Streamline-based microfluidic device
a microfluidic device and streamline technology, applied in the direction of positive displacement liquid engine, laboratory glassware, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to separate all, pore clogging or membrane fouling may be an issue, and the separation becomes difficul
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
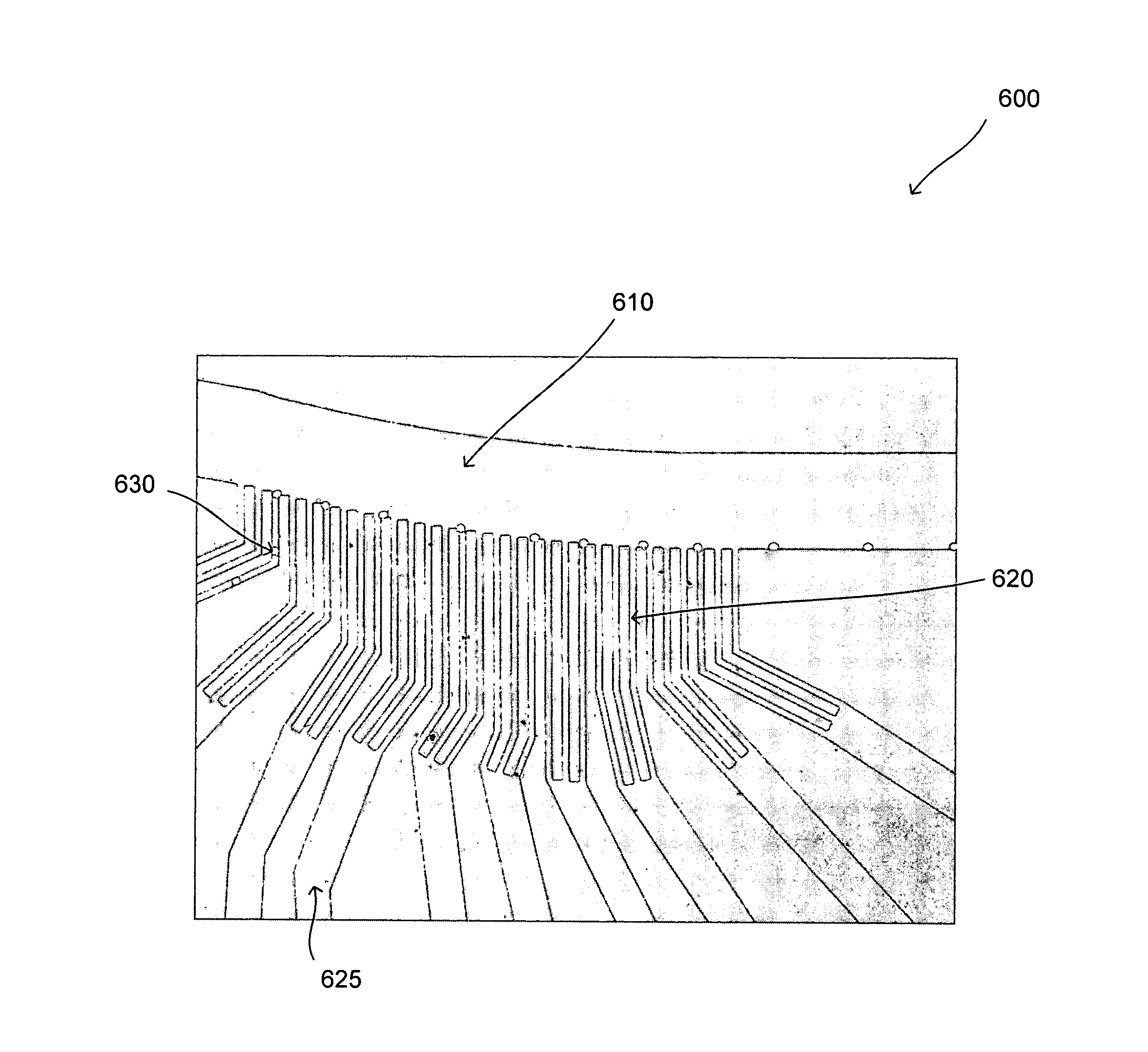
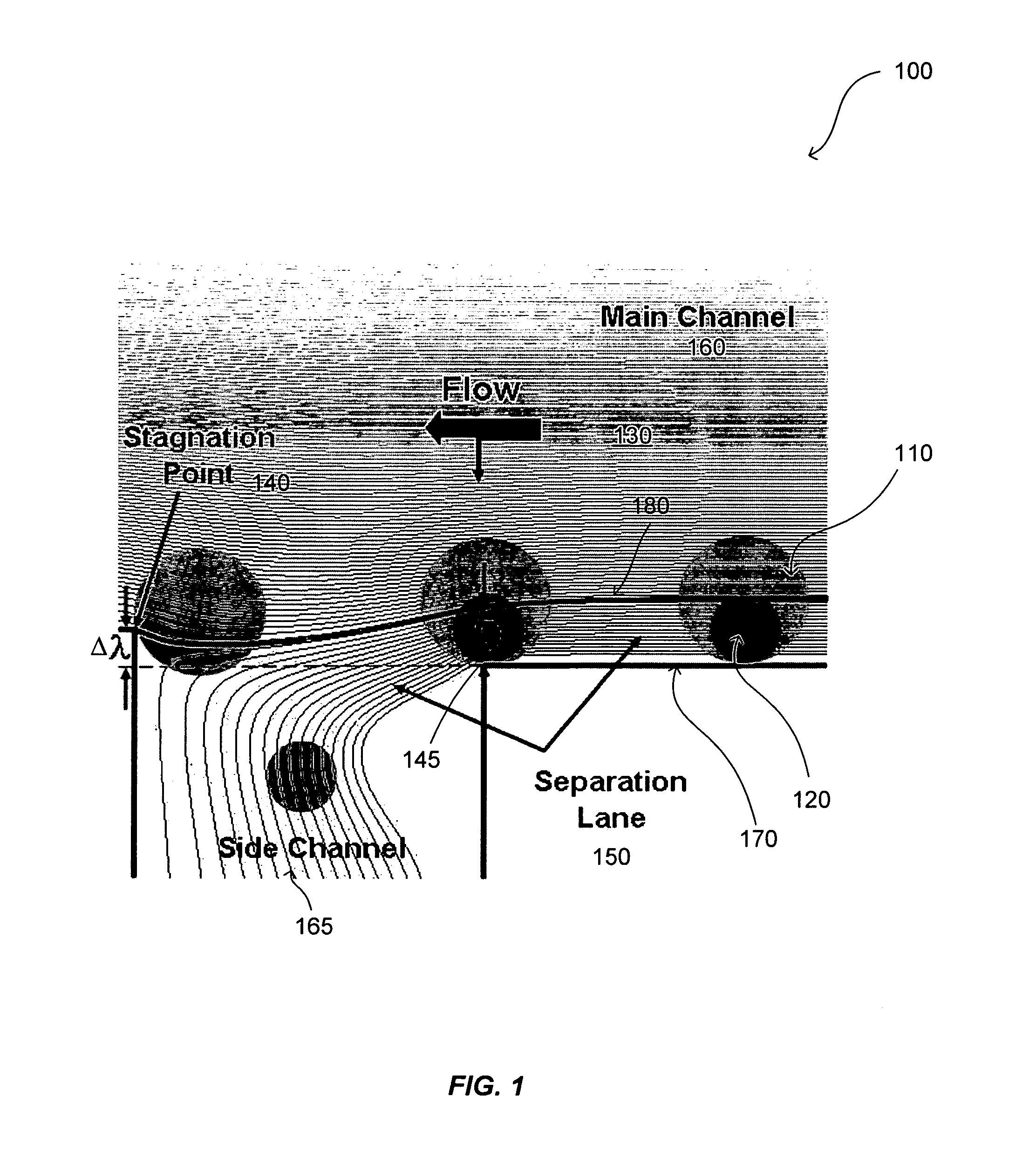
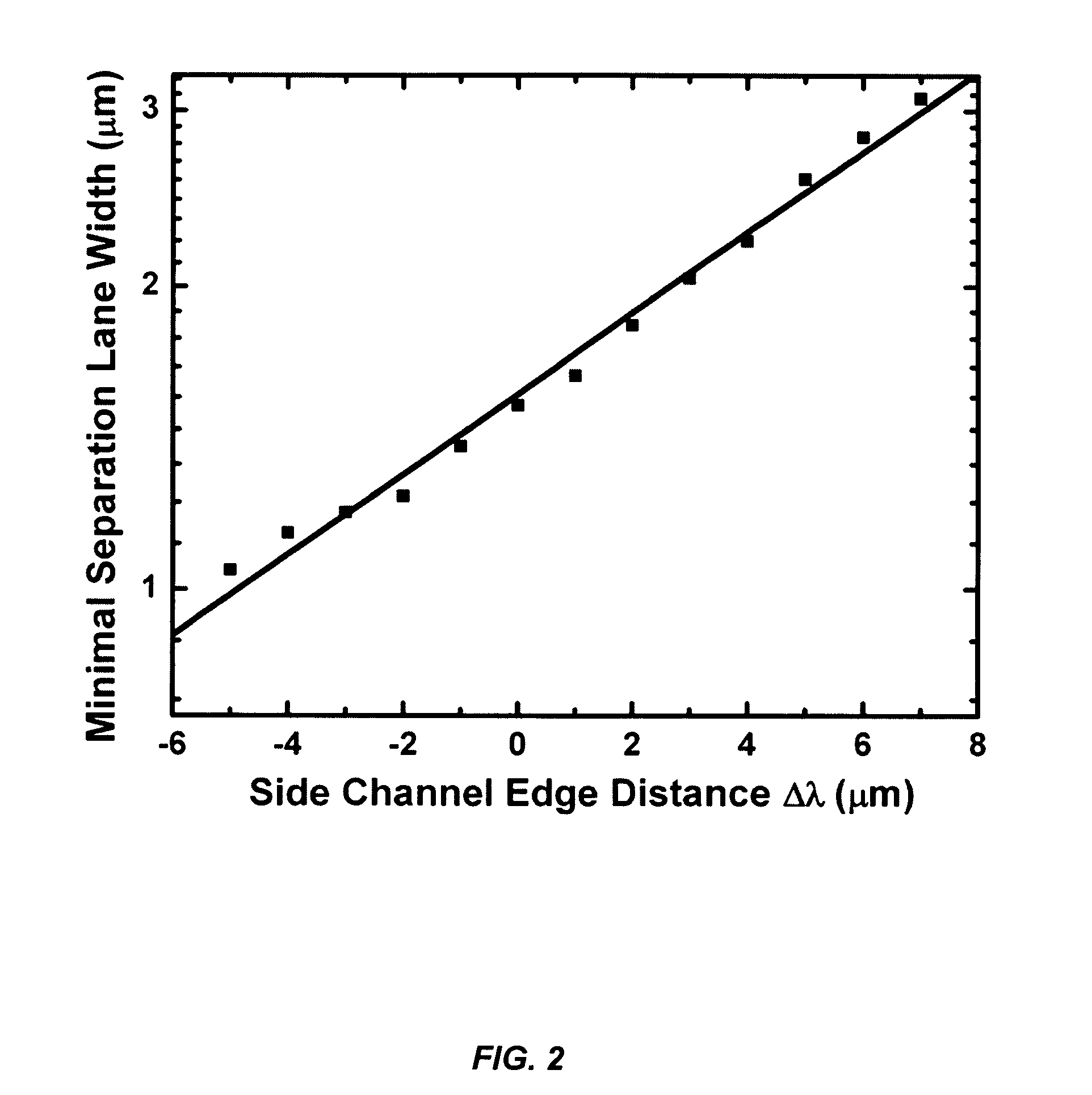
[0023]The present invention provides a novel streamline-based microfluidic device and a method of using such a device for continuous separation of particles of various sizes. The device is especially useful for the separation of erythrocytes from leukocytes in the blood. In certain instances, the present invention provides a system, which does not require moving parts, and thus it is desirable for integration with other kinds of micro unit operation for other treatment, analysis and utilization. The present invention demonstrates a high separation efficiency, an ease of operation, capability of simultaneous particle concentration and size dependent separation and elimination of channel clogging. Advantageously, the microfluidic device can have a tailored design with a tunable capability to allow easy and accurate manipulation of particles of various sizes found in biological, ecological and industrial environments, especially in the separation of particles and cells in the blood to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com