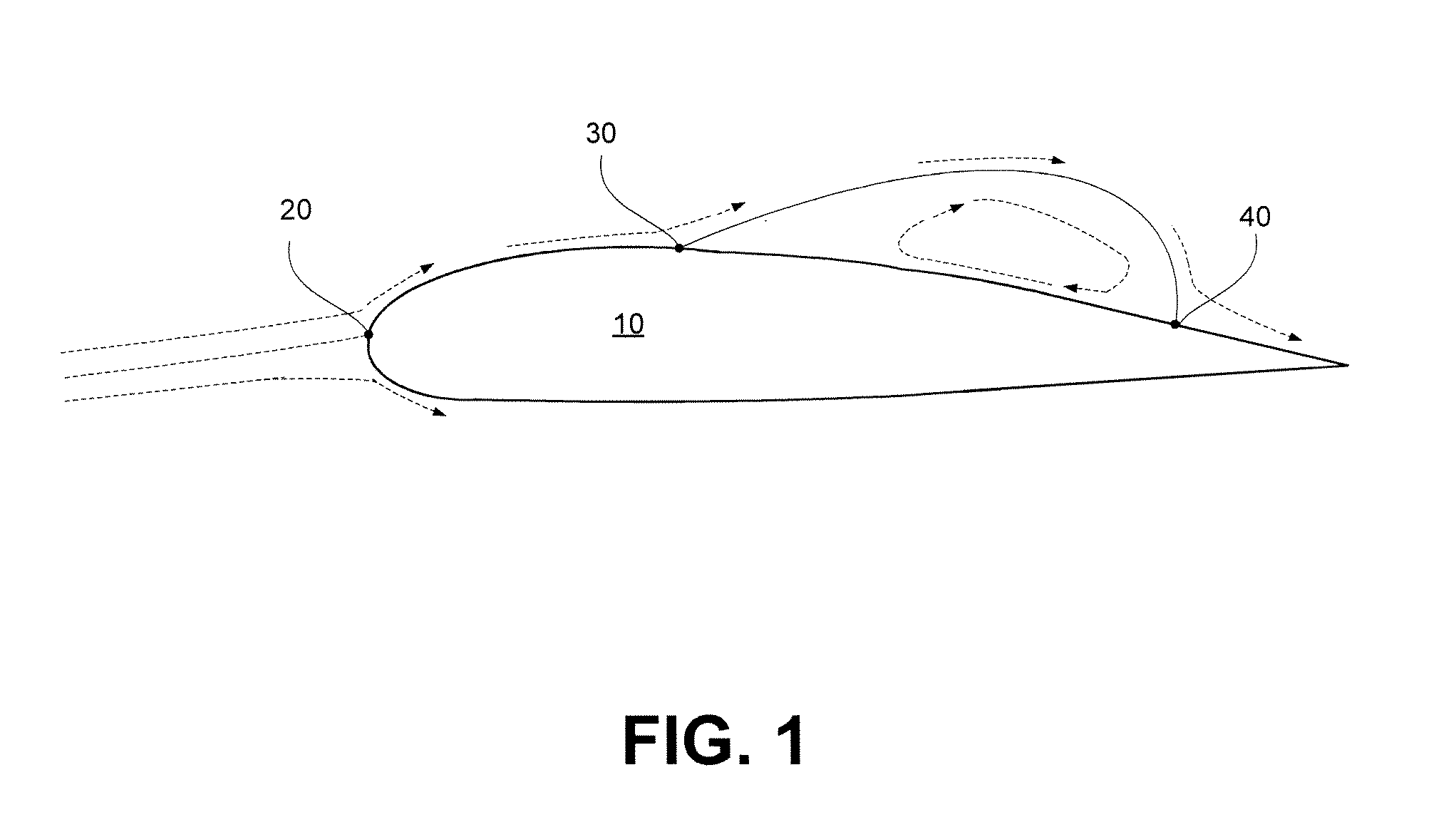
In fluid dynamics, a stagnation point is a point in a flow field where the local velocity of the fluid is zero. Stagnation points exist at the surface of objects in the flow field, where the fluid is brought to rest by the object. The Bernoulli equation shows that the static pressure is highest when the velocity is zero and hence static pressure is at its maximum value at stagnation points. This static pressure is called the stagnation pressure.
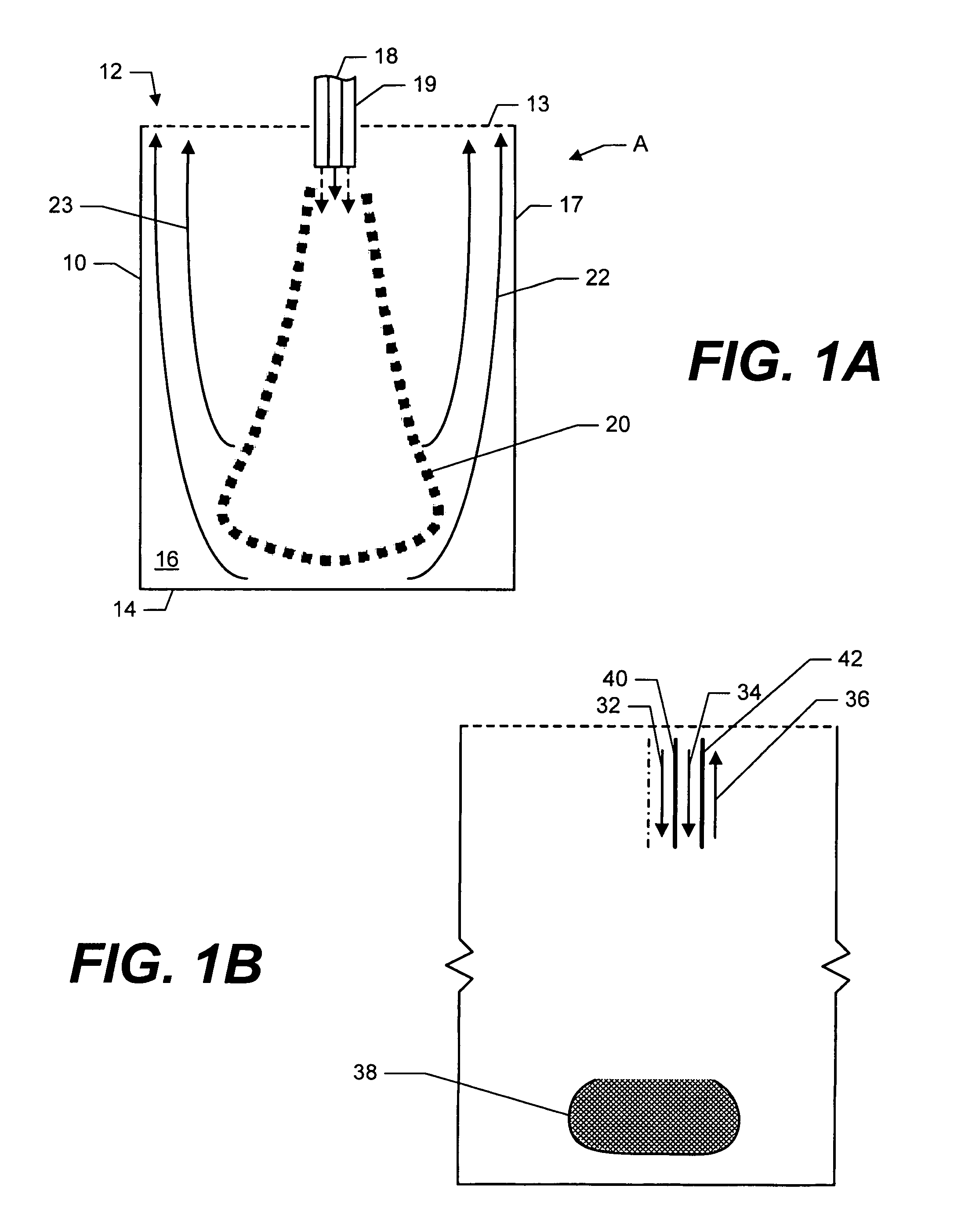
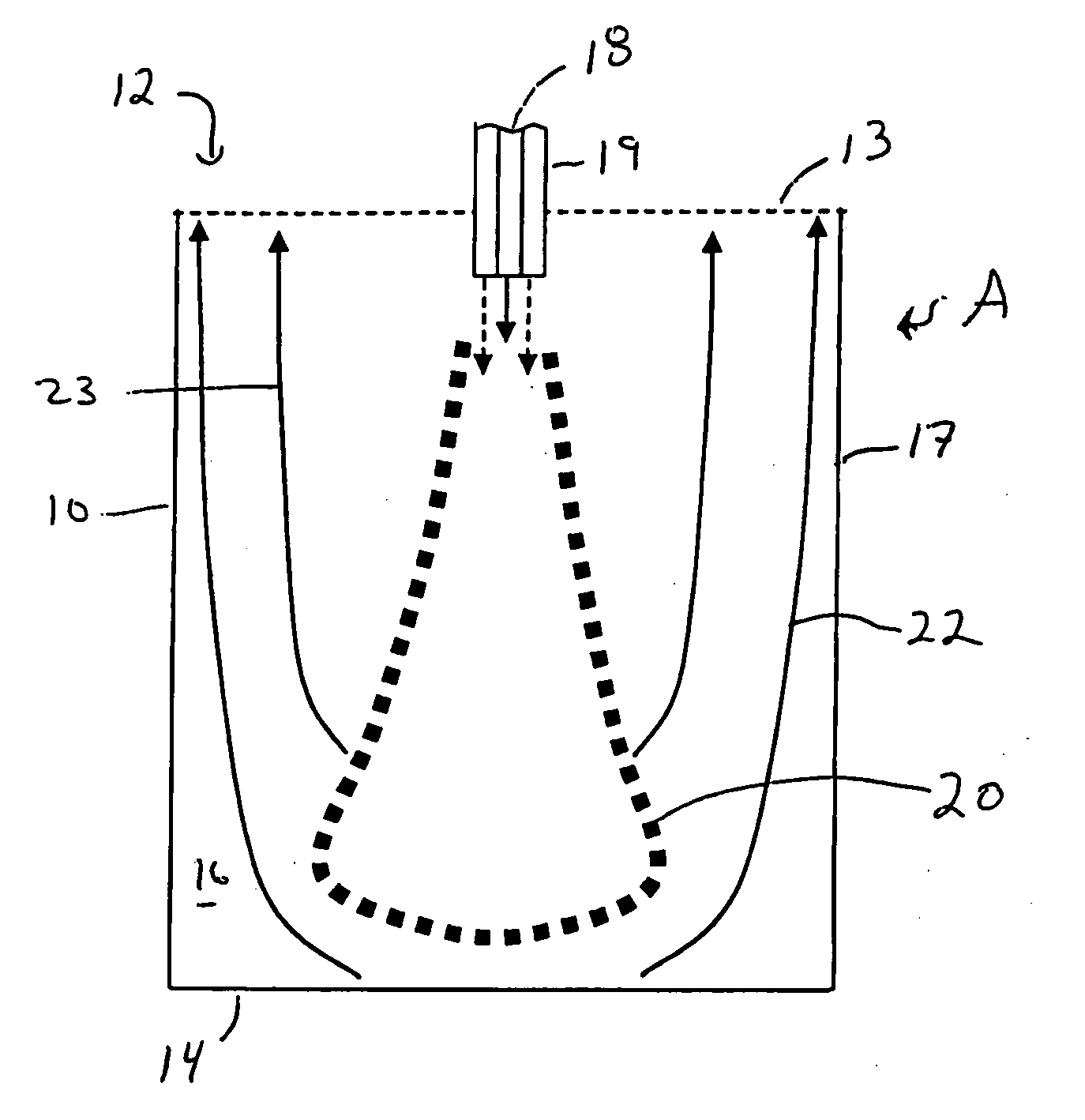
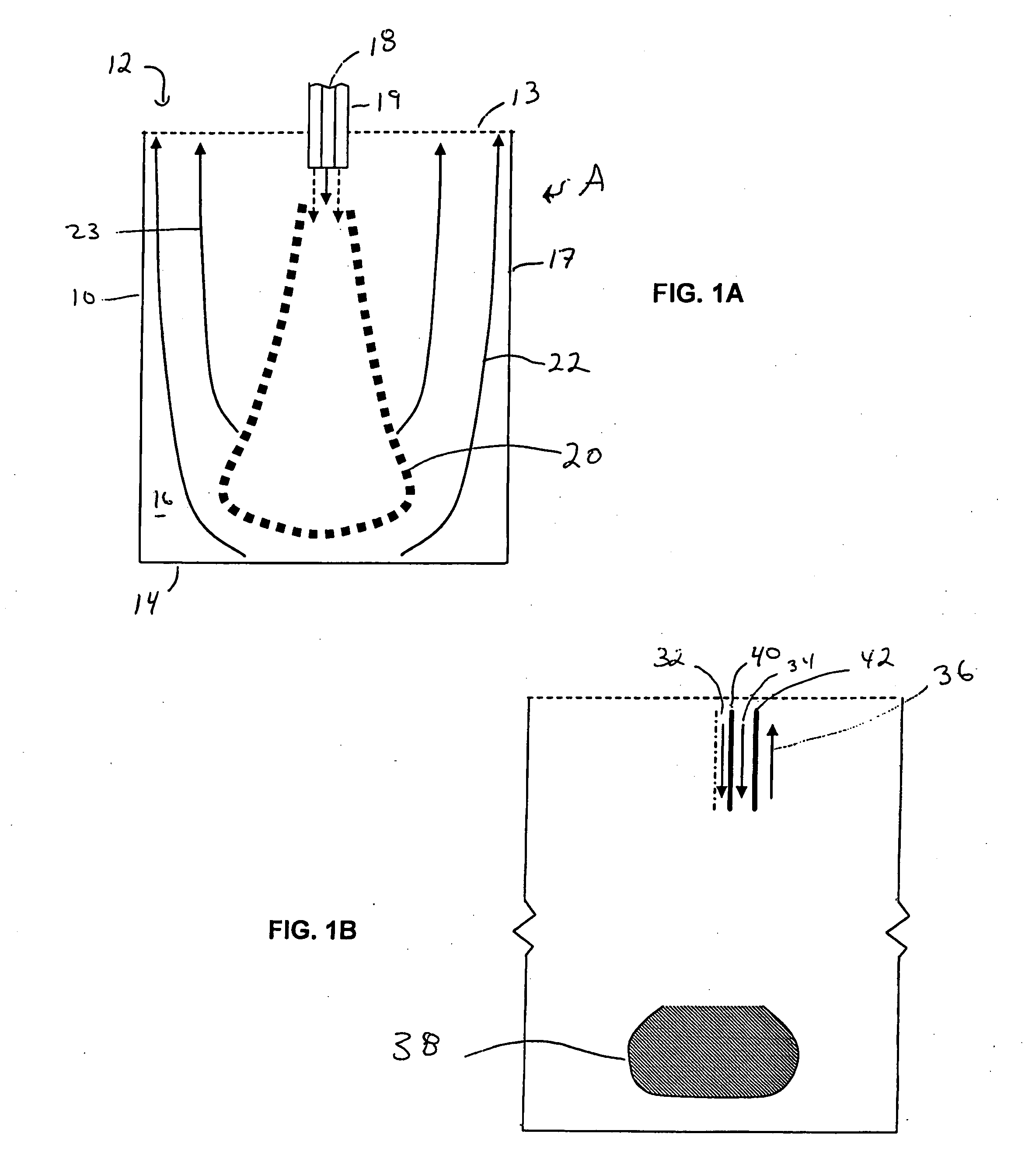
Stagnation point reverse flow combustor for a combustion system
InactiveUS7168949B2Combustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelContinuous combustion chamberStagnation pointCombustion system
A combustor assembly includes a combustor vessel having a wall, a proximate end defining an opening and a closed distal end opposite said proximate end. A manifold is carried by the proximate end. The manifold defines a combustion products exit. The combustion products exit being axially aligned with a portion of the closed distal end. A plurality of combustible reactant ports is carried by the manifold for directing combustible reactants into the combustion vessel from the region of the proximate end towards the closed distal end.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Stagnation point reverse flow combustor
InactiveUS7425127B2Combustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelContinuous combustion chamberStagnation pointCombustor
A method for combusting a combustible fuel includes providing a vessel having an opening near a proximate end and a closed distal end defining a combustion chamber. A combustible reactants mixture is presented into the combustion chamber. The combustible reactants mixture is ignited creating a flame and combustion products. The closed end of the combustion chamber is utilized for directing combustion products toward the opening of the combustion chamber creating a reverse flow of combustion products within the combustion chamber. The reverse flow of combustion products is intermixed with combustible reactants mixture to maintain the flame.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
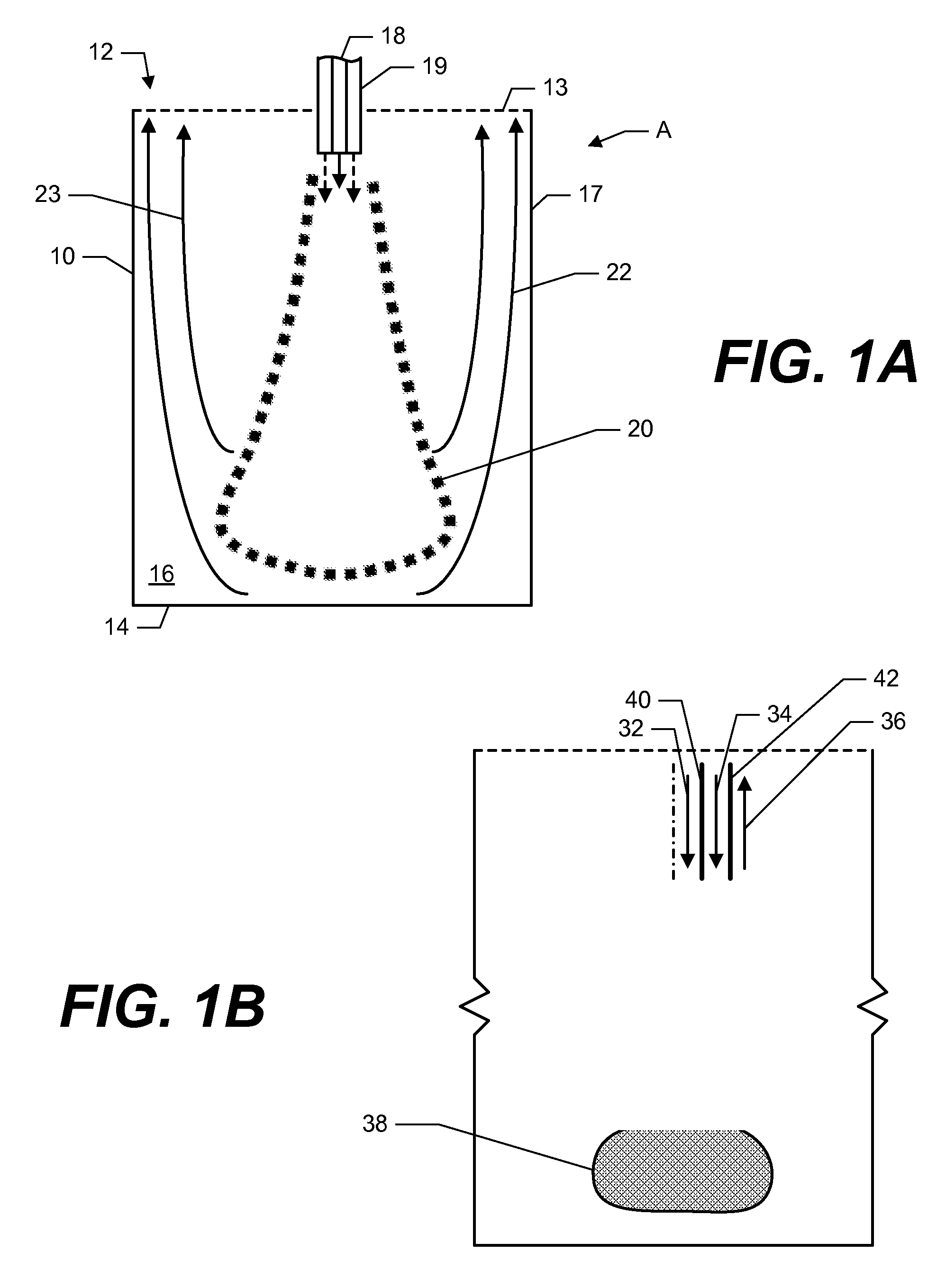
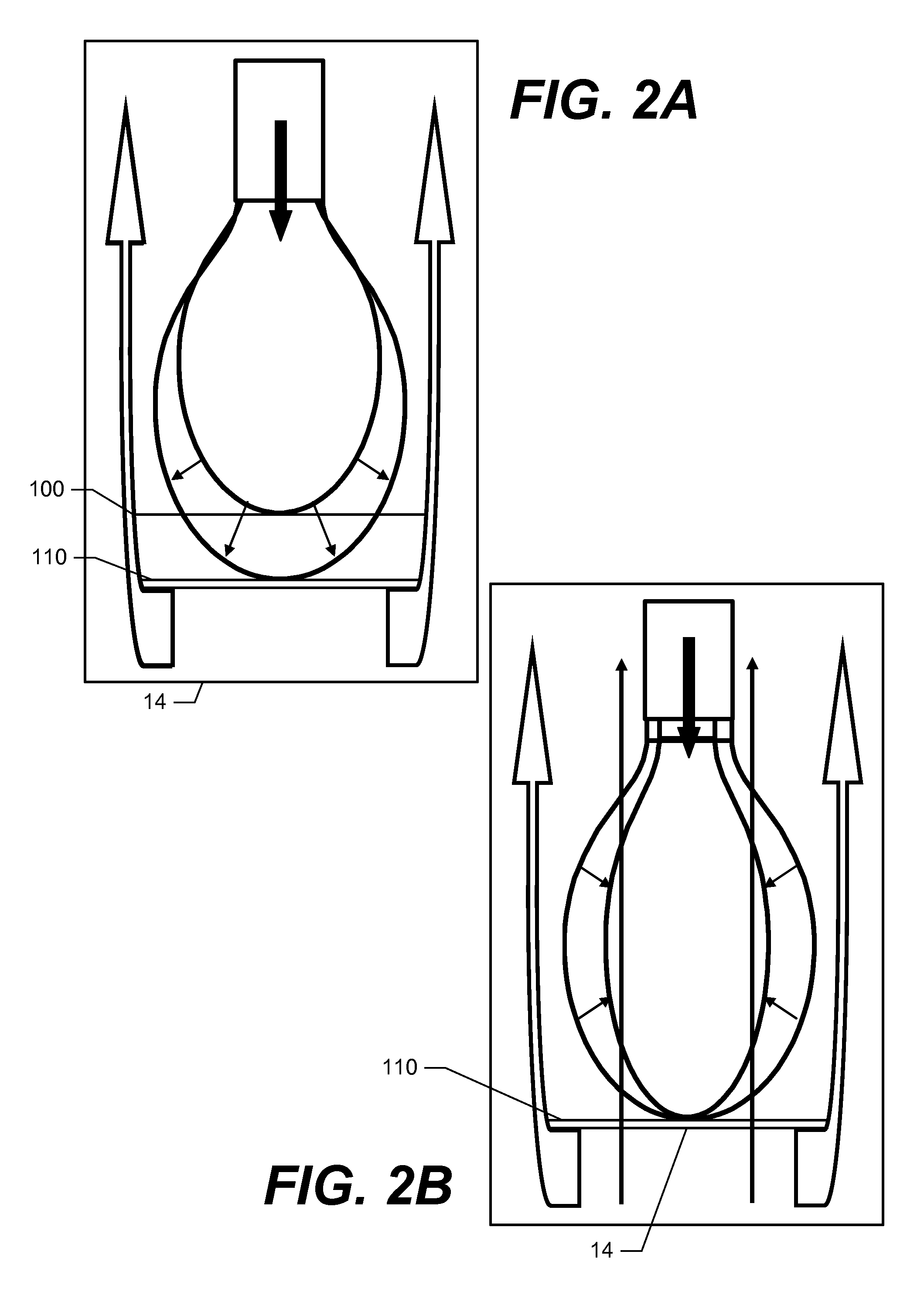
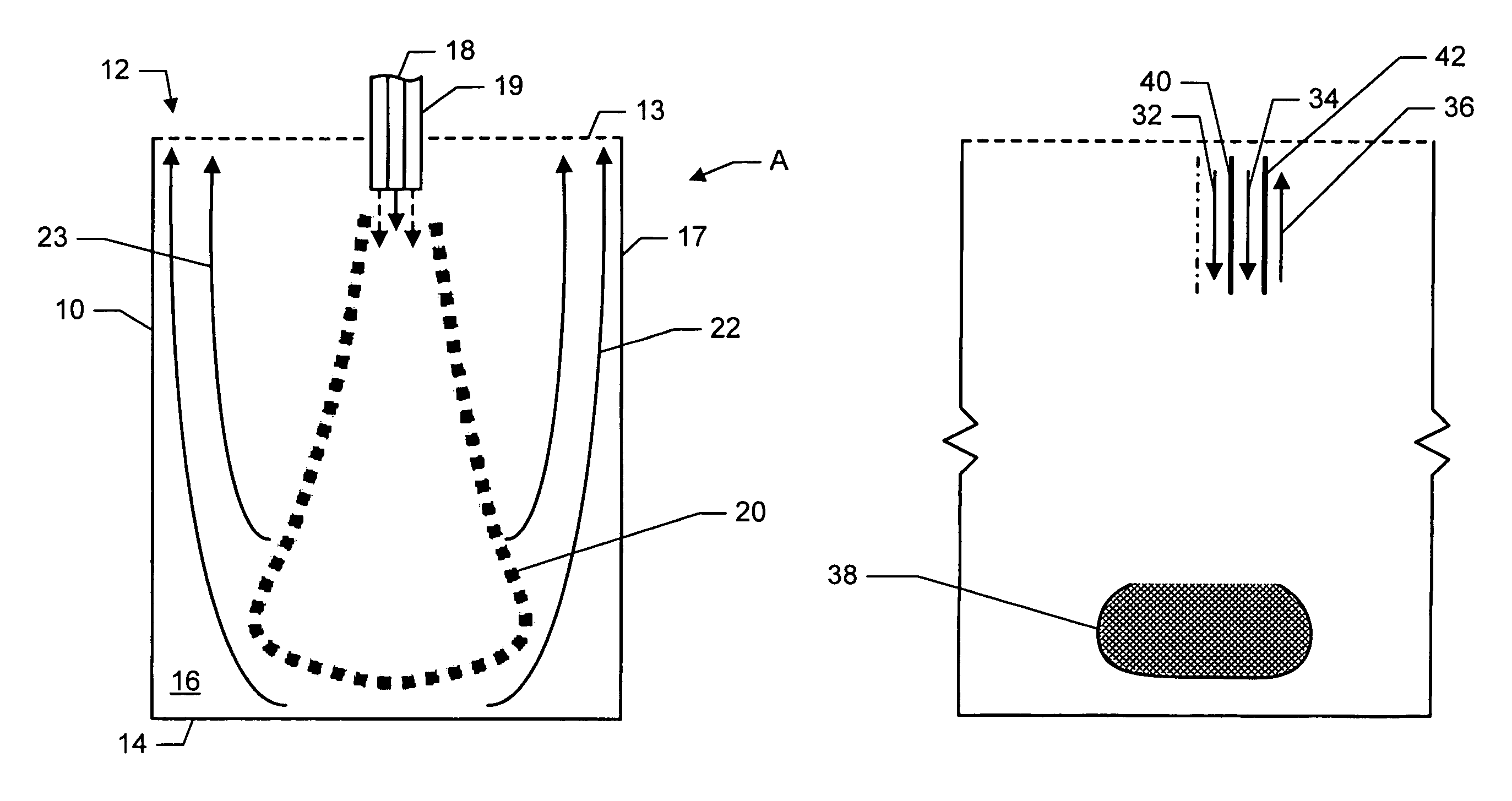
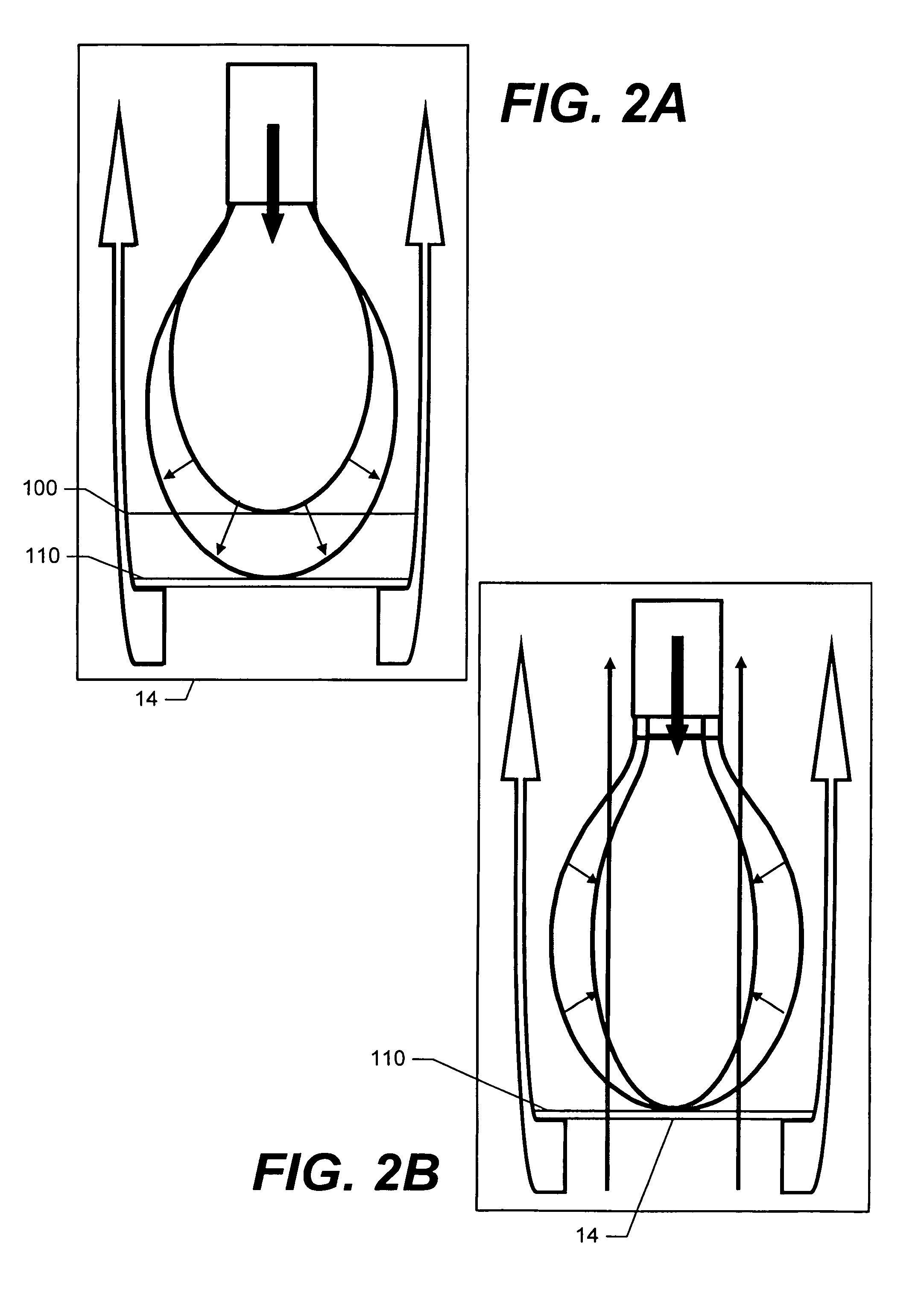
System and method for confining an object to a region of fluid flow having a stagnation point
InactiveUS20060005634A1Avoid leavingVolume/mass flow measurementLaboratory glasswaresStagnation pointEngineering
A device for confining an object to a region proximate to a fluid flow stagnation point includes one or more inlets for carrying the fluid into the region, one or more outlets for carrying the fluid out of the region, and a controller, in fluidic communication with the inlets and outlets, for adjusting the motion of the fluid to produce a stagnation point in the region, thereby confining the object to the region. Applications include, for example, prolonged observation of the object, manipulation of the object, etc. The device optionally may employ a feedback control mechanism, a sensing apparatus (e.g., for imaging), and a storage medium for storing, and a computer for analyzing and manipulating, data acquired from observing the object. The invention further provides methods of using such a device and system in a number of fields, including biology, chemistry, physics, material science, and medical science.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Count of Infectious Agents in Intravenous Access Systems
InactiveUS20110085936A1Avoid problemsReduce pollutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryStagnation pointStopcock
Methods and apparatus for preventing patient bloodstream infection by microorganisms during administration of various medications or fluids through IV lines. In particular, the invention reduces contamination of IV lines, connecters, stopcock valves, manifolds, ports, etc. by means of irradiation by violet and / or blue light. Each embodiment comprises a source of violet and / or blue light and an optical element optically coupled to that light source for shaping the radiation pattern of the light emitted by the light source. Preferably, a light-emitting diode or a laser diode that emits light in the desired wavelength can be used. The optical element, optically coupled to the light source, is embedded or installed in or attached to a component of an IV set, the emitted light being directed to a “point of entry” or any other stagnation point of an IV set.
Owner:BACTRIBLUE
Stagnation point reverse flow combustor for a combustion system
InactiveUS20060029894A1Combustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelContinuous combustion chamberCombustion systemStagnation point
A combustor assembly includes a combustor vessel having a wall, a proximate end defining an opening and a closed distal end opposite said proximate end. A manifold is carried by the proximate end. The manifold defines a combustion products exit. The combustion products exit being axially aligned with a portion of the closed distal end. A plurality of combustible reactant ports is carried by the manifold for directing combustible reactants into the combustion vessel from the region of the proximate end towards the closed distal end.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
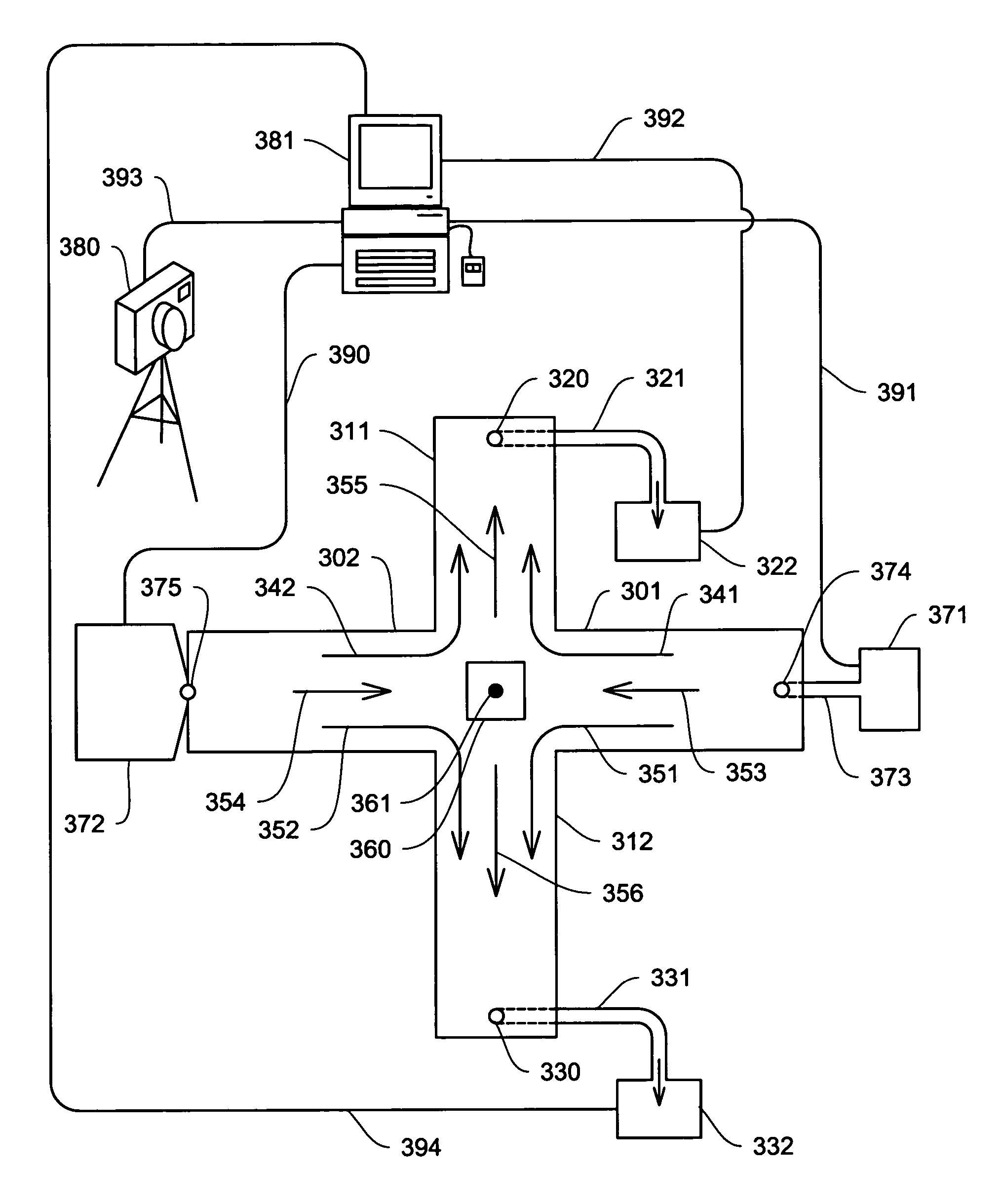
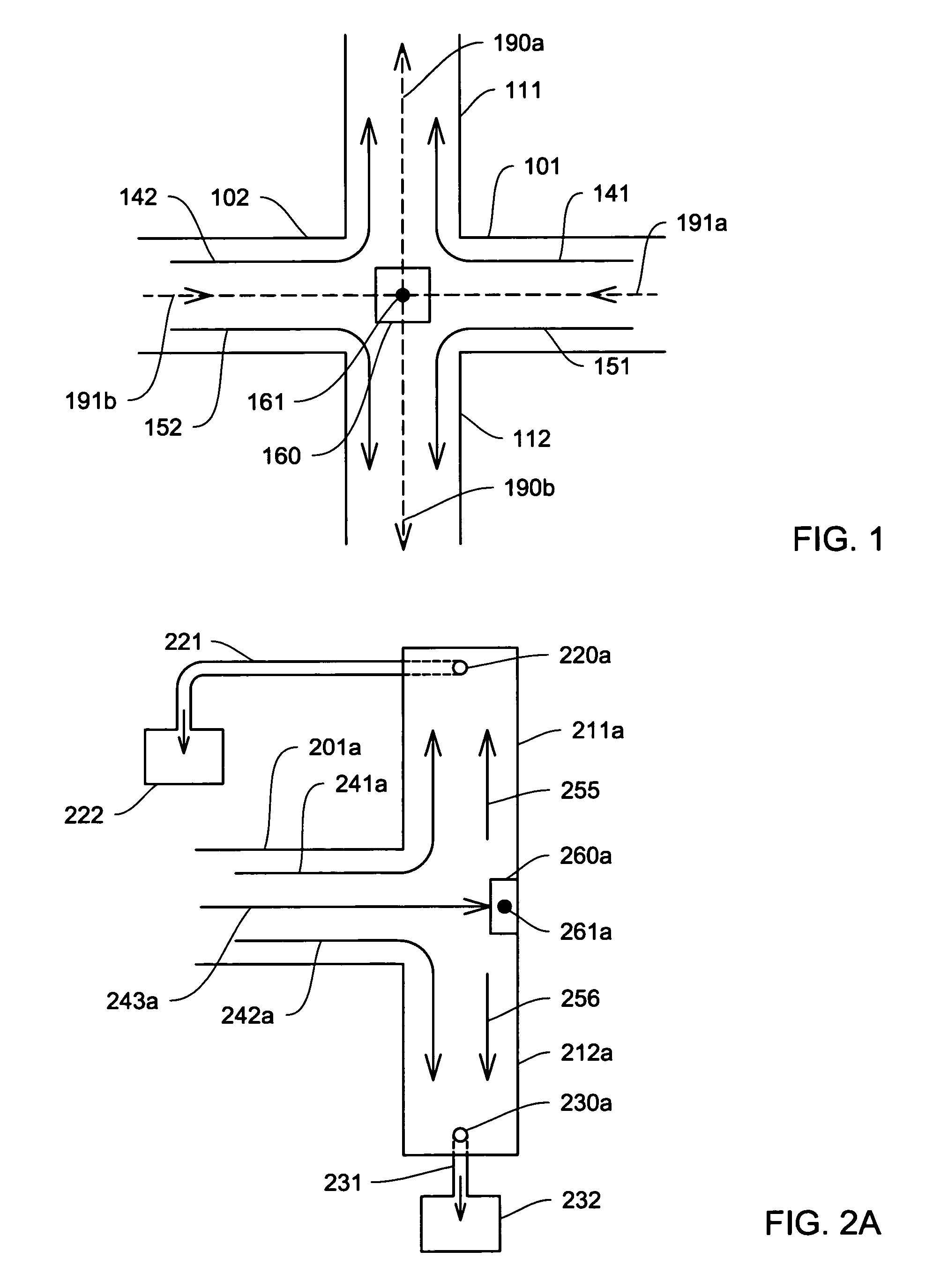
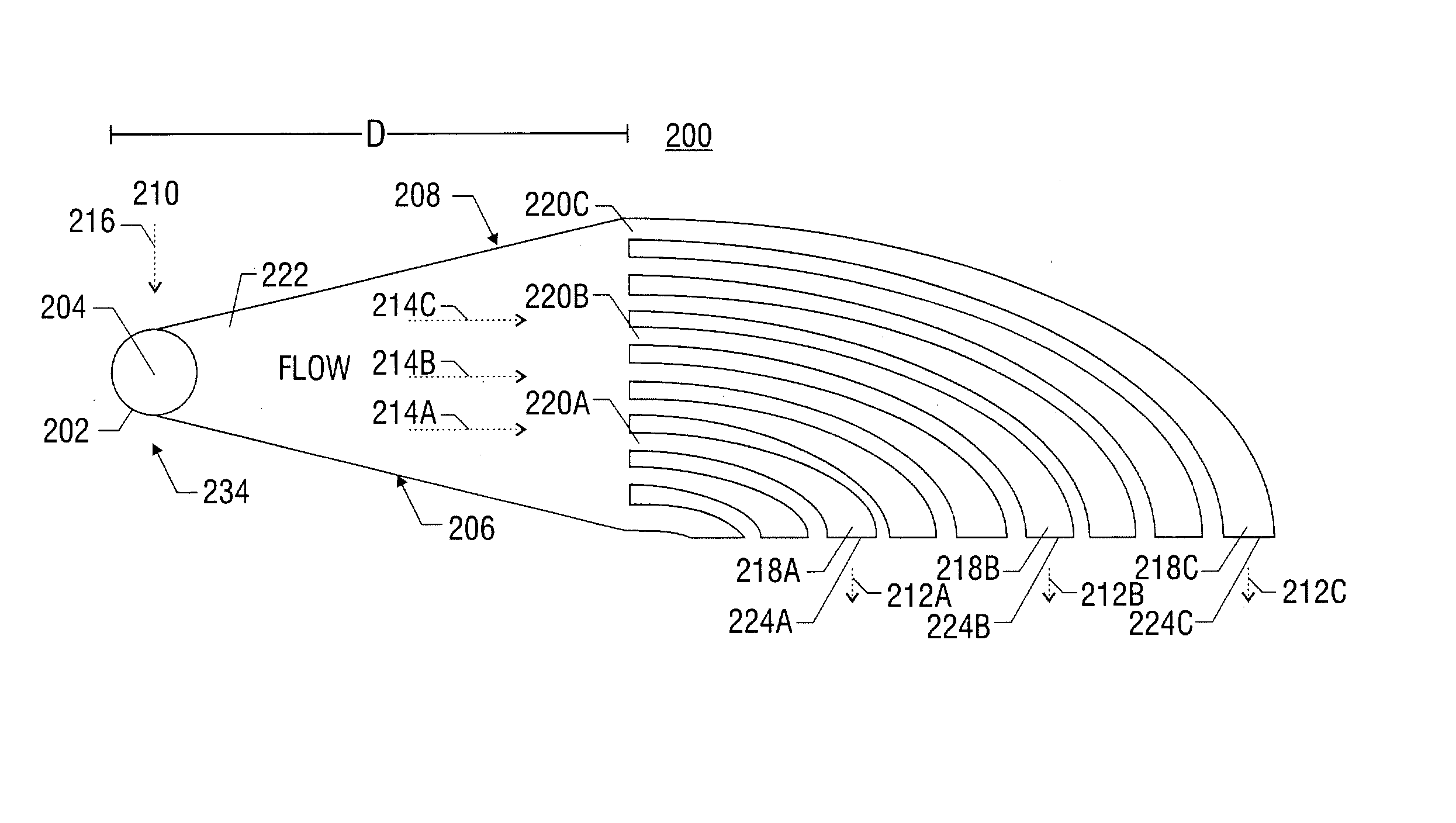
Manifold for fuel cell system
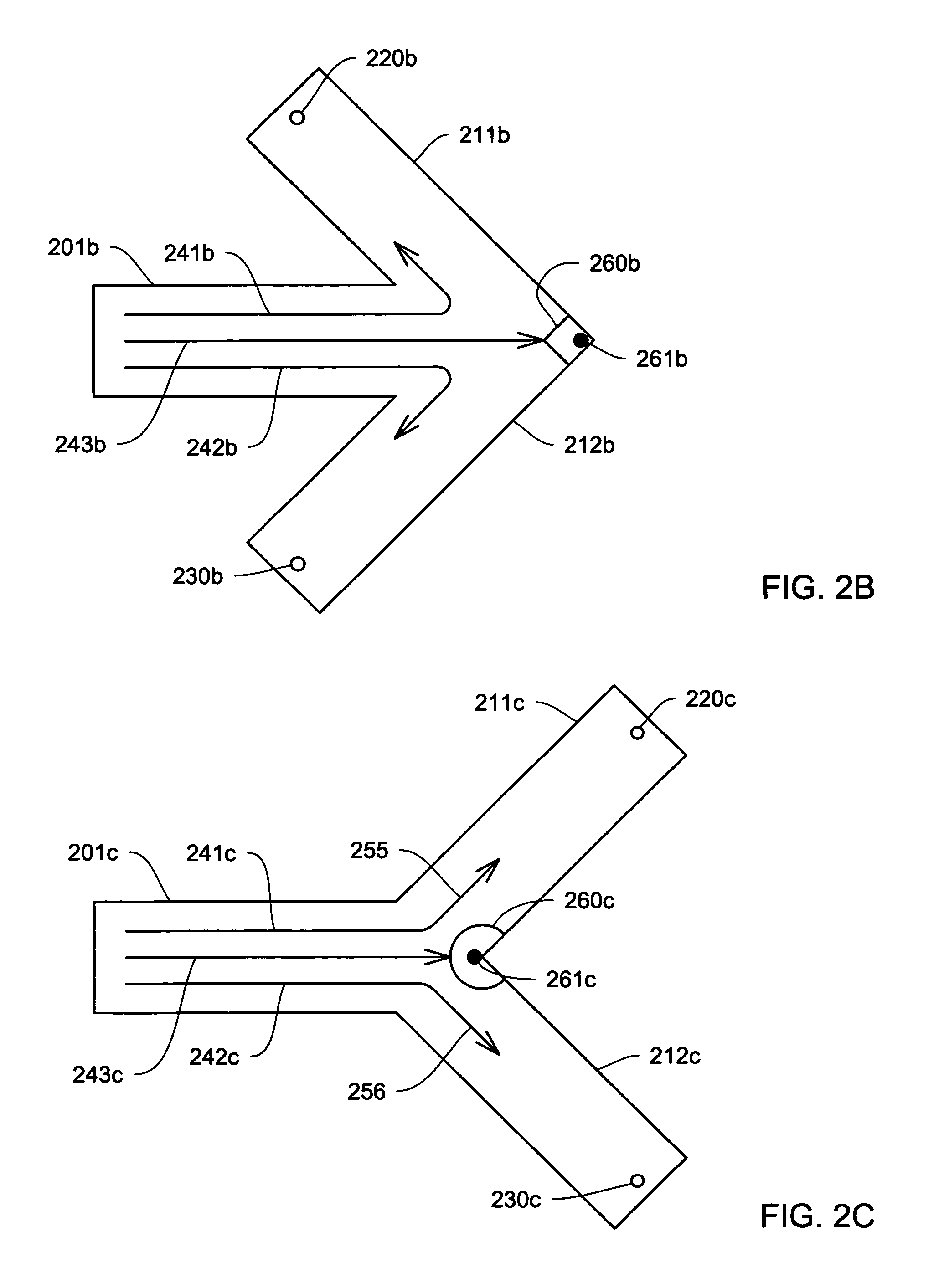
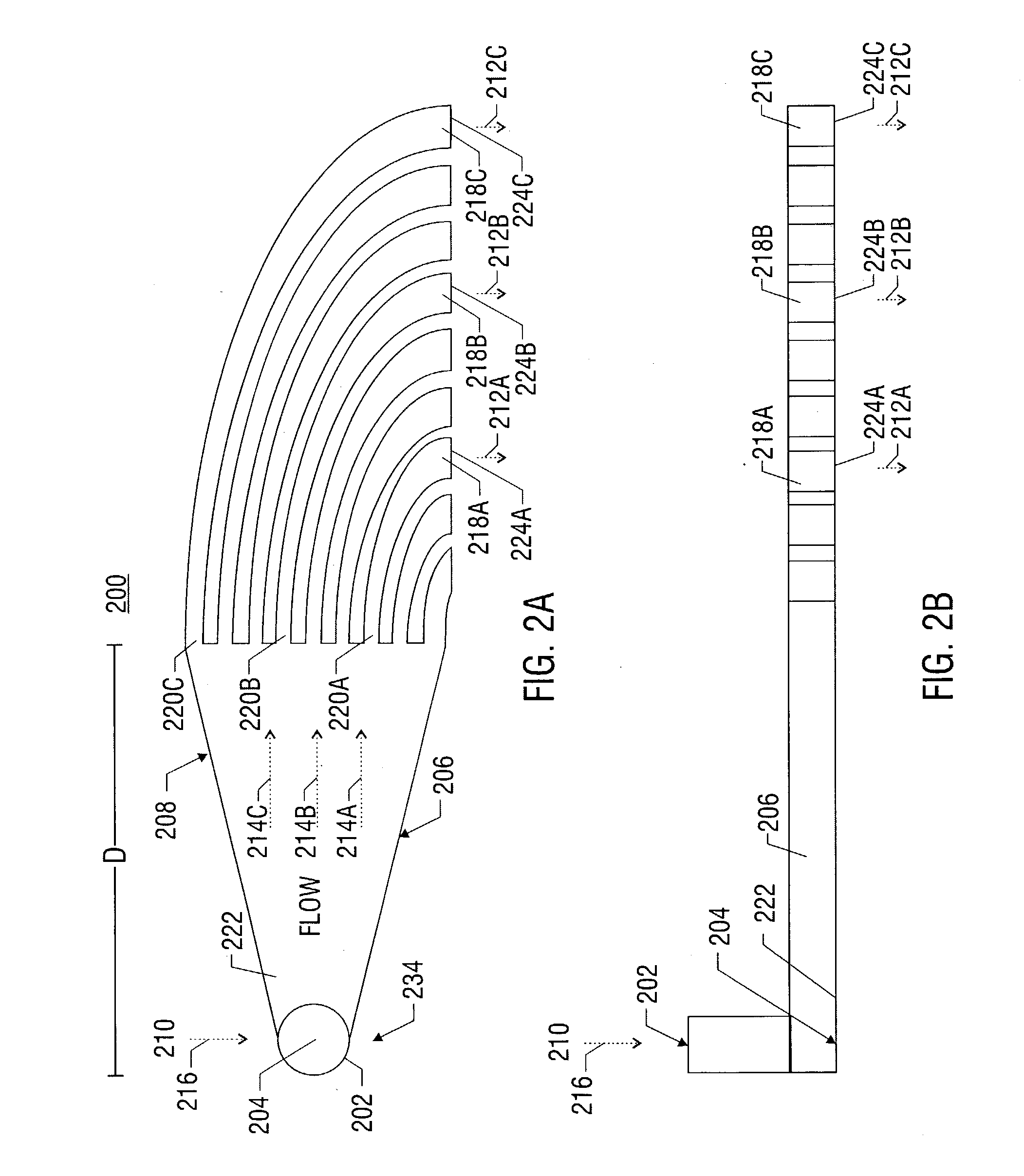
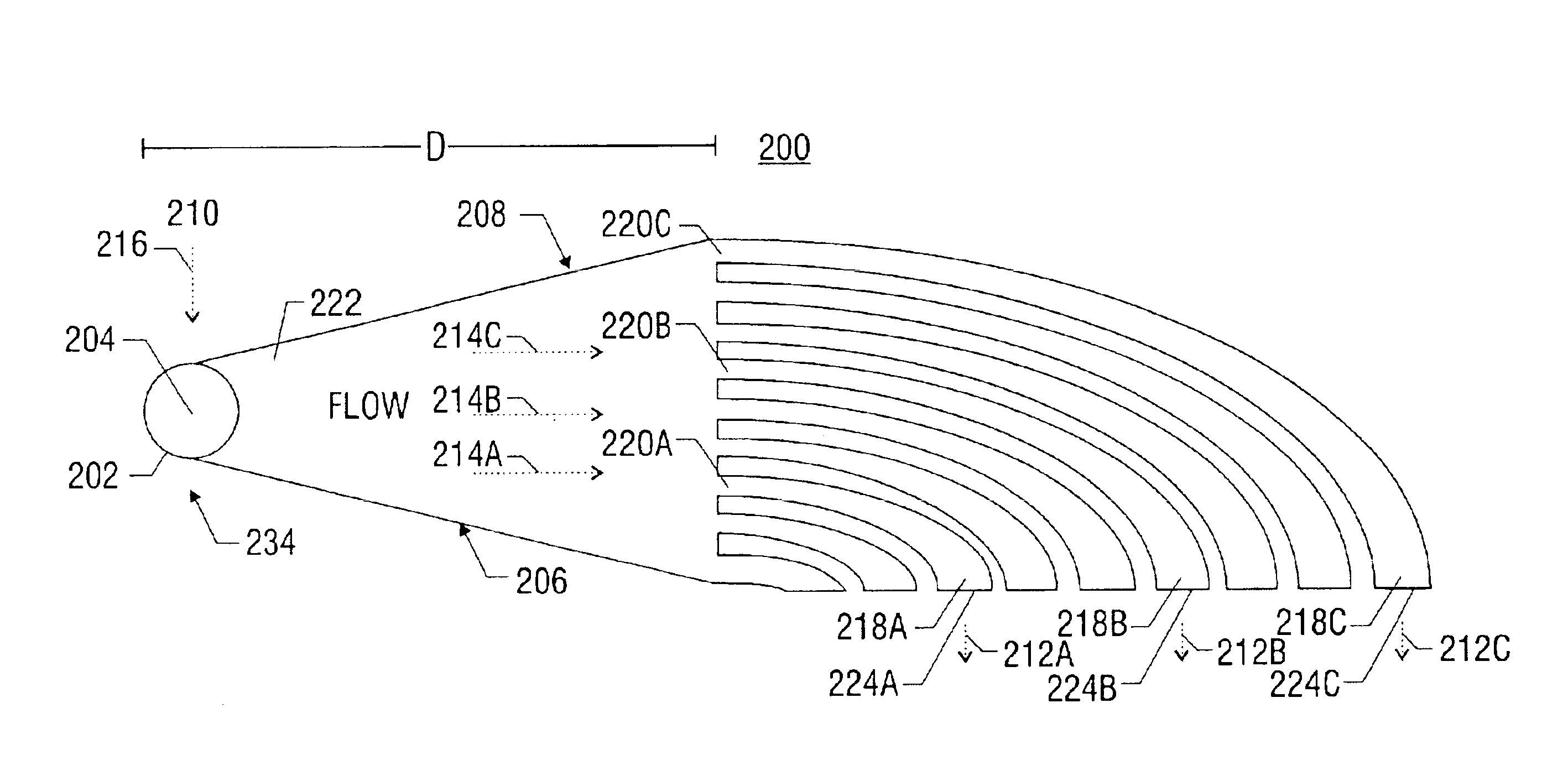
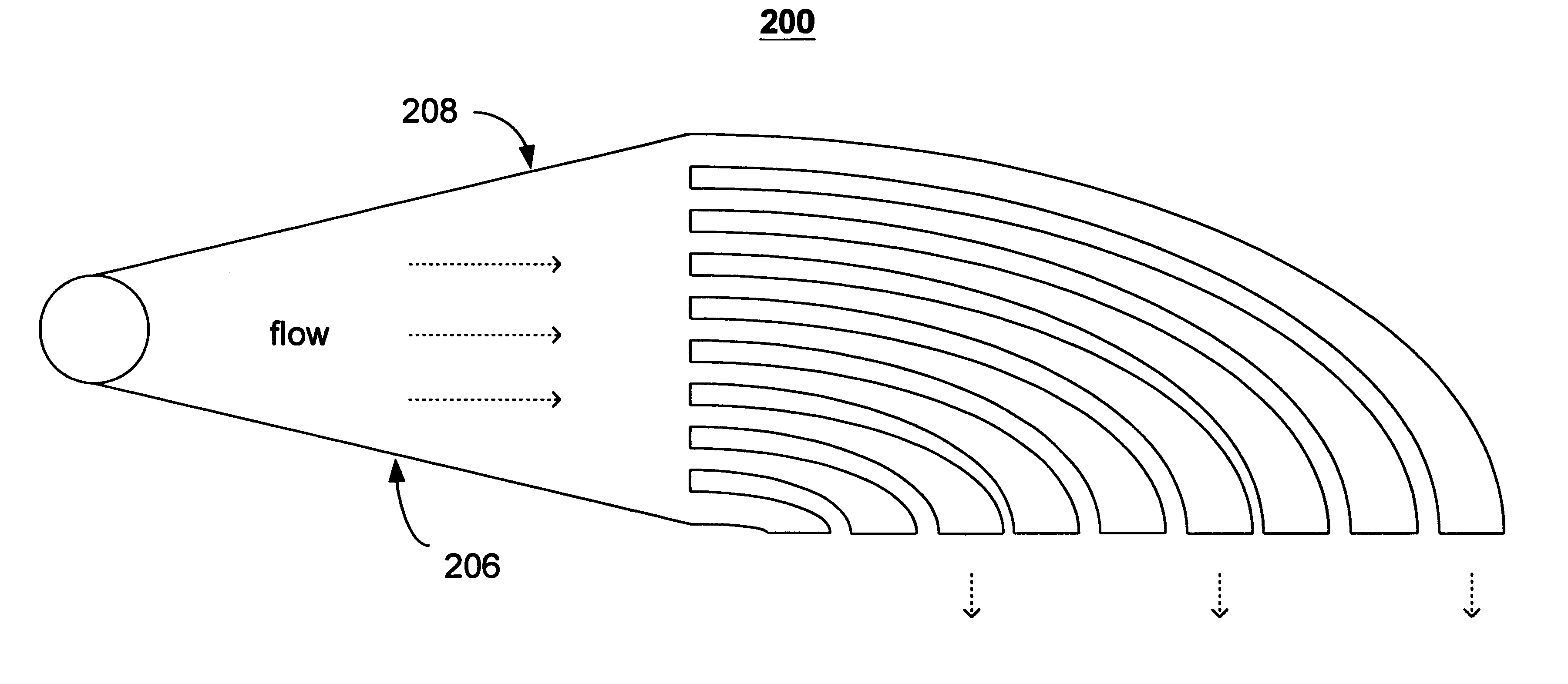
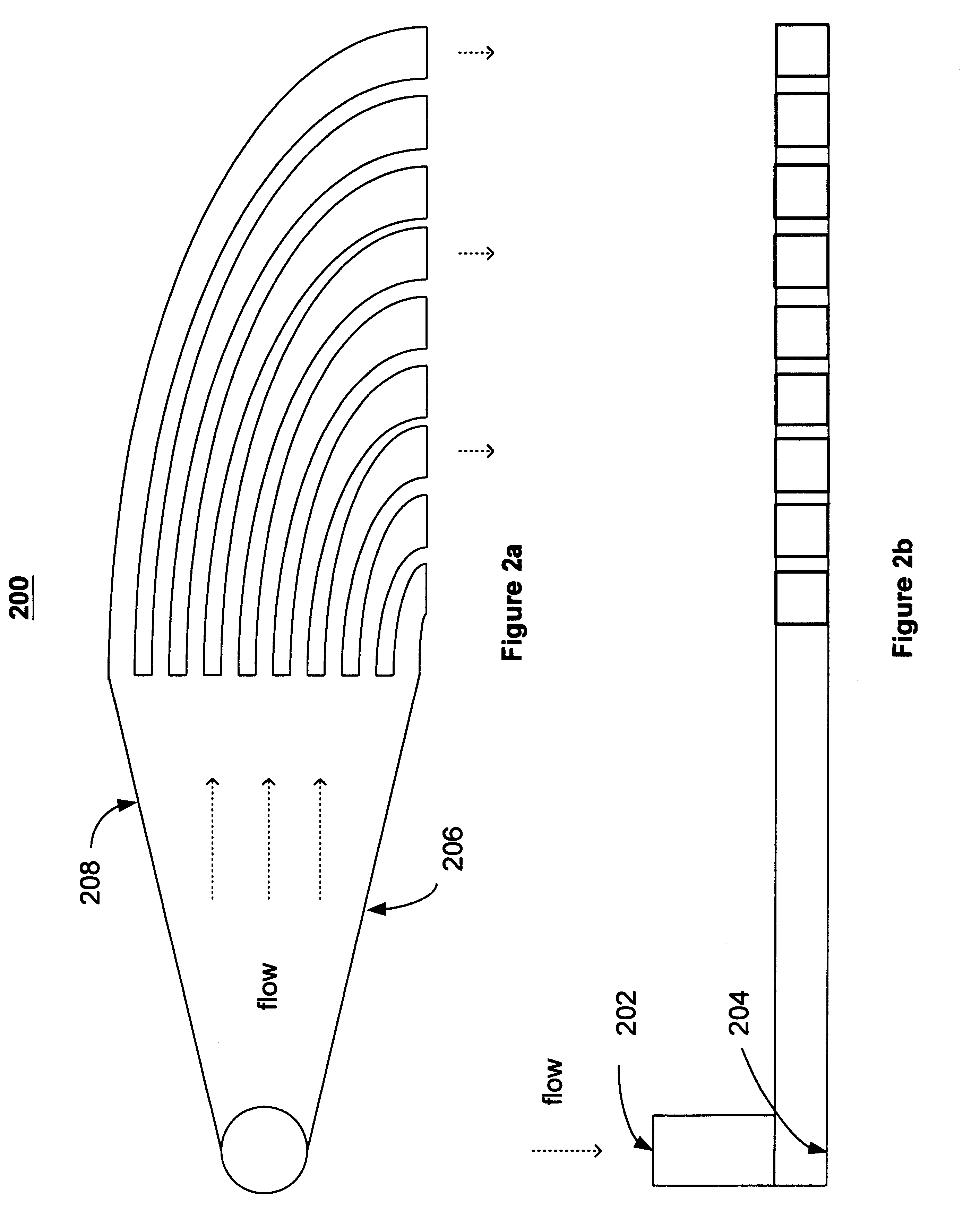
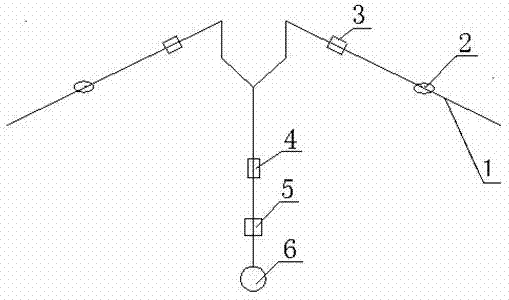
A method and apparatus for converting single multiphase fluid flow into plural multiphase fluid flows having substantially uniform composition and flow properties. A manifold comprises an enclosure having an inlet and an inner surface perpendicular to the inlet such that the incident angle of input flow impacts the surface to form a stagnation point whereby an intermediate flow is deflected along the surface substantially symmetrically outward from the stagnation point and channeled to a plurality of parallel fluid outlets connected to the enclosure. The distance between the stagnation point and the plurality of outlets is selected to maintain substantially equivalent fluid pressures and uniform flow rates at the outlets. A preferred embodiment of the manifold channels the intermediate flow between two walls forming a triangular shaped nozzle directing the flow from the stagnation point to the base of the triangle for communication of electrolyte to a metal-based fuel cell through the plurality of outlets.
Owner:TECK COMINCO METALS LTD
Manifold for fuel cell system
Owner:TECK COMINCO METALS LTD
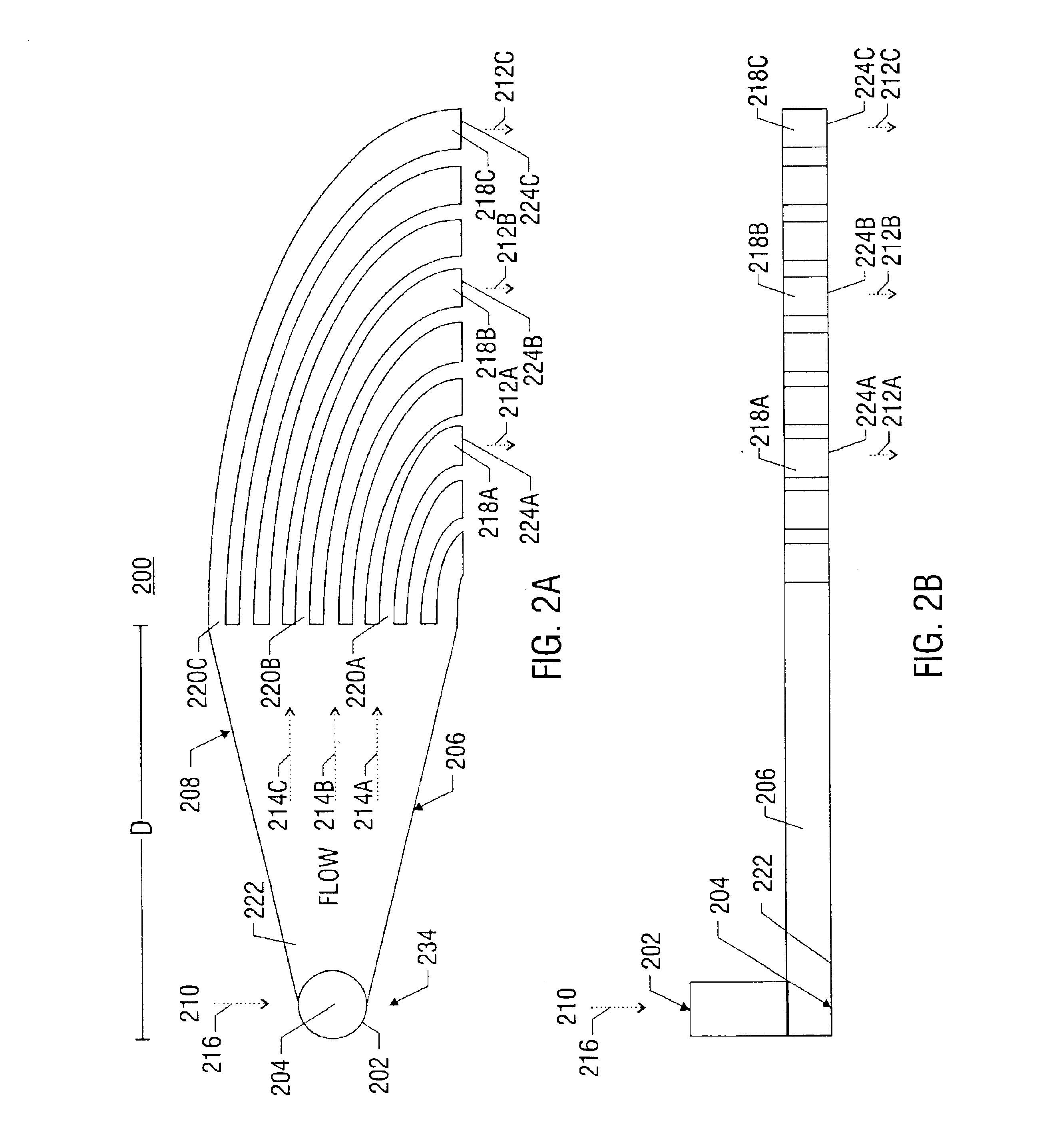
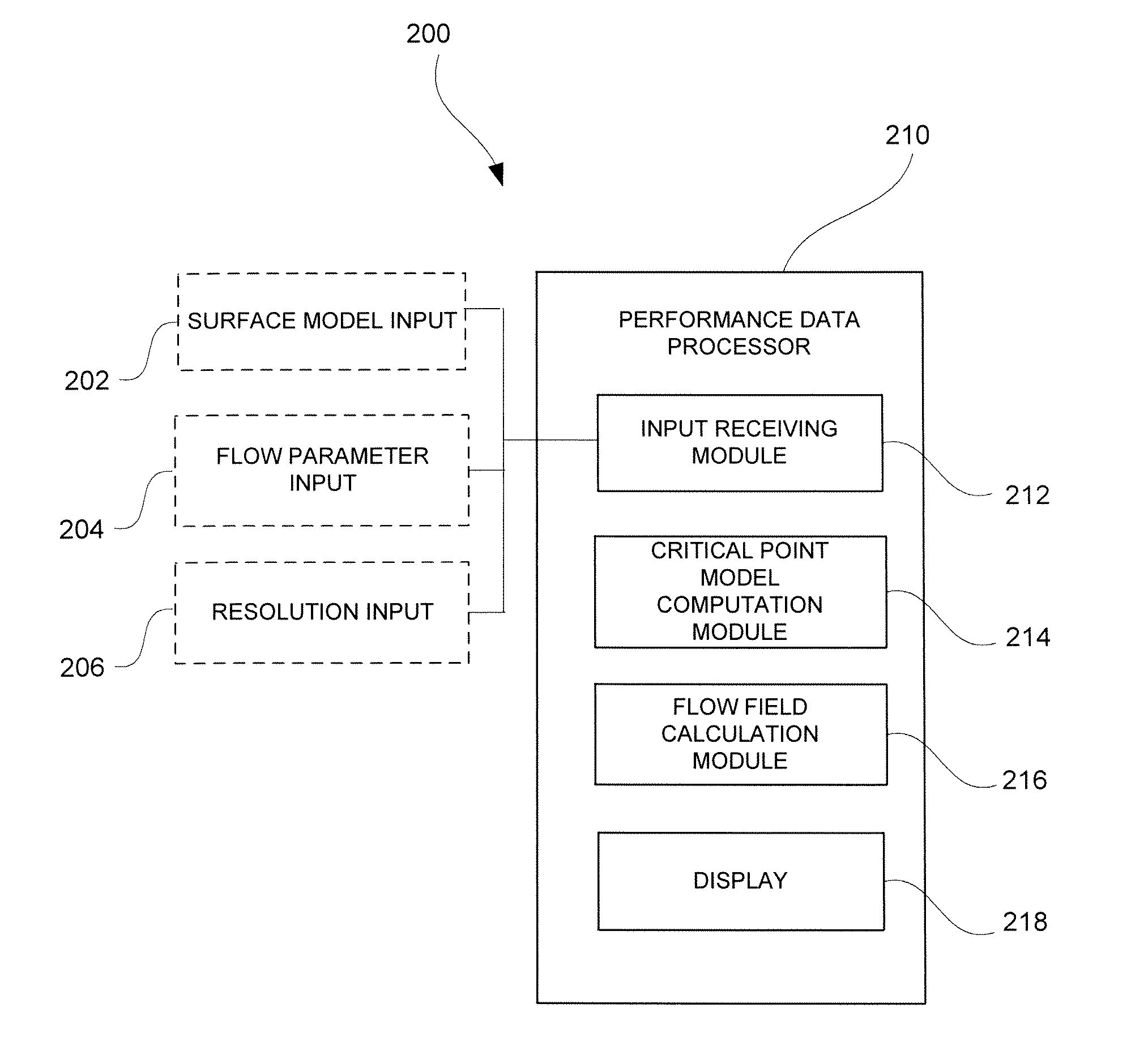
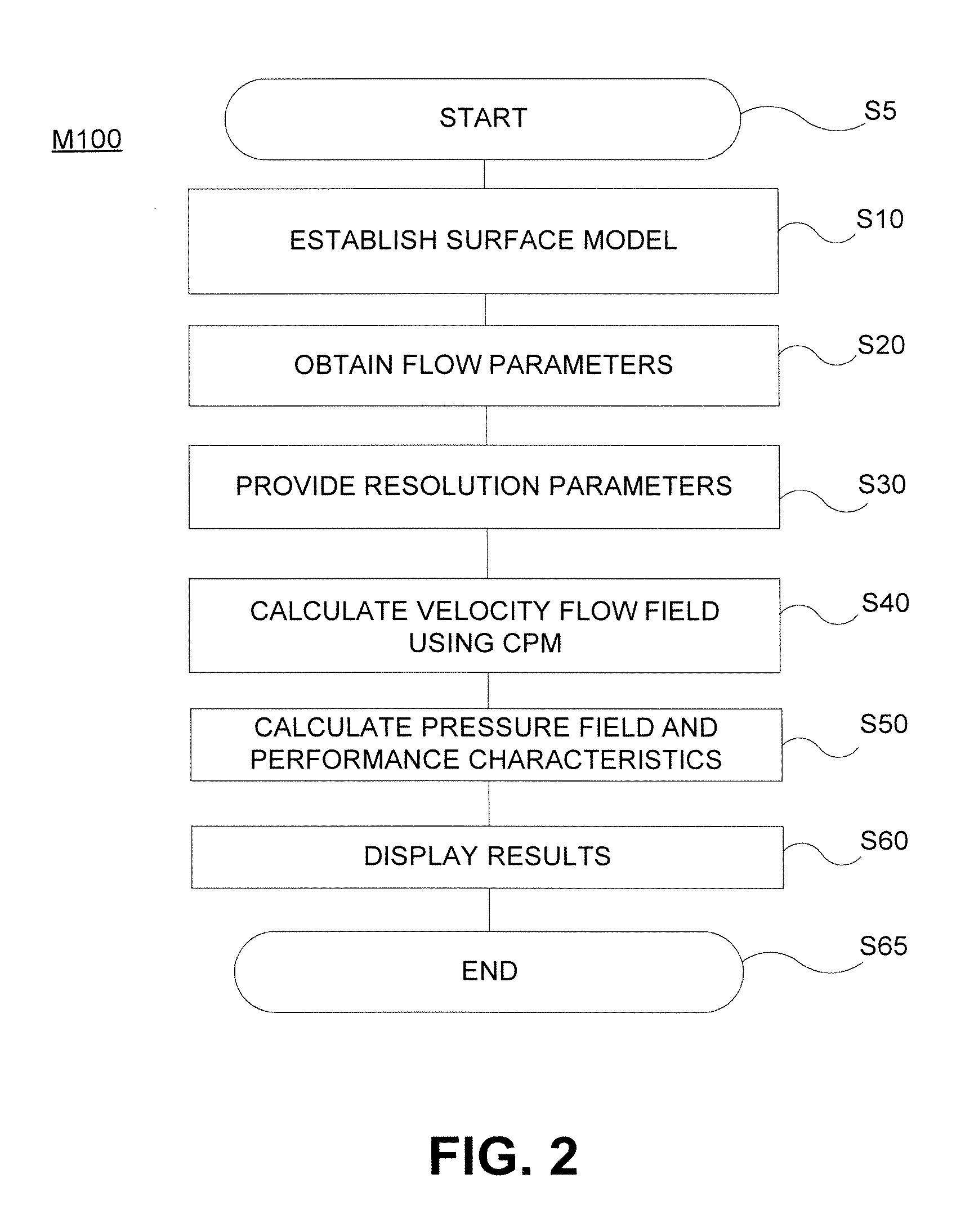
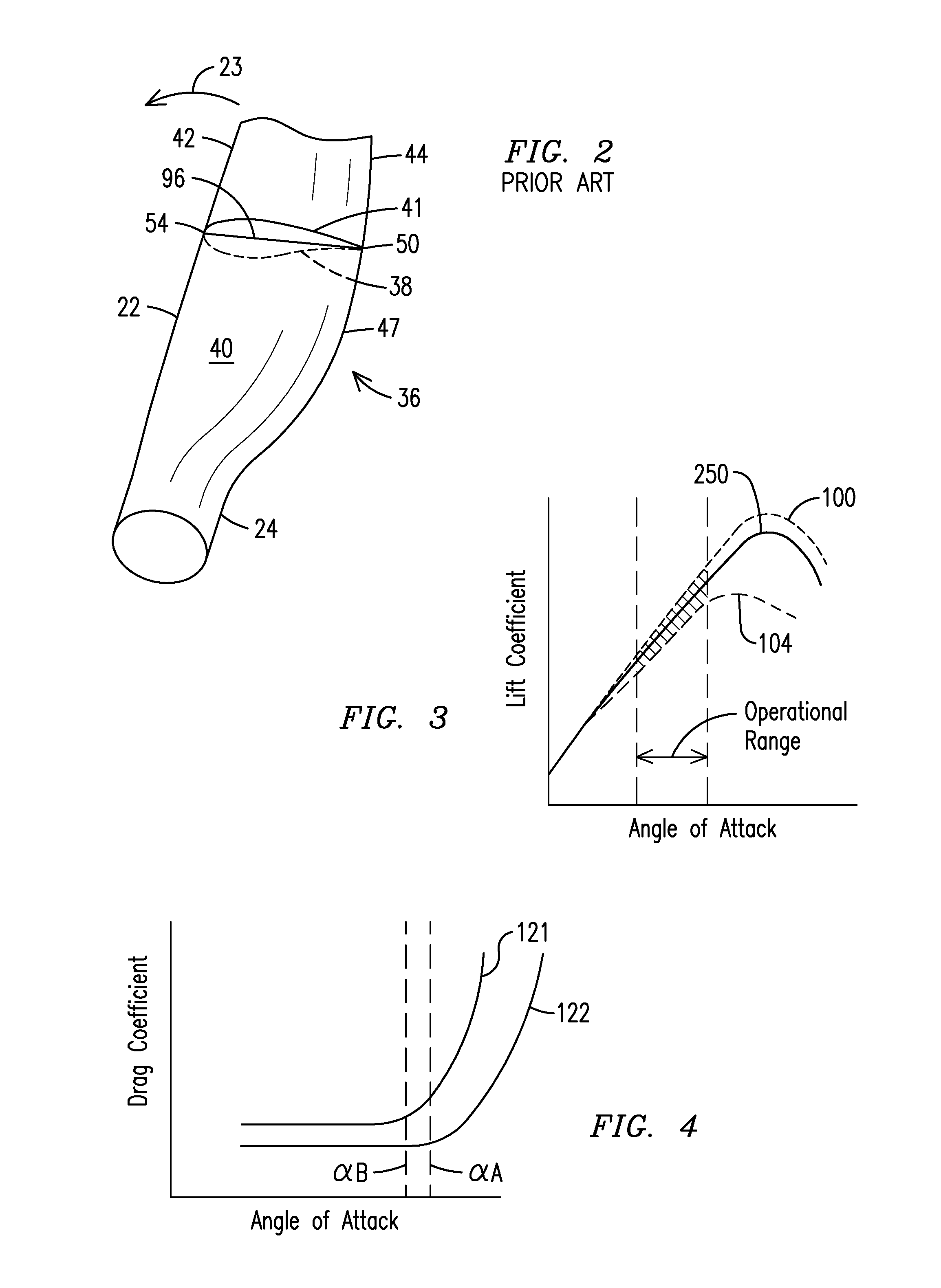
Method for Predicting Flow and Performance Characteristics of a Body Using Critical Point Location
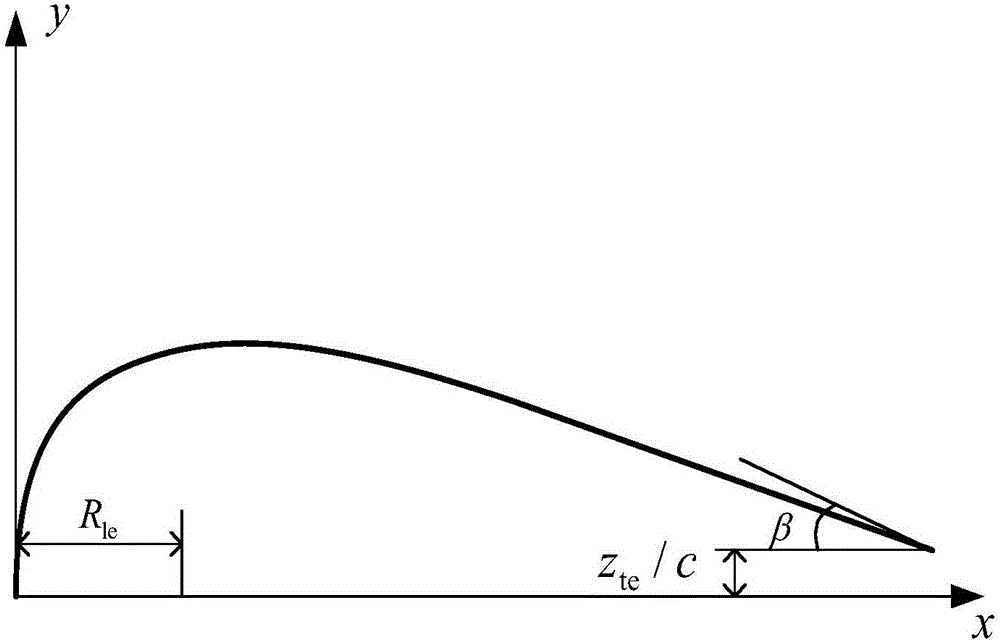
InactiveUS20100036648A1Easy to predictSimple designComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationStagnation pointLeading edge
A method is provided for calculating flow performance characteristics of a body immersed in a fluid under a set of fluid flow conditions. The method comprises providing a geometrical description of a surface of the body and determining the set of fluid flow conditions. The set of fluid flow conditions includes a combination selected from the combination set consisting of angle of attack and leading edge stagnation point location, angle of attack and flow separation point location, and leading edge stagnation point location and flow separation point location. The method further comprises calculating a velocity flow field for the body using a critical point potential flow methodology and calculating flow performance characteristics.
Owner:TAO OF SYST INTEGRATION
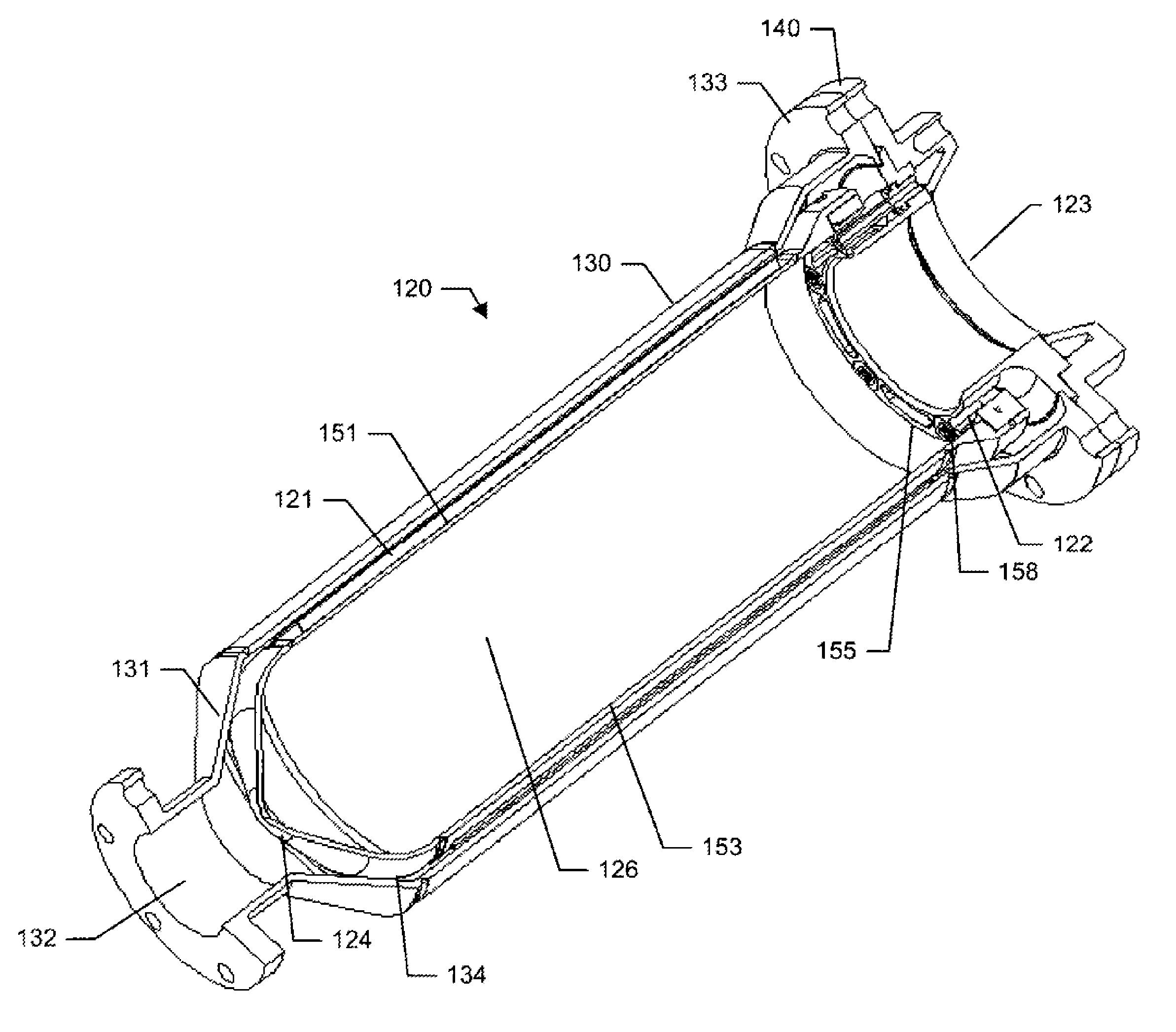
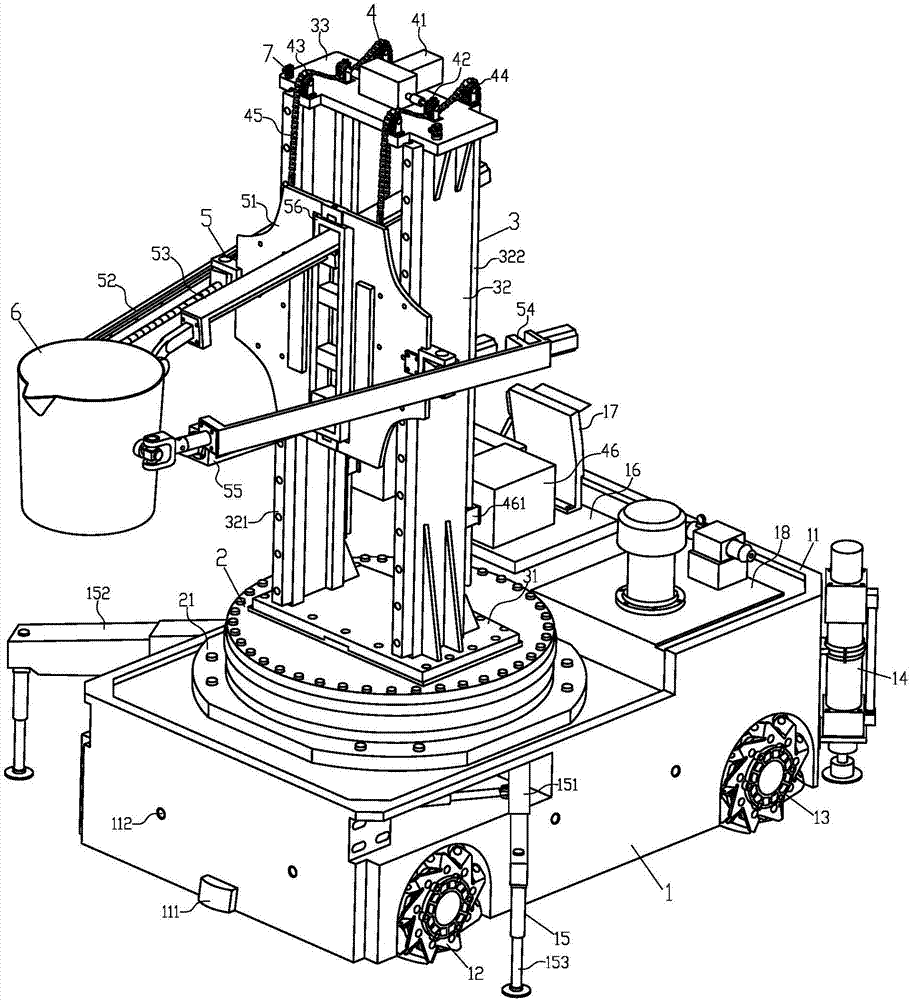
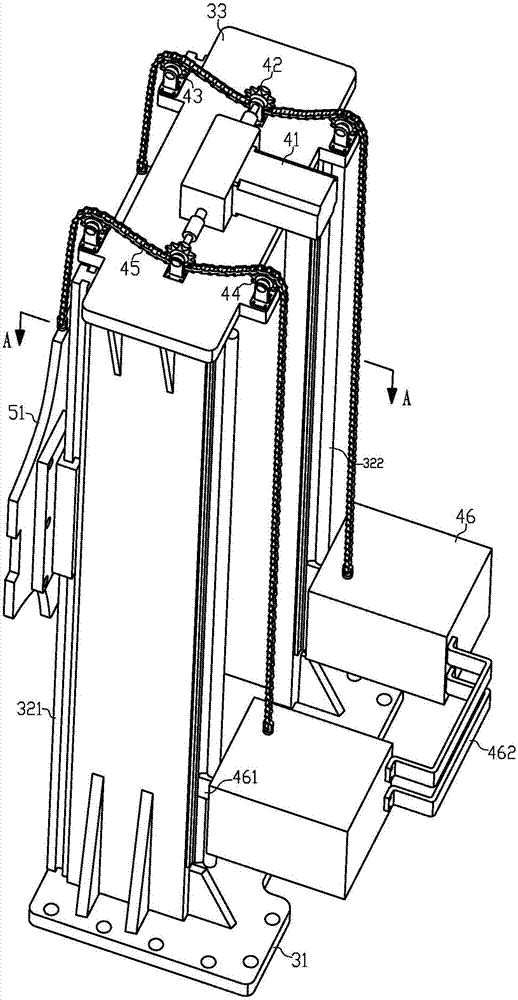
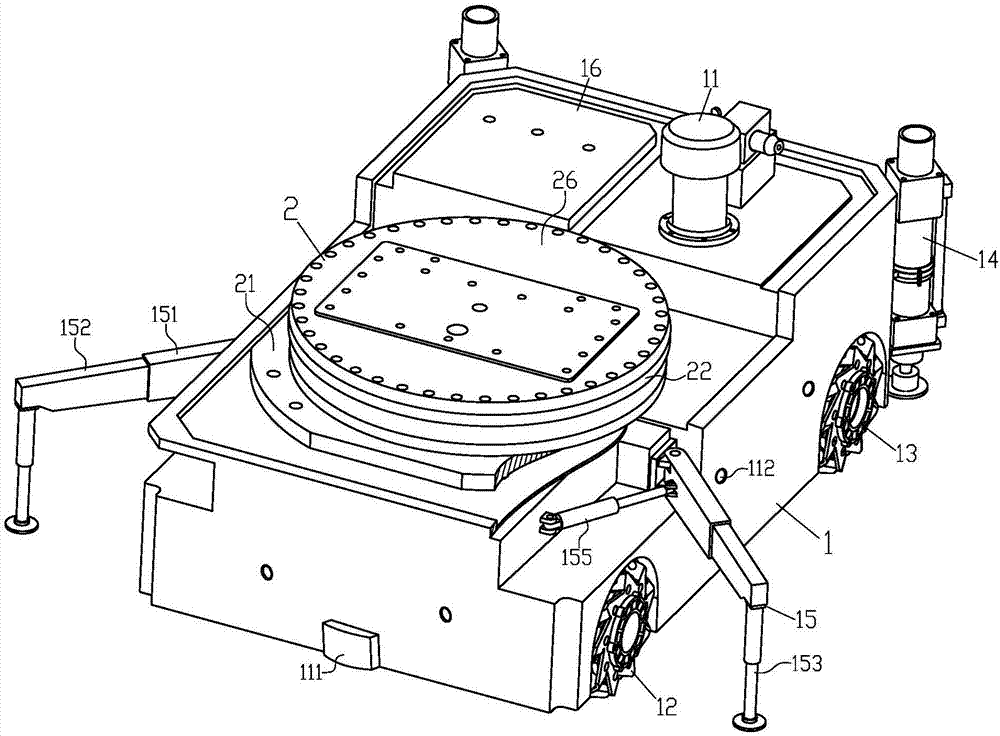
Series-parallel movable heavy load casting robot
ActiveCN107243622ALarge working spaceImprove motor flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMolten metal pouring equipmentsStagnation pointEngineering
The invention discloses a series-parallel movable heavy load casting robot. The series-parallel movable heavy load casting robot comprises a four-wheel drive type moving platform, a rotation device, a stand column assembly, a lifting drive device, a parallel work arm, a tail end executor and a binocular visual system. Four-wheel omnidirectional wheel drive is adopted in the four-wheel drive type moving platform to achieve long-distance flexible stable walking, a rear hydraulic supporting leg and an adjustable hydraulic supporting leg are used for achieving stagnation point self-balance support, work supporting stability is improved, a robot body has five space motion freedom degrees, the rotation device and the lifting drive device can achieve rotation and lifting adjustment, the four-freedom-degree parallel work arm can carry out posture adjustment on the tail end executor, different tail end executors can be replaced according to work needs, different work needs of core assembling, core discharging, casting, carrying and the like of a large casting can be met, the casting core assembling and discharging and casting work efficiency, quality and safety can be improved, and labor intensity and production cost of operators can be reduced.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for thermal management and gradient reduction
InactiveUS20070290702A1Reduce and prevent stagnation pointAvoid intersectionIndividual semiconductor device testingContactless circuit testingStagnation pointJet flow
A micro-spray cooling system beneficial for use in testers of electrically stimulated integrated circuit chips is disclosed. The system includes micro-spray heads disposed about a probe head, which provide a coolant flow onto the IC. A flow inducing injector is provided that directs a fluid jet onto zones where stagnation of the coolant flow is present. This reduces or eliminates any stagnation points and enhance temperature uniformity over the area of the IC.
Owner:DCG SYST
Heat transfer device
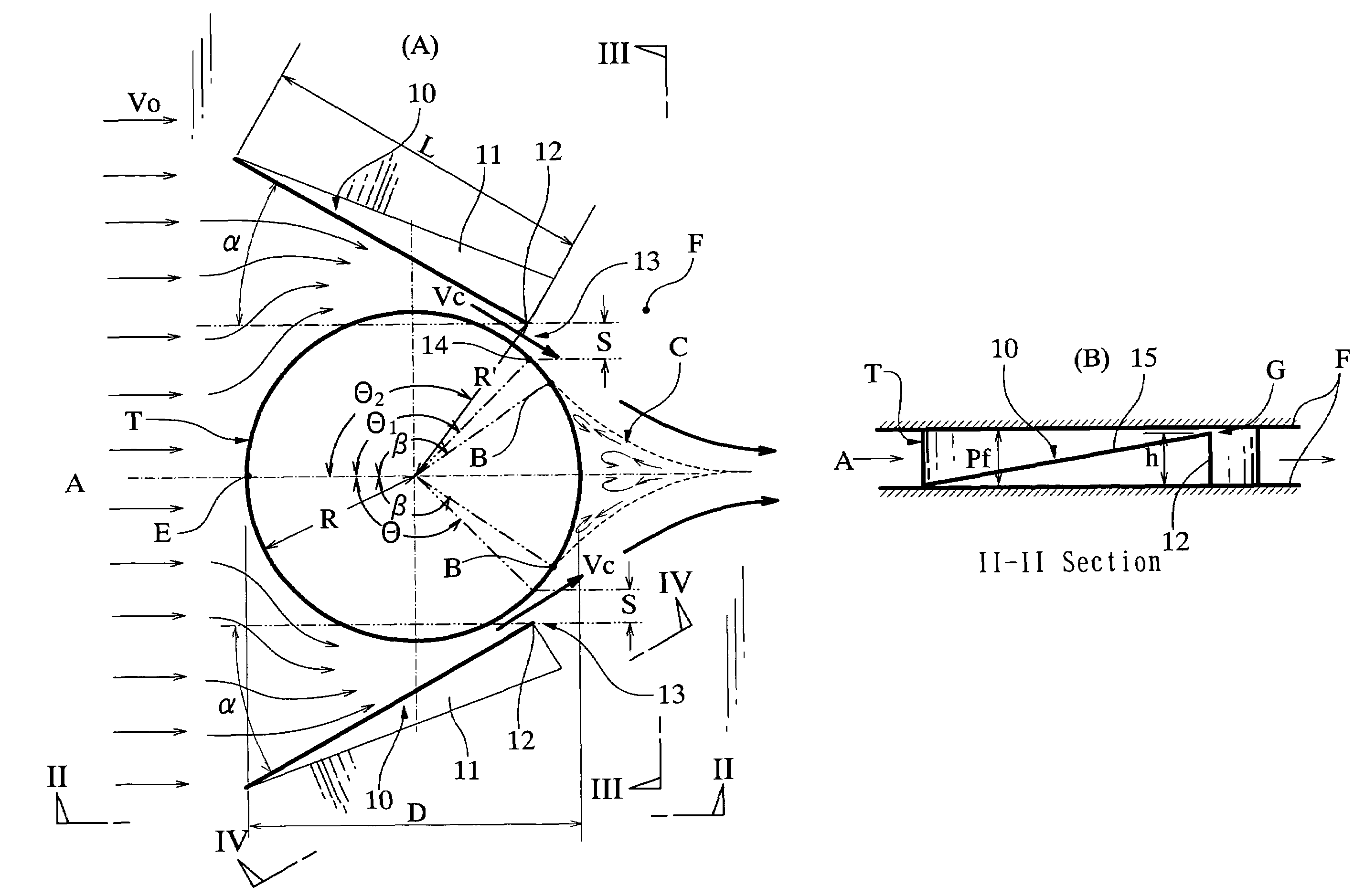
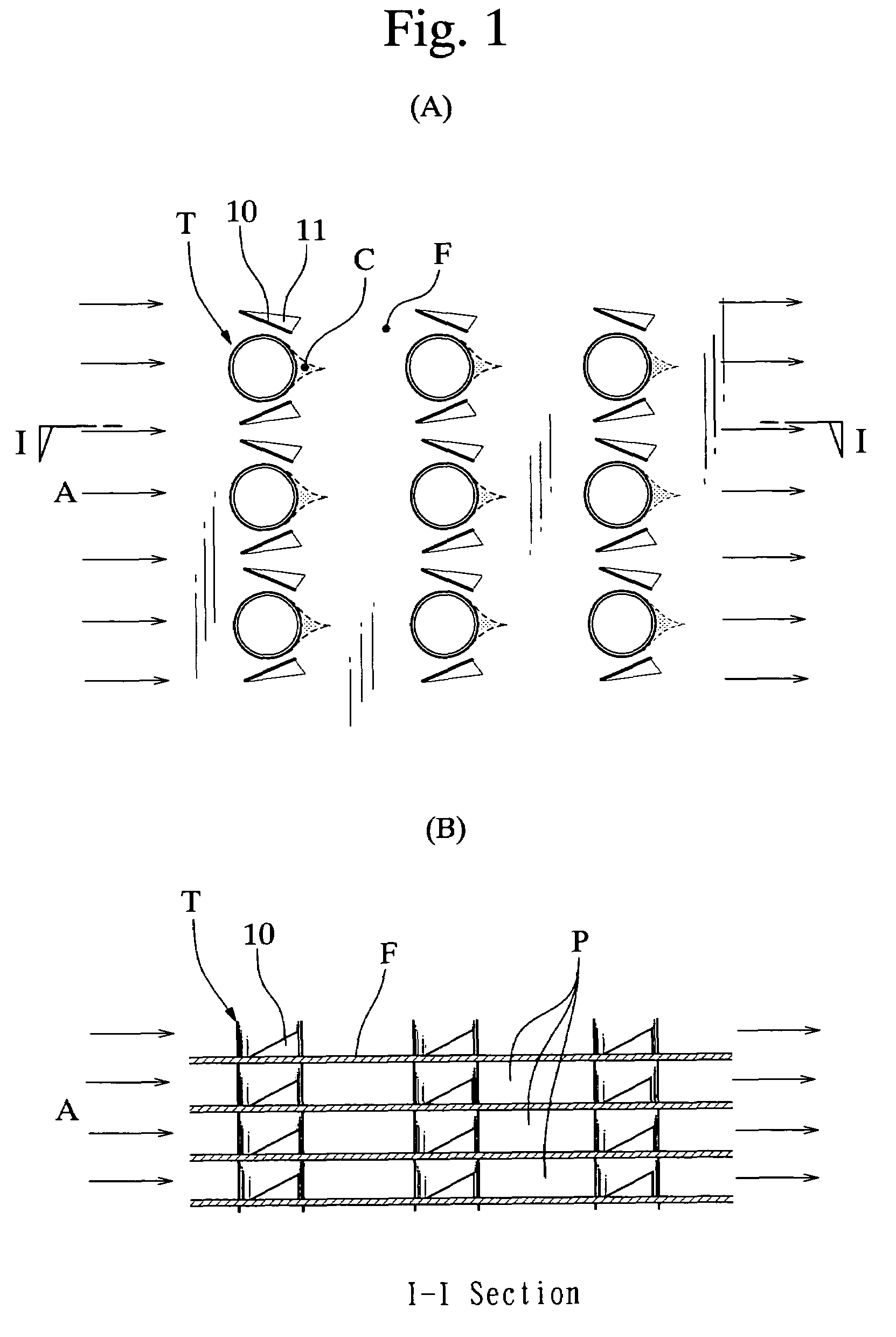
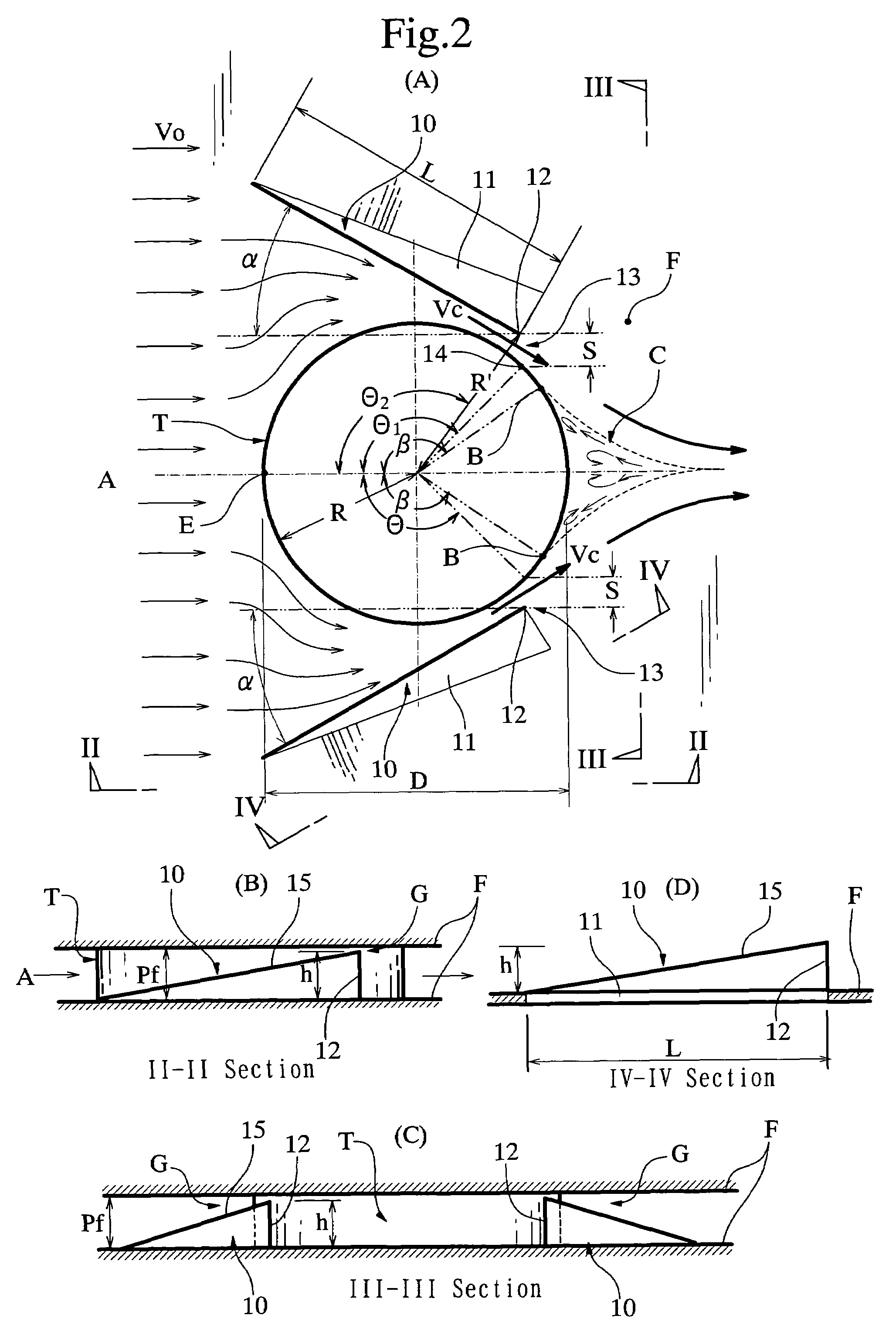
InactiveUS7337831B2Separation wake zone C could be considerably reduced or eliminatedEasy to separateSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusStationary conduit assembliesStagnation pointHeat carrier
A separation wake zone behind a heat transfer tube in a heat transfer device of a heat exchanger or the like is reduced, whereby a heat transfer action of the heat transfer device can be augmented and a pressure loss thereof can be reduced. The heat transfer device of the heat exchanger has a linear or tubular heat transfer object (T) in heat transfer contact with a heat carrier fluid (A), and a heat transfer fin (F) integrally formed with the heat transfer object for heat transmission therebetween. The heat transfer fin is provided with a guide fin (10) positioned in vicinity of the heat transfer object, and the guide fin conducts the fluid to the rear of the heat transfer object, thereby reducing the separation wake zone behind the heat transfer object. A position (B) of separation point of the fluid is set to be at an angular position (β) equal to or greater than 90° from a stagnation point (E) on the heat transfer object by setting of an attack angle, configuration, position and dimensional proportion of the guide fin.
Owner:YOKOHAMA TLO
Wireless sensor network data acquisition method based on predictable mobile Sink position
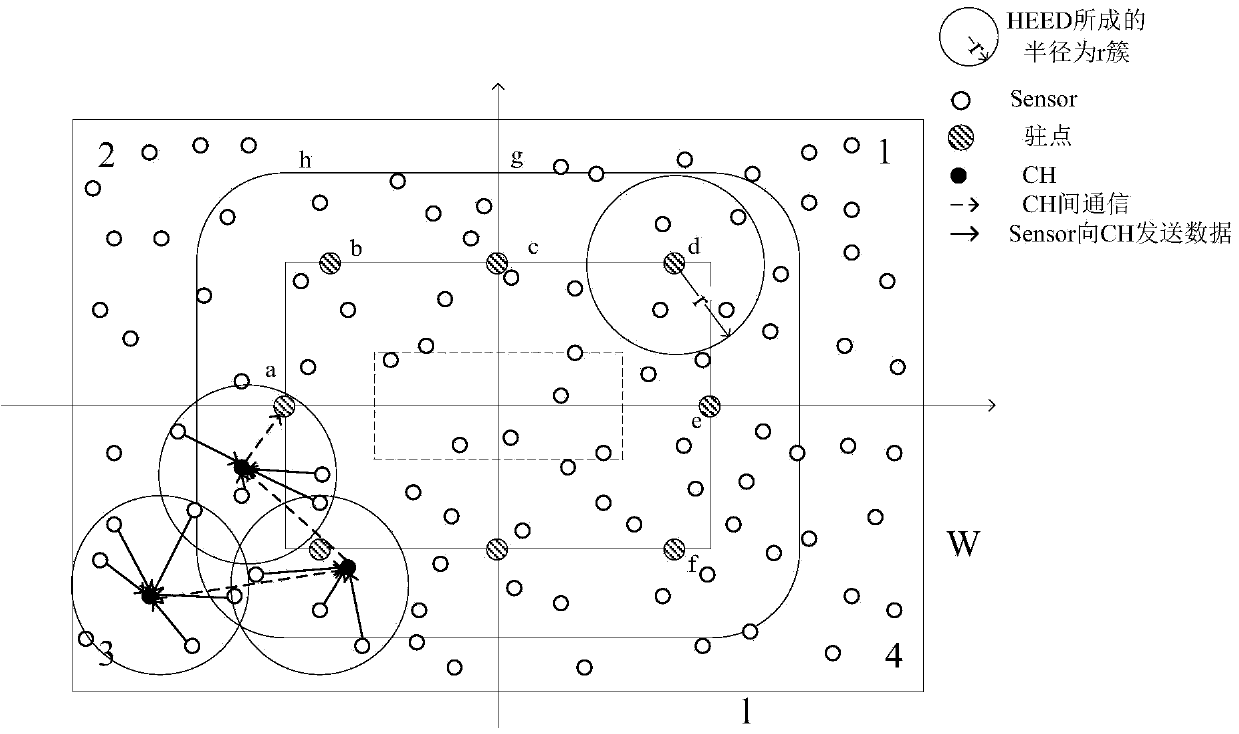
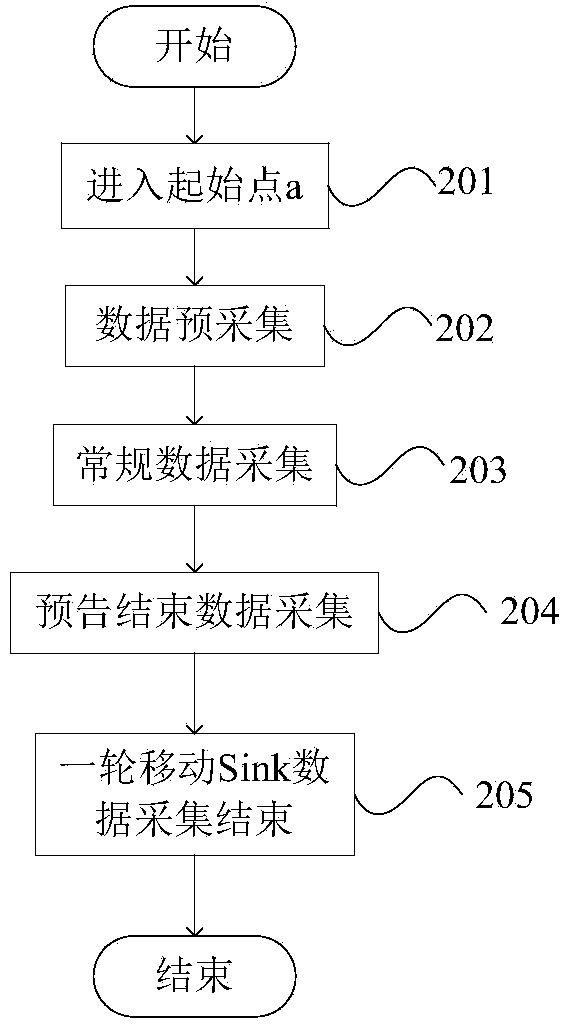
InactiveCN103596222AExtended service lifeBalanced energy consumptionNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesStagnation pointData acquisition
The invention discloses a wireless sensor network data acquisition method based on a predictable mobile Sink position. The method includes the steps of on the basis of sensor nodes undergoing periodical network clustering through an HEED algorithm, calculating coordinate information of a mobile Sink node in a network on the basis of a known network parameter, carrying out routing of data packets to the position where the Sink node is located, and the Sink node periodically collects data from the sensor nodes within specific dwell time of stagnation points on a preset track according to the proportion of data amount generated by each quadrant node in the whole network data amount. Therefore, the method supports the fact that the sensor nodes of the whole network route the data packets to the mobile Sink node in real time, and data collection delay is shortened. The mobile Sink node does not need to broadcast current position information when moving between the stagnation points, so that communication cost is reduced. The dwell time is adjusted continuously at each quadrant stagnation point, so that network energy consumption is balanced and service life of the network is prolonged.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Experimental facility and experimental method for fire suppression effectiveness evaluation of additive-containing water mists
InactiveCN104614485AUniform speedReduce testing costsChemical analysis using combustionMaterial heat developmentStagnation pointData acquisition
The invention discloses an experimental facility and an experimental method for the fire suppression effectiveness evaluation of additive-containing water mists. The experimental facility comprises an oxidizing agent flow quantitative supplying and conveying system, a combustible gas quantitative supplying and conveying system, a representation system, and a data acquisition and remote control system, wherein the oxidizing agent flow quantitative supplying and conveying system is composed of a frequency conversion vortex fan, a vortex shedding flowmeter, a small wind tunnel, an atomization device and a sprayer support; the combustible gas quantitative supplying and conveying system is composed of a columnar porous burner and an automatic gas distributing system; the representation system is composed of a water mist and flame action observation device, a flame temperature measurement device and a condensed phase grain size and speed measurement device. The experimental facility can realize quantitative supplying of air and combustible gas, the adjustability of the particle size distribution and the release amount of the liquid phase fire extinguishing agent and the adjustability of the concentration of additive, and the representation of the temperature of a position nearby a stagnation point, the particle diameter and the speed. The experimental facility can be used for screening high-efficiency water mist additives, quantitatively evaluating the fire suppression effectiveness for specific flames in the aspects of the variety and the concentration of the additive, and researching the physical and chemical mechanism of the action of the condensed phase fire extinguishing agent and the flame.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Layout method for embedded air data sensing system pressure hole based on genetic algorithm
InactiveCN102122372AHigh measurement accuracyImprove anti-interference abilityGenetic modelsStagnation pointMean square
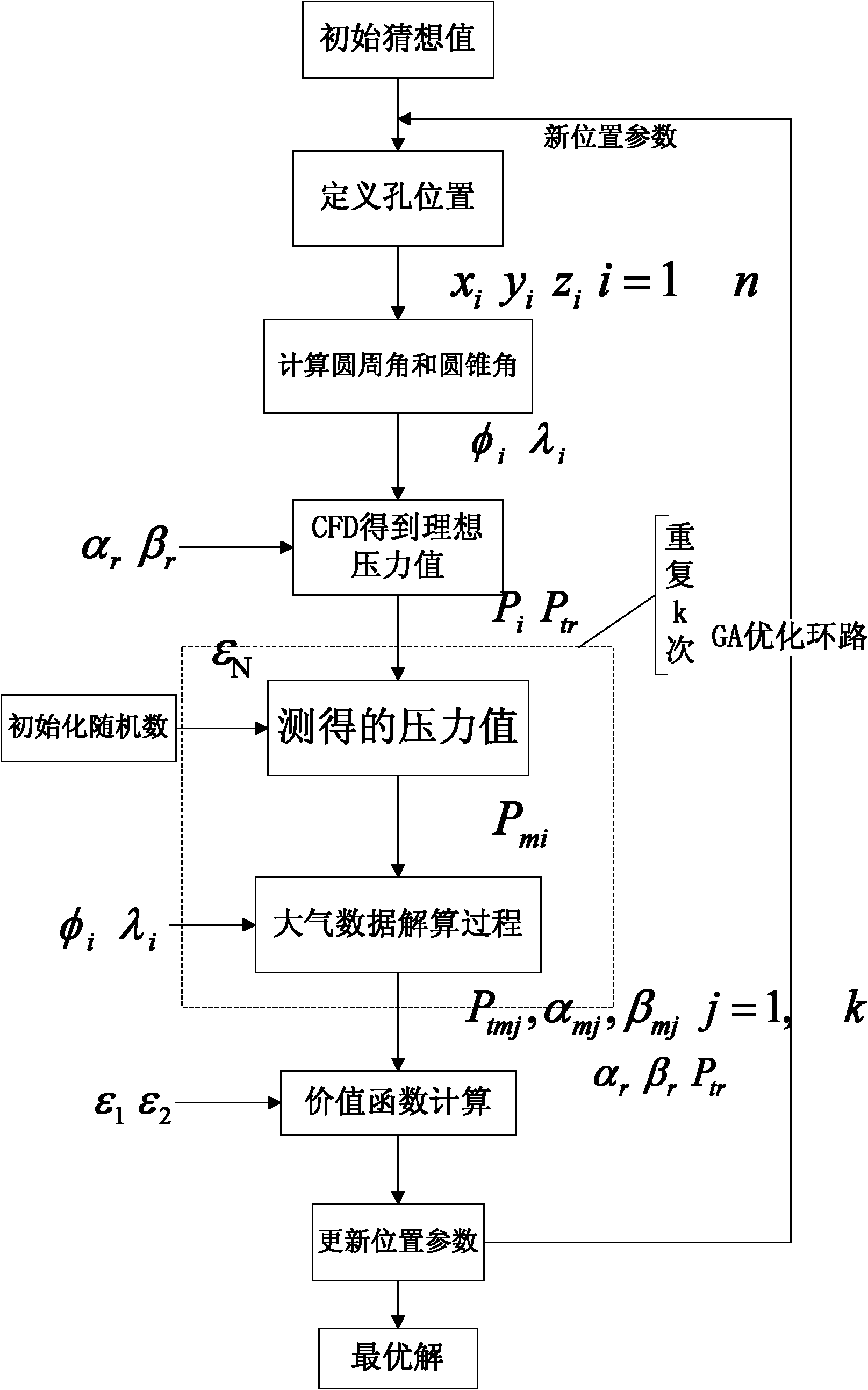
The invention discloses a layout method for an embedded air data sensing system pressure hole based on a genetic algorithm, comprising the following steps: taking an initial supposition position (xi, yi and zi) as the input of a value function; converting coordinates xi, yi and zi into a circumferential angle phi i of and a conical angle lambda i; simulating to obtain the pressure value Pi of the point on the surface of an aircraft by the computational fluid mechanics according to a real angle of attack alpha r, a sideslip angle beta r and a given mach number, wherein the pressure value of a stagnation point is real total pressure Ptr; adding generally distributed random noise epsilon N on the pressure value Pi to simulate pressure measuring inaccuracy; calculating the angle of attack, the sideslip angle and the pressure of the stagnation point by the values with 'noise'; comparing the angle and the pressure of the stagnation point which are obtained by estimation, with a reference value under each simulation situation; and calculating the value function by the weighted sum of an error ( which is the difference of an estimation value and the reference value) mean square root.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
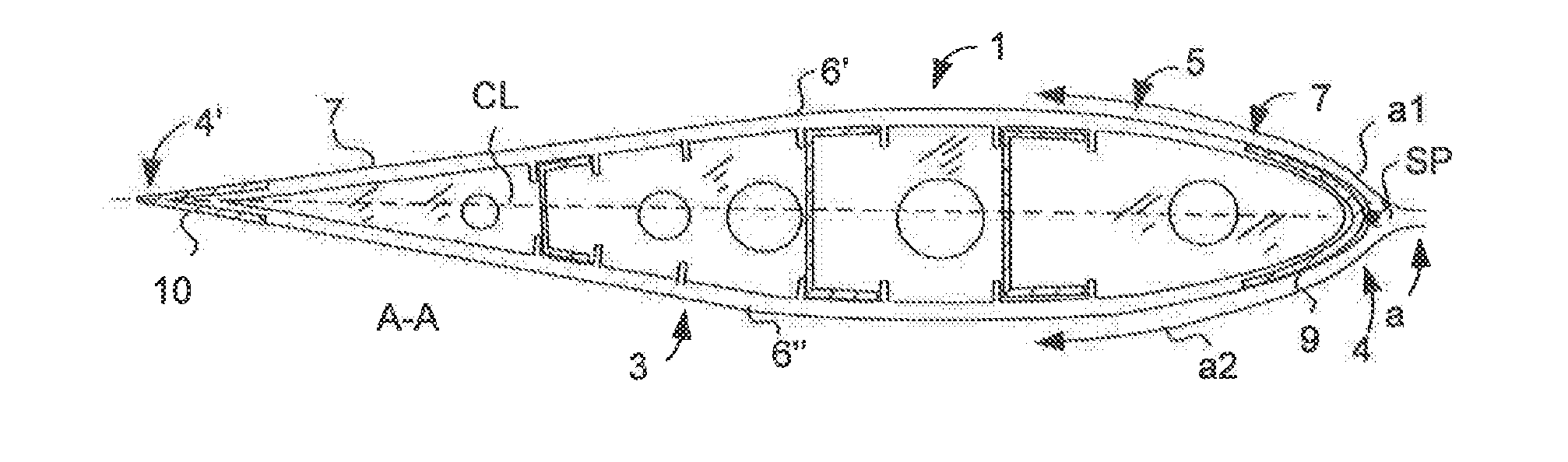
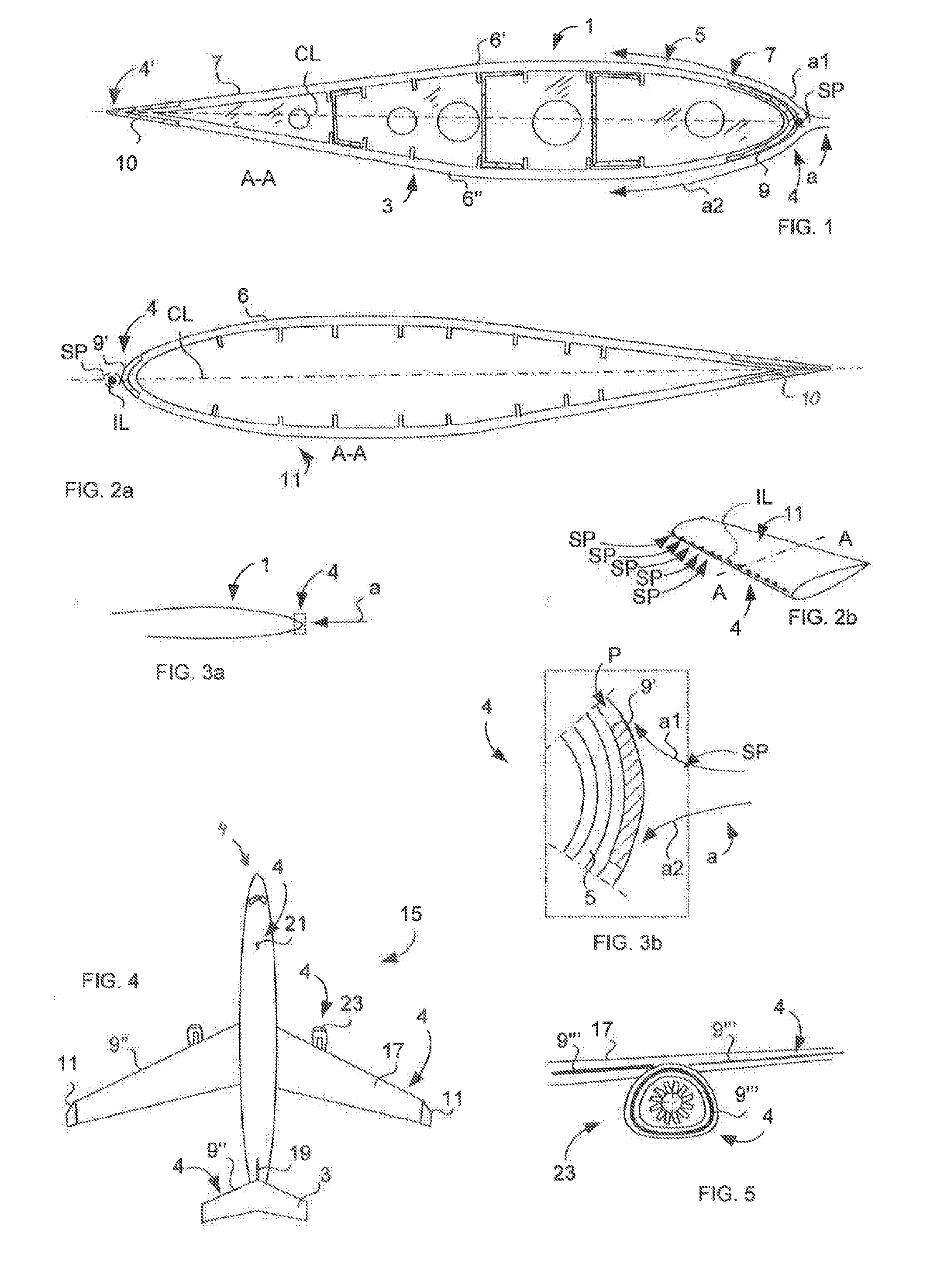
Method of steering aircraft by moving the stagnation point and aircraft using the method
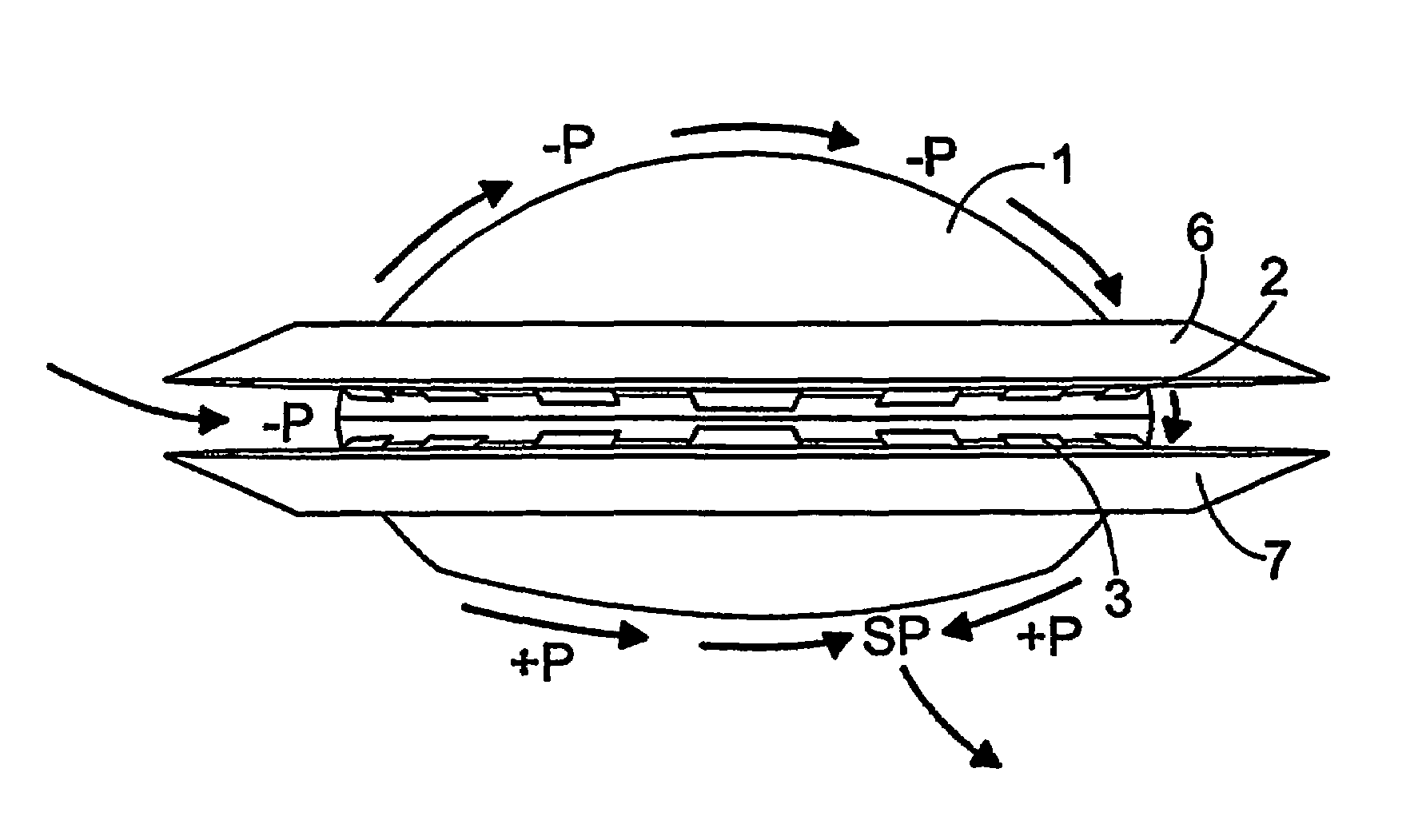
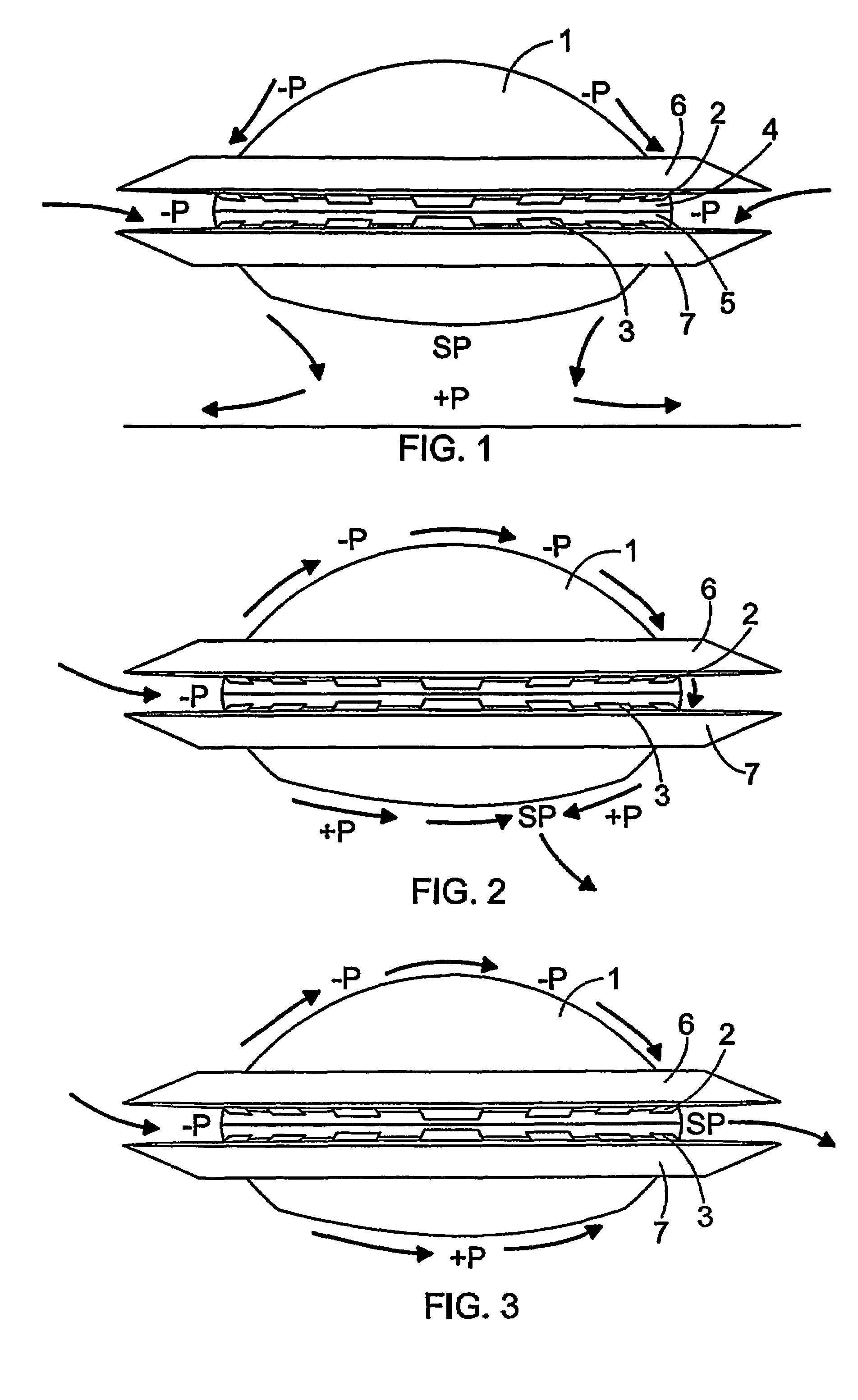
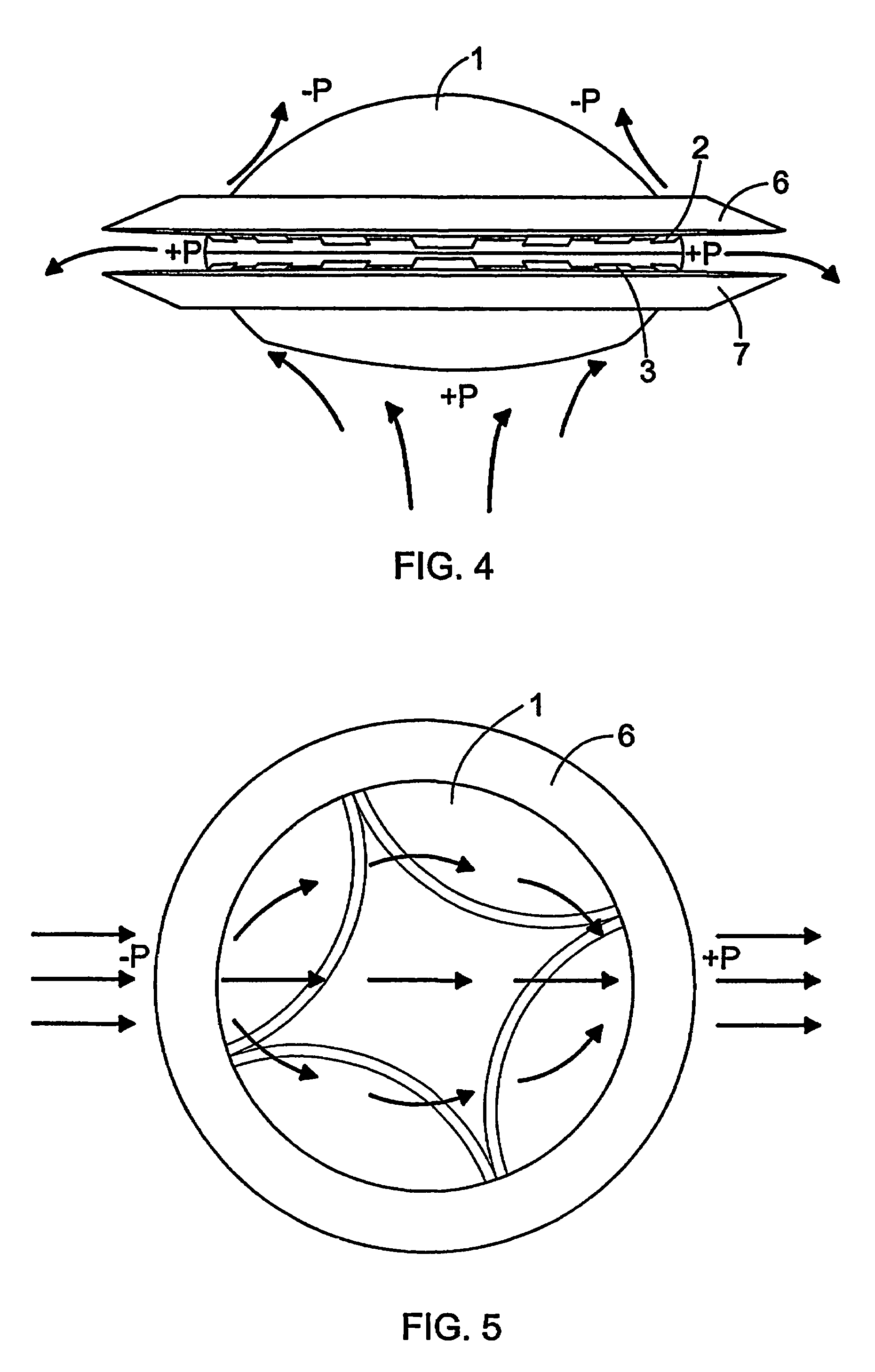
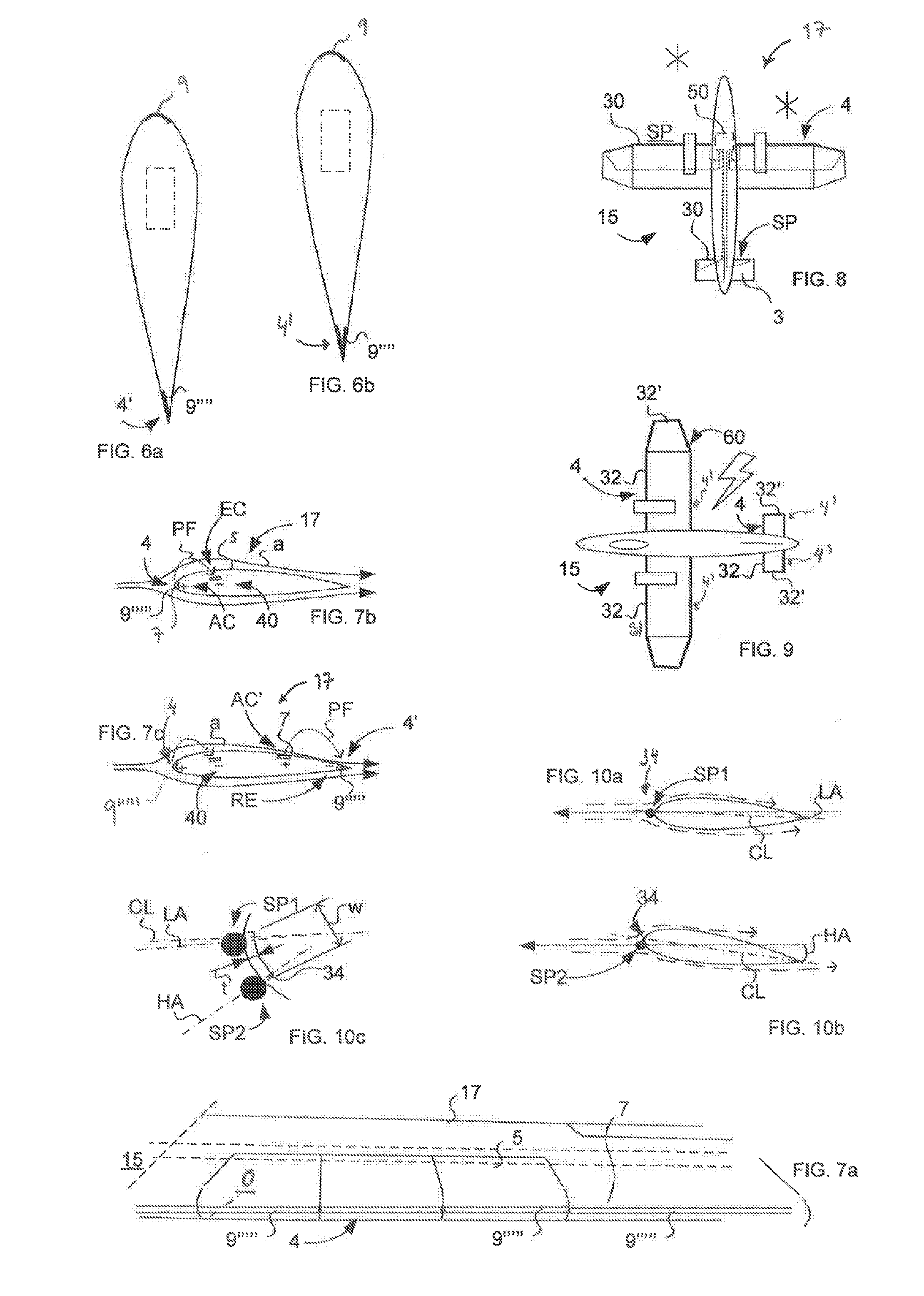
InactiveUS7407132B2Easy maintenanceImprove efficiencyAircraft navigation controlFlying saucersAir cycleStagnation point
An aircraft which includes elements providing air circulation and directing the circulation along a housing. Different operational stages of the aircraft such as take off and level flight are achieved by using the same functionally inter-connected elements. The circulation is achieved by fan elements that allow adjusting the blow direction and the blowing force of the flow. A stagnation point (SP) associated with the circulation is also formed if necessary below the housing and the aircraft can be steered by controlling the circulation and the position of the stagnation point (SP).
Owner:LIGHTWAY
Methods and apparatus for reducing count of infectious agents in intravenous access systems
InactiveUS8574490B2Reduce pollutionShorten the counting processUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryStagnation pointStopcock
Methods and apparatus for preventing patient bloodstream infection by microorganisms during administration of various medications or fluids through IV lines. In particular, the invention reduces contamination of IV lines, connecters, stopcock valves, manifolds, ports, etc. by means of irradiation by violet and / or blue light. Each embodiment comprises a source of violet and / or blue light and an optical element optically coupled to that light source for shaping the radiation pattern of the light emitted by the light source. Preferably, a light-emitting diode or a laser diode that emits light in the desired wavelength can be used. The optical element, optically coupled to the light source, is embedded or installed in or attached to a component of an IV set, the emitted light being directed to a “point of entry” or any other stagnation point of an IV set.
Owner:BACTRIBLUE
Air film and micro straight channel cooling structure for front edge of hypersonic vehicle
InactiveCN102145745AImprove heat transfer efficiencyTake advantage ofHeat reducing structuresFuselagesStagnation pointHigh pressure water
The invention discloses an air film and micro straight channel cooling structure for a front edge of a hypersonic vehicle, which comprises an air film cavity, air film holes and micro straight channels. The air film cavity is positioned inside the front edge of the hypersonic vehicle; the air film holes which are arranged in a stagger mode are formed near stagnation points of the front edge at the periphery of the air film cavity; two rows of micro straight channels are formed next to both upper and lower surfaces of a wedge-shaped body of the hypersonic vehicle; and the micro straight channels are communicated with the air film cavity and a high pressure water tank. On the premise of not changing the pneumatic appearance of the air vehicle, the air film cooling mode is combined with the micro channel cooling mode, so that the heat exchange efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
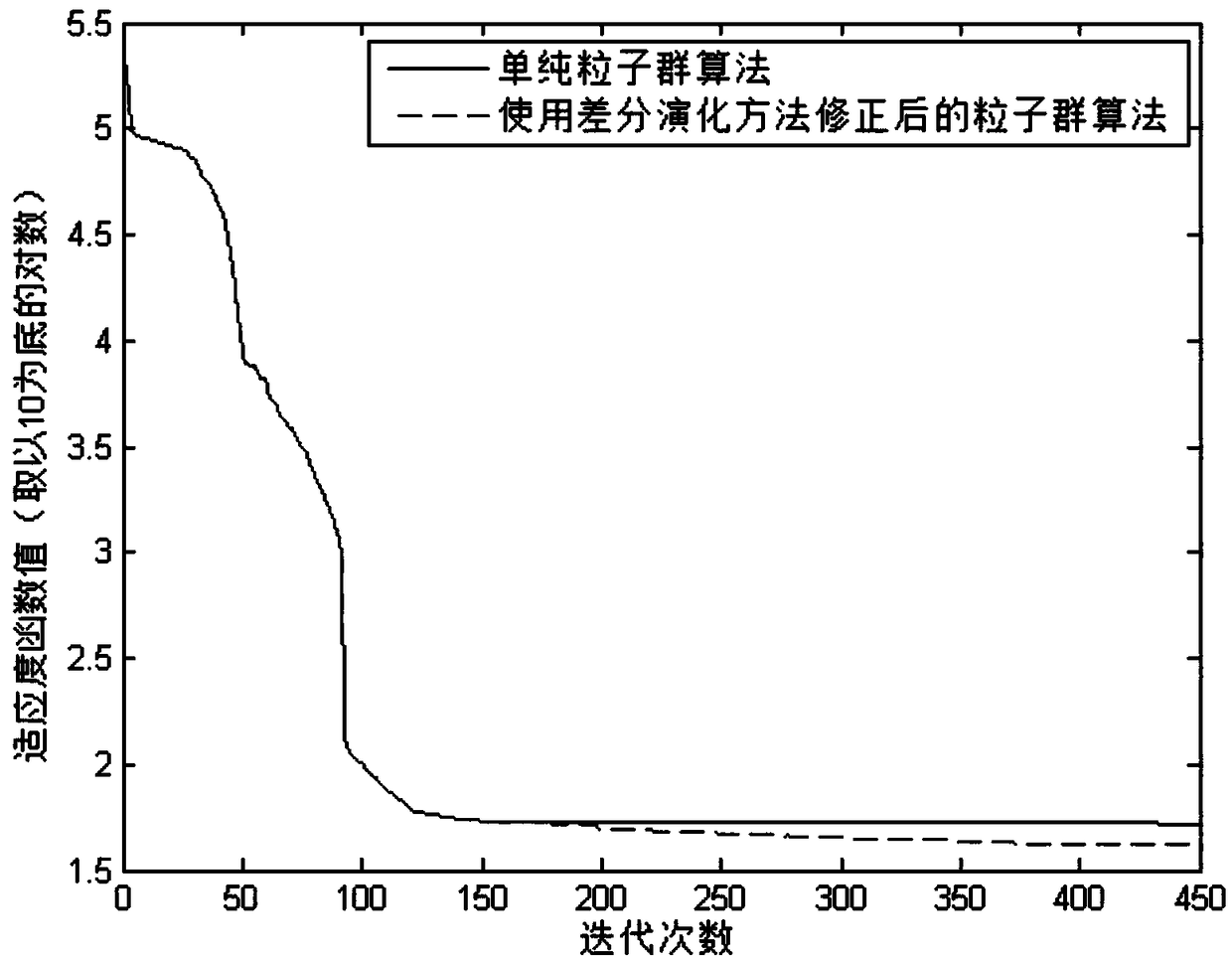
Space multi-joint robot path planning method based on differential evolution particle swarm optimization
ActiveCN109108963AReduce energy consumptionShorten the timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorStagnation pointDynamic models
The invention discloses a space multi-joint robot path planning method based on differential evolution particle swarm optimization. The method comprises the steps of building a kinematic model and a dynamic model of mechanical arm joint angle changes of a space multi-joint robot, then building a model of disturbance caused by collision of a multi-joint robot, expressing a changing track curve of joint angles as a polynomial function relative to time, and building a total fitness function; and in iteration solution, firstly, using particle swarm optimization, and starting a differential evolution algorithm when a stagnation point appears in particle swarm optimization, and exchanging partial individuals of the populations of the two algorithms so as to enlarge the population size, and completing path planning of the space multi-joint robot. According to the space multi-joint robot path planning method based on differential evolution particle swarm optimization, grasp path planning of the space mechanical arm is carried out by utilizing the particle swarm optimization corrected with differential evolution; and because the purpose of planning is to make the end effector of the mechanical arm arrive at the fixed position and be in the fixed gesture, and to control the structure of the mechanical arm at the termination of time, the disturbance caused to the base by collision betweenthe end effector and a target is the least, and total energy consumption of a traveling path is the least.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multifunctional erosion protection strip
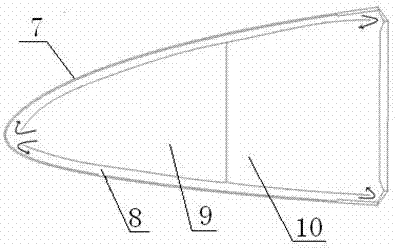
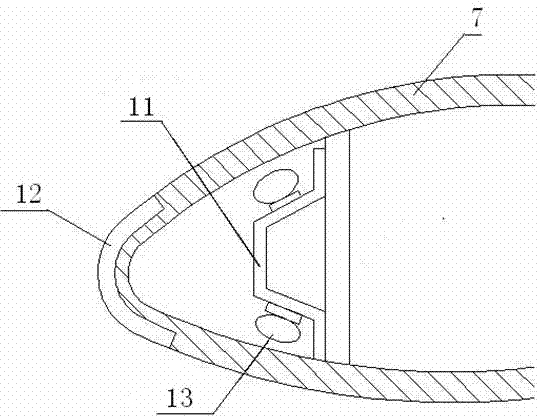
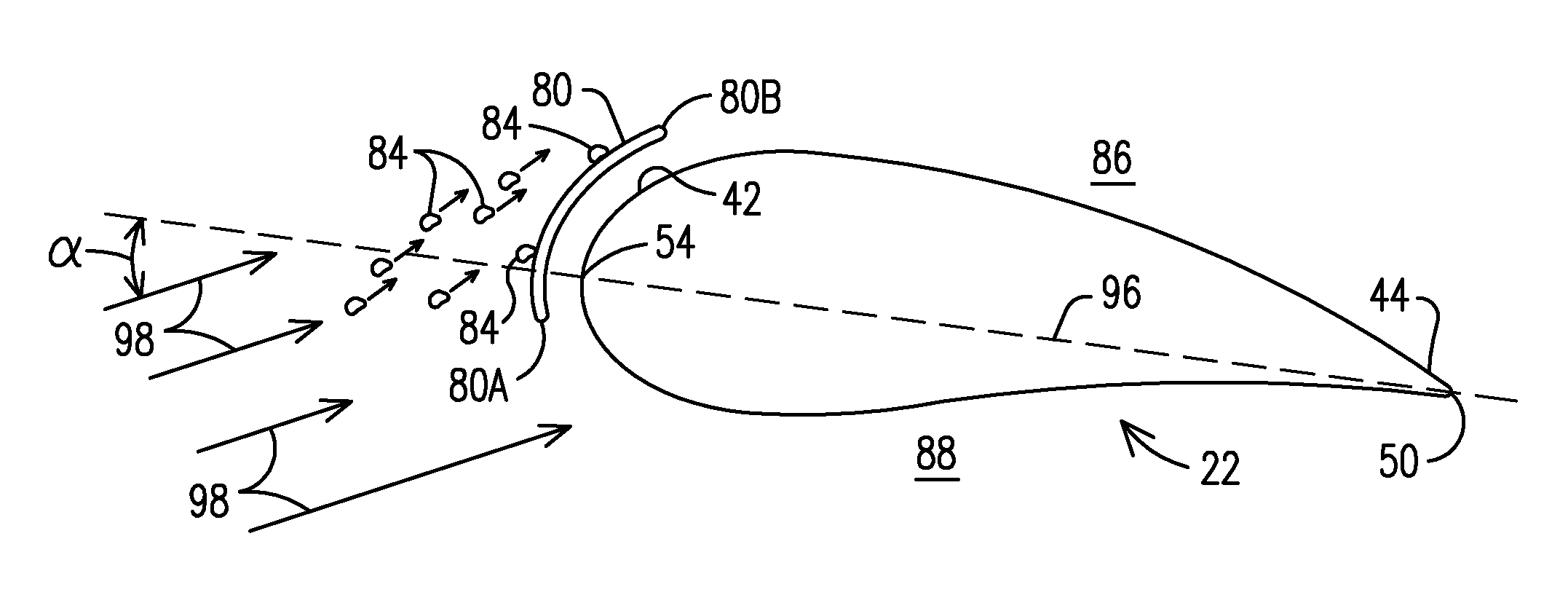
ActiveUS20150298791A1Reduce weightAvoid erosionAircraft lighting protectorsBlade accessoriesStagnation pointLeading edge
An airfoil article including a composite skin having a first surface and a second surface opposite first surface, forming a leading edge. The leading edge is during use subjected to an airflow meeting the leading edge at stagnation points. The leading edge includes an elongated member. The outer surface of the elongated member is arranged flush with the first surface of the composite skin such that an essentially smooth aerodynamic surface of the leading edge is formed. The elongated member is adapted to serve as an erosion protection of the leading edge and to function as an electrode of a plasma generating system.
Owner:SAAB AB
System and method for confining an object to a region of fluid flow having a stagnation point
A device for confining an object to a region proximate to a fluid flow stagnation point includes one or more inlets for carrying the fluid into the region, one or more outlets for carrying the fluid out of the region, and a controller, in fluidic communication with the inlets and outlets, for adjusting the motion of the fluid to produce a stagnation point in the region, thereby confining the object to the region. Applications include, for example, prolonged observation of the object, manipulation of the object, etc. The device optionally may employ a feedback control mechanism, a sensing apparatus (e.g., for imaging), and a storage medium for storing, and a computer for analyzing and manipulating, data acquired from observing the object. The invention further provides methods of using such a device and system in a number of fields, including biology, chemistry, physics, material science, and medical science.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Manifold for fuel cell system
A method and apparatus for converting single multiphase fluid flow into plural multiphase fluid flows having substantially uniform composition and flow properties. A manifold comprises an enclosure having an inlet and an inner surface perpendicular to the inlet such that the incident angle of input flow impacts the surface to form a stagnation point whereby an intermediate flow is deflected along the surface substantially symmetrically outward from the stagnation point and channeled to a plurality of parallel fluid outlets connected to the enclosure. The distance between the stagnation point and the plurality of outlets is selected to maintain substantially equivalent fluid pressures and uniform flow rates at the outlets. A preferred embodiment of the manifold channels the intermediate flow between two walls forming a triangular shaped nozzle directing the flow from the stagnation point to the base of the triangle for communication of electrolyte to a metal-based fuel cell through the plurality of outlets.
Owner:METALLIC POWER INC
Resistive contact sensors for large blade and airfoil pressure and flow separation measurements
A wind turbine blade instrumentation structure and method is provided for fluid dynamic polymer-based contact sensors measuring ambient pressure based on the resistivity changes across the sensor. The pressure sensors may applied in predetermined patterns to airfoil structures, such as wind turbine blades, without impacting the blade structure and fluid dynamic characteristics. The pressure sensors measure blade performance with high fidelity. The pressure measurements are transmitted to processing to determine blade characteristics and environment including flow separation, stagnation point, angle of attack, lift and drag and wind speed. Further processing of the pressure distribution may identify wind shear, up-flow and yaw error.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Hypersonic velocity wing robust optimization design method considering machining errors
ActiveCN106126860AEnsure safetyReduce sensitivityGeometric CADSustainable transportationThermal engineeringStagnation point
The invention discloses a hypersonic velocity wing robust optimization design method considering machining errors and belongs to the technical field of optimization design. The method comprises the following steps: fully considering geometric machining errors existing in hypersonic velocity wing design, and realizing quantitative characterization of a machining error coefficient by utilizing an interval vector under the condition that a probability density function of machining error parameters is unknown; establishing aerodynamic configuration of the hypersonic velocity wing through a parametrization method, and performing nonstructured surface mesh division; combining an interval parameter vertex method with an aerodynamic / thermal engineering algorithm, and calculating upper and lower bound of intervals of total stagnation point heating capacity and lift-drag ratio of the wings; and on the basis, establishing a multi-target interval robust optimization model, and performing optimization design on the wing shape by using a genetic algorithm. The numerical result shows that according to the method, the total stagnation point heating capacity of the designed wing is reduced under the precondition that lift-drag ratio constraint of the wing is maintained; meanwhile, a fluctuation range of the total stagnation point heating capacity is narrowed, and a new thought is provided for shape design of the hypersonic velocity wing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Anti-icing system and aircraft
ActiveUS20170217593A1Efficient ejectionEfficiently ejectedDe-icing equipmentsStagnation pointIce protection system
There is provided an anti-icing system that has a simple structure and makes it possible to exert anti-icing performance by dealing with displacement of a stagnation point without increasing air resistance. The anti-icing system according to the present invention blows heated gas to an inner surface of a wing of an aircraft, and includes: a piccolo tube that includes a flow path through which the heated gas flows in a longitudinal direction from a rear end to a front end, and a plurality of ejection holes provided along the longitudinal direction to make the flow path communicate with an outside; and a supply source that supplies the heated gas toward the piccolo tube. The piccolo tube is held to cause positions of the respective ejection holes to be fixed in a gravity direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI AIRCRAFT
Streamline-based microfluidic device
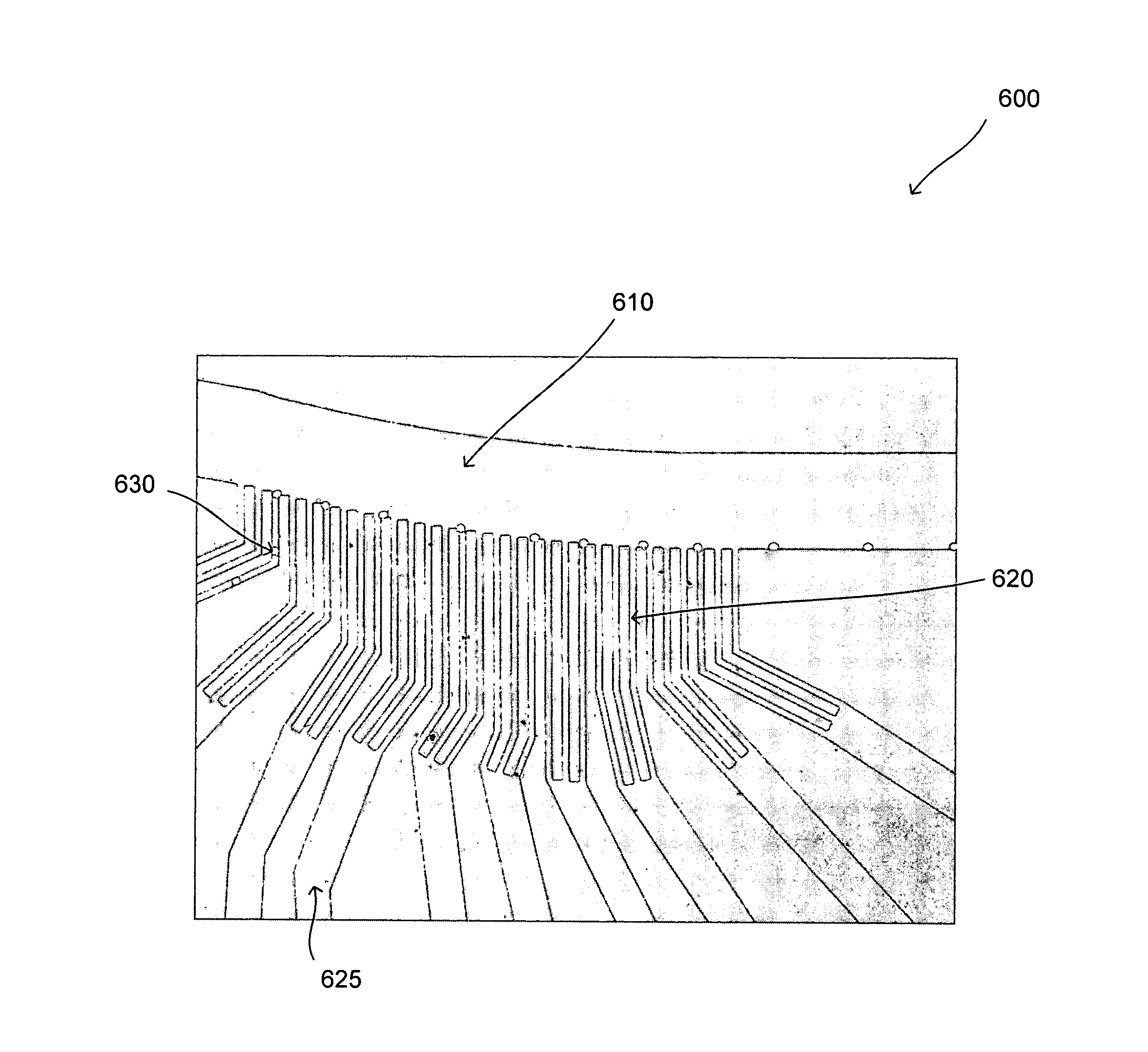
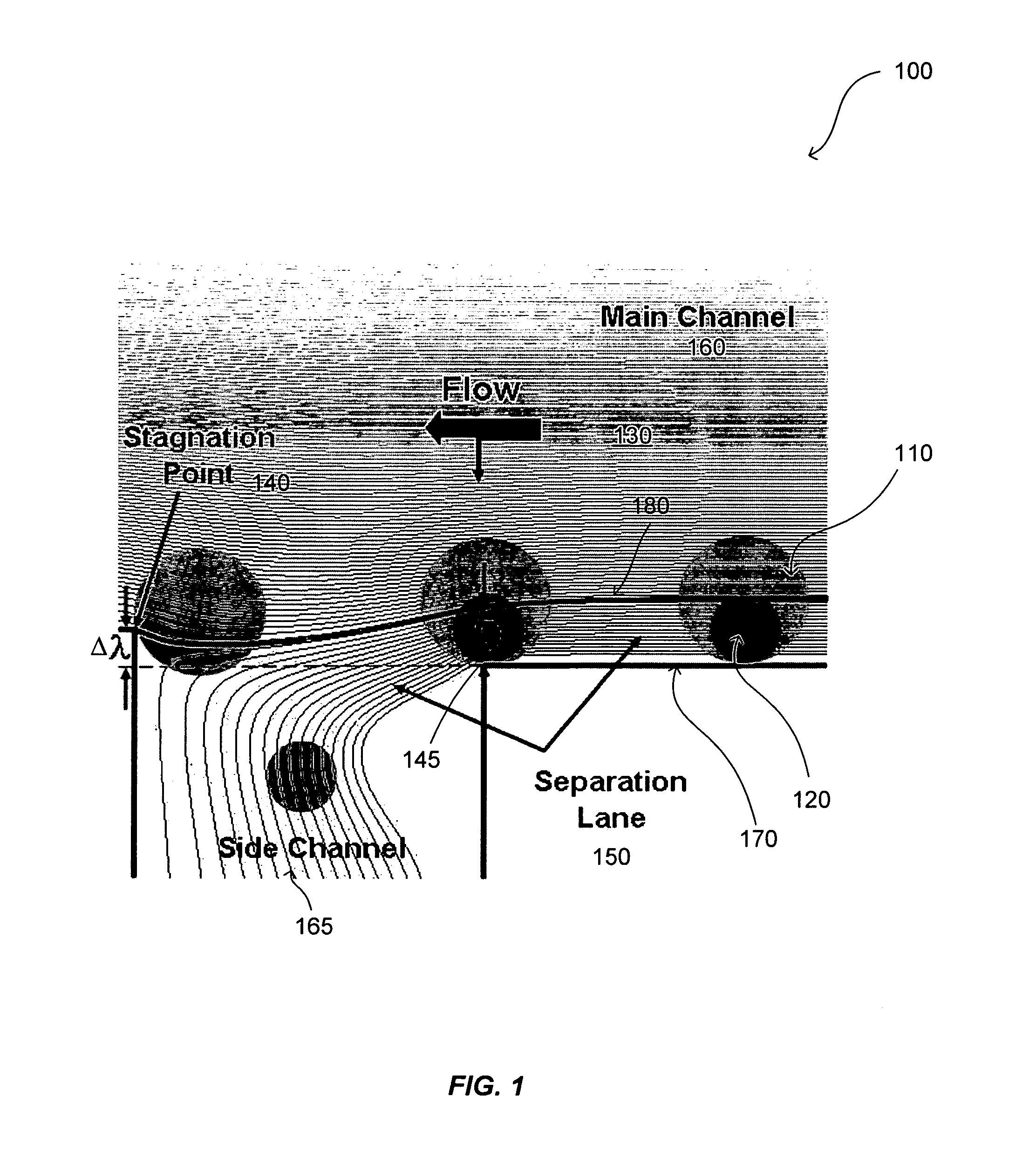
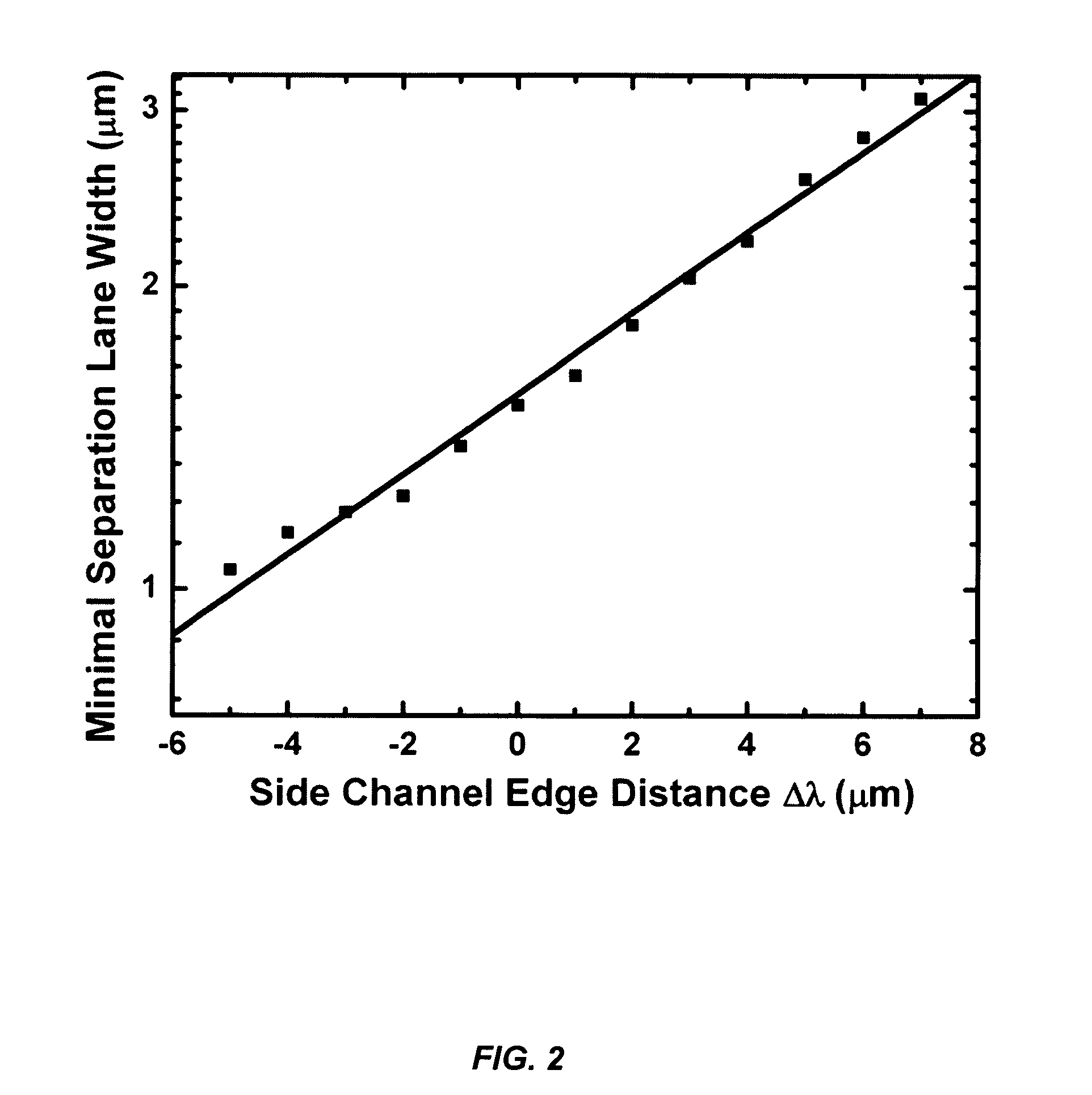
The present invention provides a streamline-based device and a method for using the device for continuous separation of particles including cells in biological fluids. The device includes a main microchannel and an array of side microchannels disposed on a substrate. The main microchannel has a plurality of stagnation points with a predetermined geometric design, for example, each of the stagnation points has a predetermined distance from the upstream edge of each of the side microchannels. The particles are separated and collected in the side microchannels.
Owner:IRIS INT +1
Staggered opposite jetting air film hole row structure used for turbine blade leading edge air film cooling
InactiveCN104832218AOvercoming processabilityOvercoming thermal insulationBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesStagnation pointLeading edge
The invention discloses a staggered opposite jetting air film hole row structure used for turbine blade leading edge air film cooling. Air film cooling hole rows are processed in a turbine blade leading edge area. The suction surface staggered opposite jetting air film hole row and the pressure surface staggered opposite jetting air film hole row are arranged at the two sides of the blade leading edge stagnation point staggered opposite jetting air film hole row. The cross section shape of each air film hole is changed from the cross section shape of the air film hole inlet to that of the air film hole outlet, and the air film holes are communicated with the cold channels the turbine blades. The radial inclination angle of the air film holes is 25-60 degrees; the aperture of the air film holes is 0.3-0.8mm; the radial hole spacing of the inclination holes in the same direction in the air film hole rows is 3d-9d; the flow direction distance between the center lines of the staggered air film holes in the air film hole rows is 0.5d-d; and the radial distance between the two adjacent staggered air film holes is 3d-9d. According to the staggered opposite jetting air film hole row structure, a relatively stable air film coverage area is enabled to be formed on the wall surface of the blade leading edge by the jetted cold air so that the air film cooling effect is improved; besides, the staggered opposite jetting air film hole row structure has the characteristics of being easy and convenient to process and low in cost.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Afterburner and aircraft engine
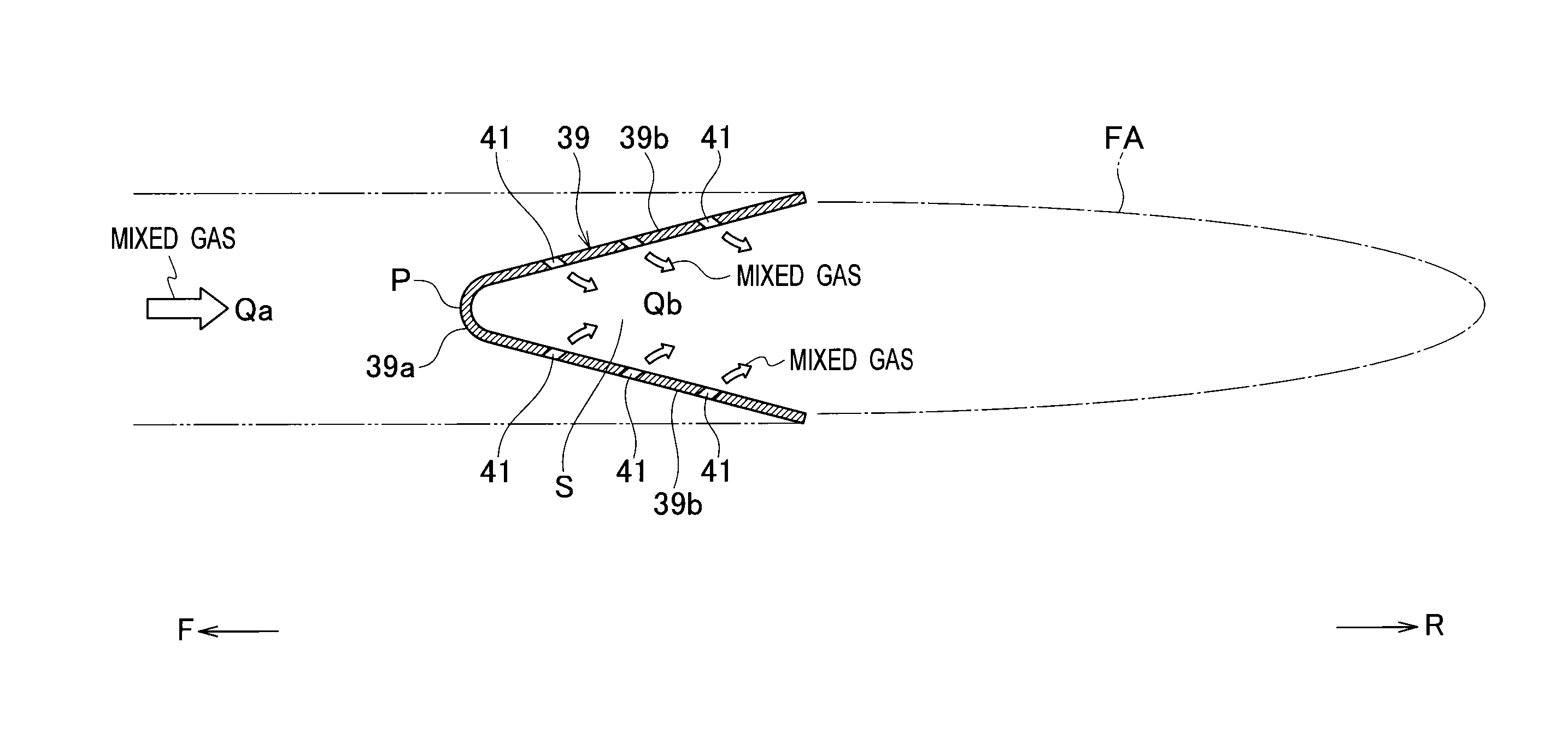
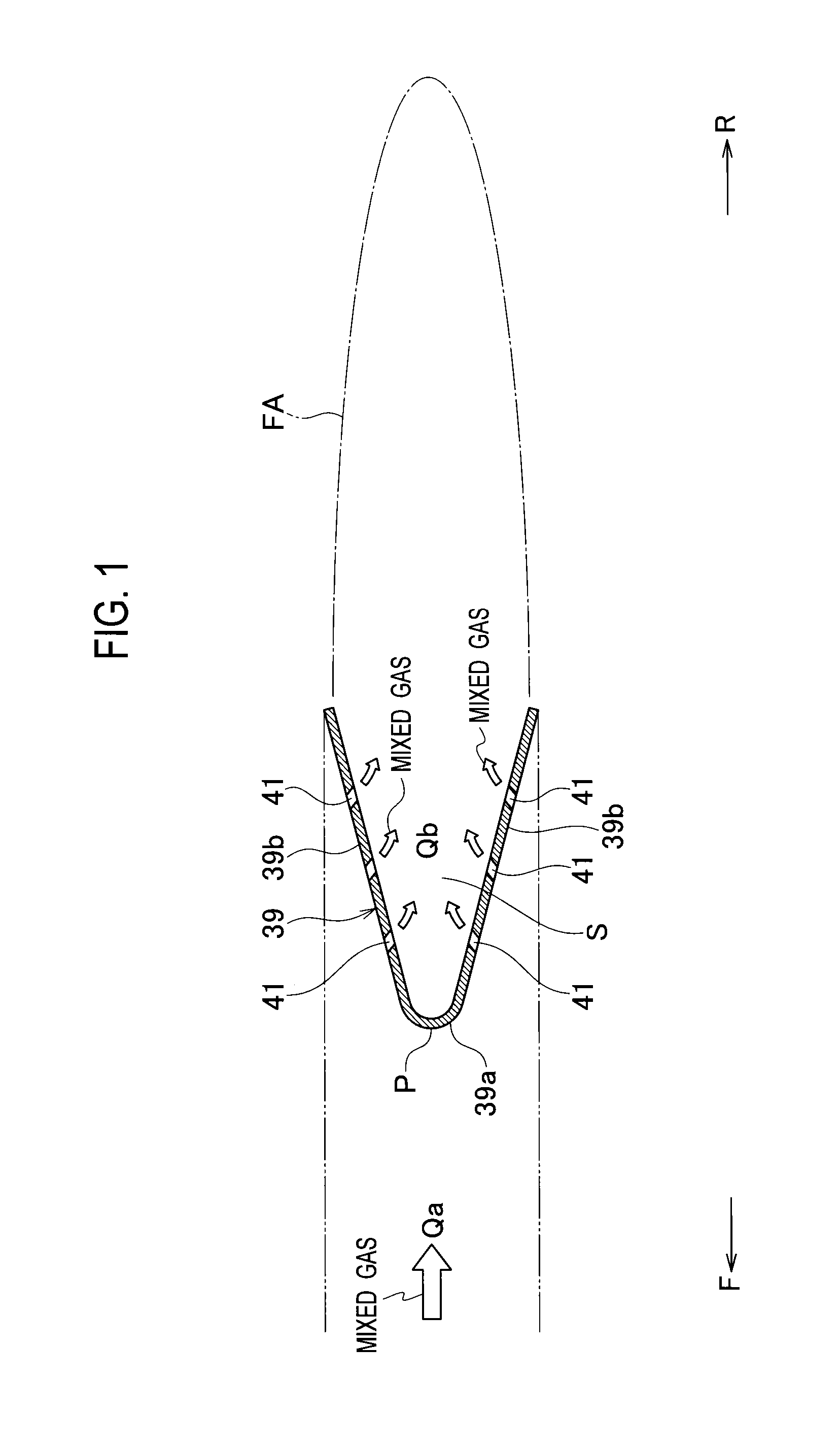
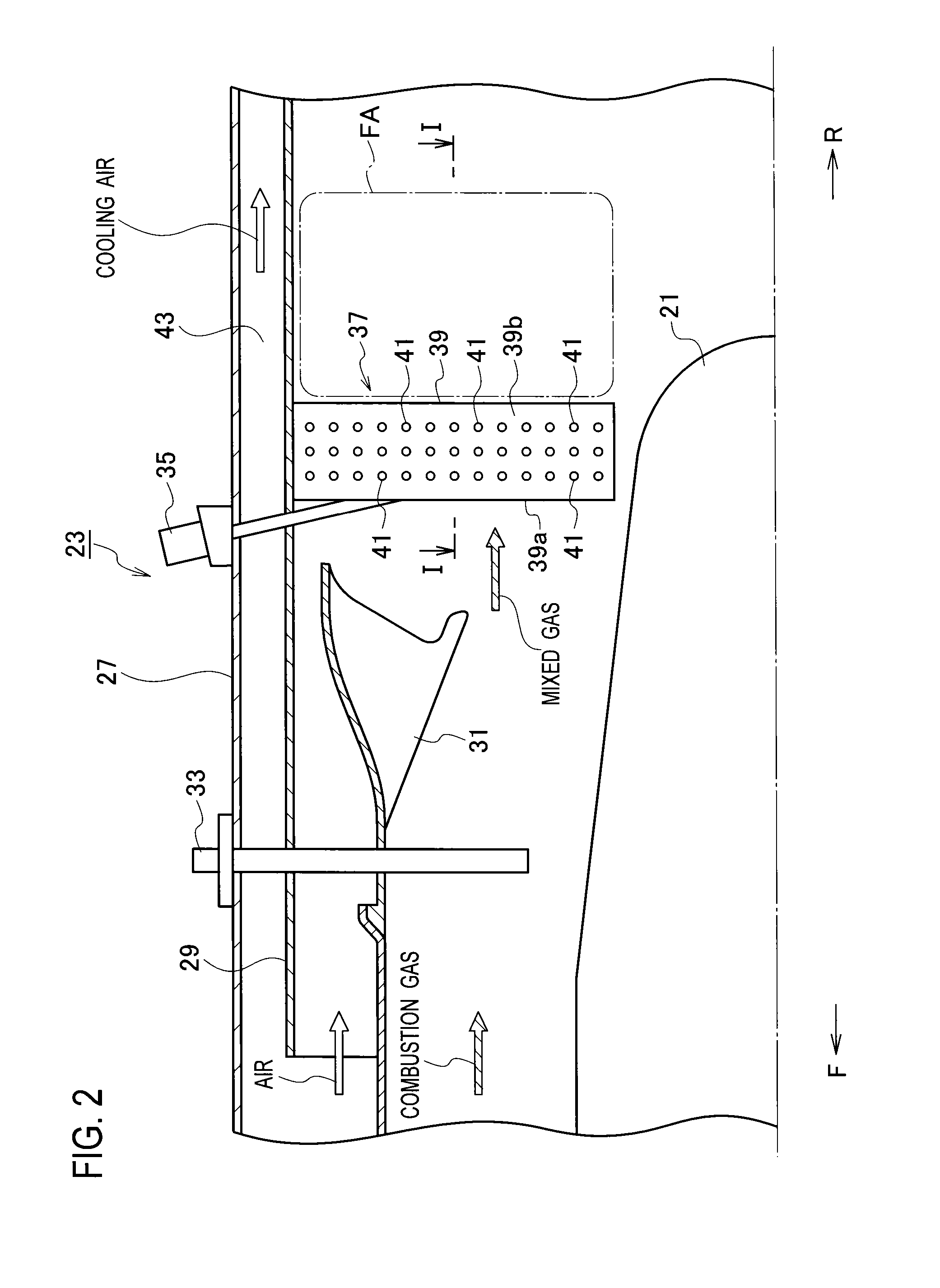
InactiveUS20140360197A1Reduce total pressure lossIncrease thrustContinuous combustion chamberJet propulsion plantsStagnation pointEngineering
An aircraft engine includes an afterburner which has a flame stabilizer. The flame stabilizer maintains a flame generated from a mixed gas of a combustion gas and air. The flame stabilizer includes multiple gutters each configured to generate a flame stabilization area for the flame on its downstream side. Each gutter is formed from: a curved apex section having a stagnation point; and flat plate-shaped side surface sections integrally formed on the respective two sides of the apex section. Each gutter has a V-shaped cross-sectional shape which is opened to the downstream side. At least one through-hole is formed only in each side surface section of each gutter.
Owner:IHI CORP
Unmanned aerial vehicle icing protection device
InactiveCN107985607AExtend your lifeImprove thermal performanceDe-icing equipmentsStagnation pointElectricity
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle icing protection device comprising wings, a heat conduction device and a heating device. The outer walls of the wings are covered with skins, and anti-icing cavities are formed in the wings. The heat conduction device comprises an engine compressor, a flow limiter, a one-way valve and anti-icing valves, and the anti-icing valves are arranged on the wings. The heating device comprises icing sensors, electric heating layers and pulse devices which are connected sequentially. According to the unmanned aerial vehicle icing protection device, heatof an engine and the electric heating and pulse devices are mixed for deicing, the advantages of the heat of the engine and the electric heating and pulse devices are combined, a good icing protection effect is formed, namely it is guaranteed that no ice layer exists nearby important parts such as stagnation points at the front edges of the wings, damage of icing to the aerodynamic shape of a vehicle is also reduced, and the power consumption of the vehicle is reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
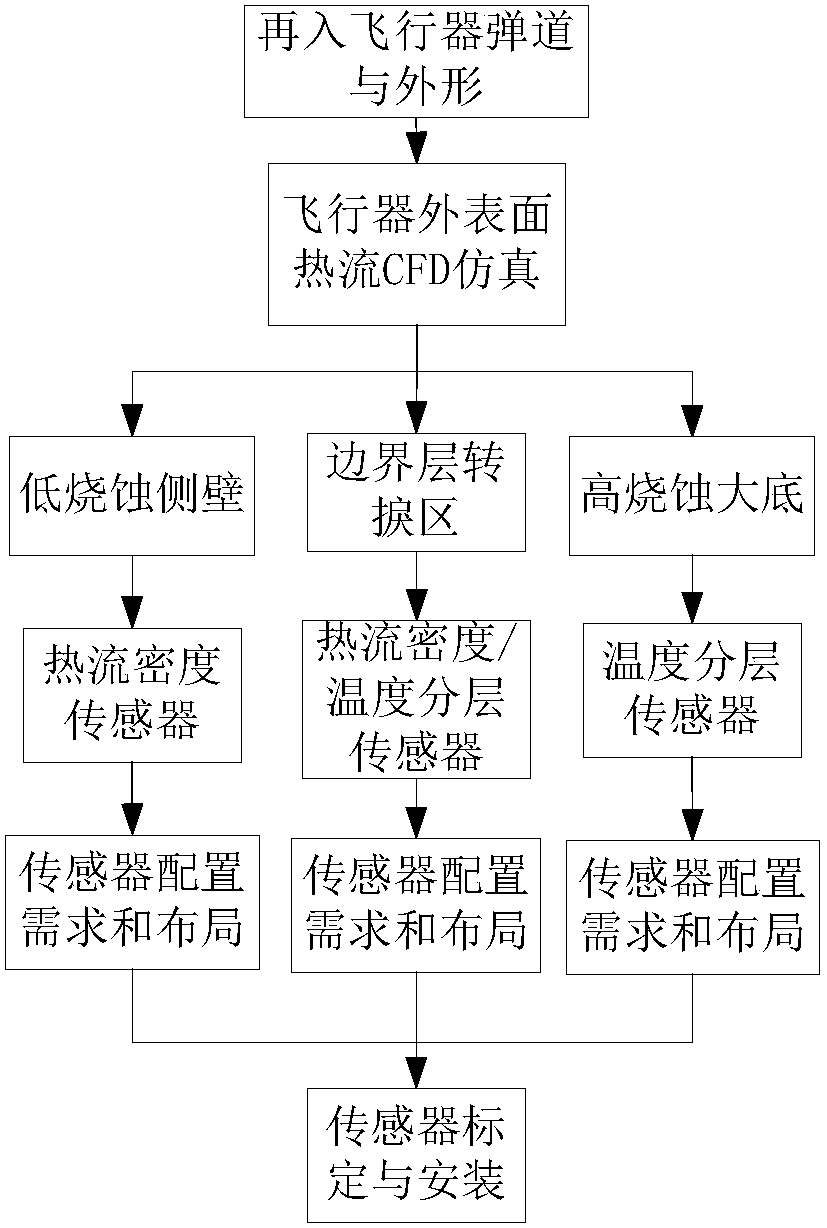
Aerodynamic heat measuring method suitable for blunt body reentry vehicle
InactiveCN108216685ATrue reentry heat flow loadGeometric CADSustainable transportationStagnation pointHeat flow
The invention provides an aerodynamic heat measuring method suitable for a blunt body reentry vehicle. The aerodynamic heat measuring method is used for measuring of surface heat flow distribution ofthe side walls, the large bottom, the stagnation point area and the boundary layer transition area of the blunt body reentry vehicle and measuring of total heating capacity of the windward side and the leeward side. The aerodynamic heat measuring method comprises the following steps that according to the appearance and a reentry trajectory of the blunt body reentry vehicle, simulation analysis onaerodynamic heat load on the surface of the blunt body reentry vehicle is conducted; according to the sizes and distribution of aerodynamic heating heat flows, sensor selecting and measuring range determining are conducted; according to the aerodynamic heat measuring task requirement of the blunt body reentry vehicle, configuration demand analysis of sensors is conducted; sensor layout design is conducted; and sensor calibration and mounting are conducted. According to the aerodynamic heat measuring method, the real reentry heat flow load can be obtained, particularly, real-time data of transition of the boundary layer on the surface of the vehicle can be provided, and guiding significance is achieved on a current calculating analysis model and the ground test technical scheme.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Soiling shield for wind turbine blade
A soiling shield (80) affixed to a blade airfoil (22) of a wind turbine generator (20). The soiling shield (80) includes a portion extending along and spaced apart from a pressure side surface (88) of the blade airfoil (22). The soiling shield (80) is positioned not to impede an air flow stream (98) flowing to a stagnation point (130) on the pressure side surface (88) during operation of the wind turbine generator (20) at or below rated power.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com