A method for implementing bandwidth sharing architecture of virtual user ring network
A technology of bandwidth sharing and virtual users, applied in the direction of ring network, transmission system, digital transmission system, etc., can solve the problems of wasting bandwidth resources, unable to make full use of ring bandwidth resources, lack of ring network fairness algorithm, etc., to improve network bandwidth The effect of usage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0019] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
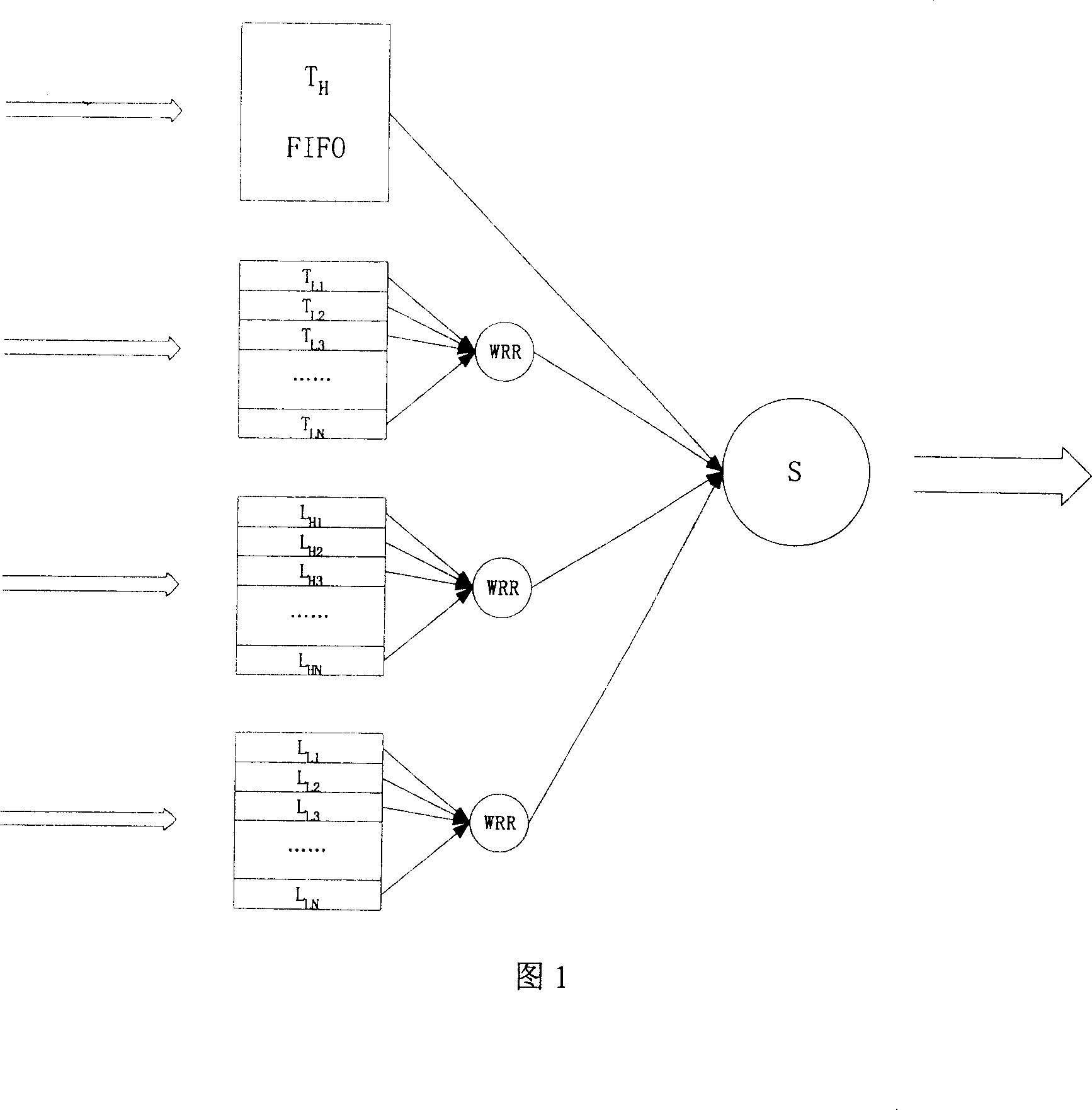
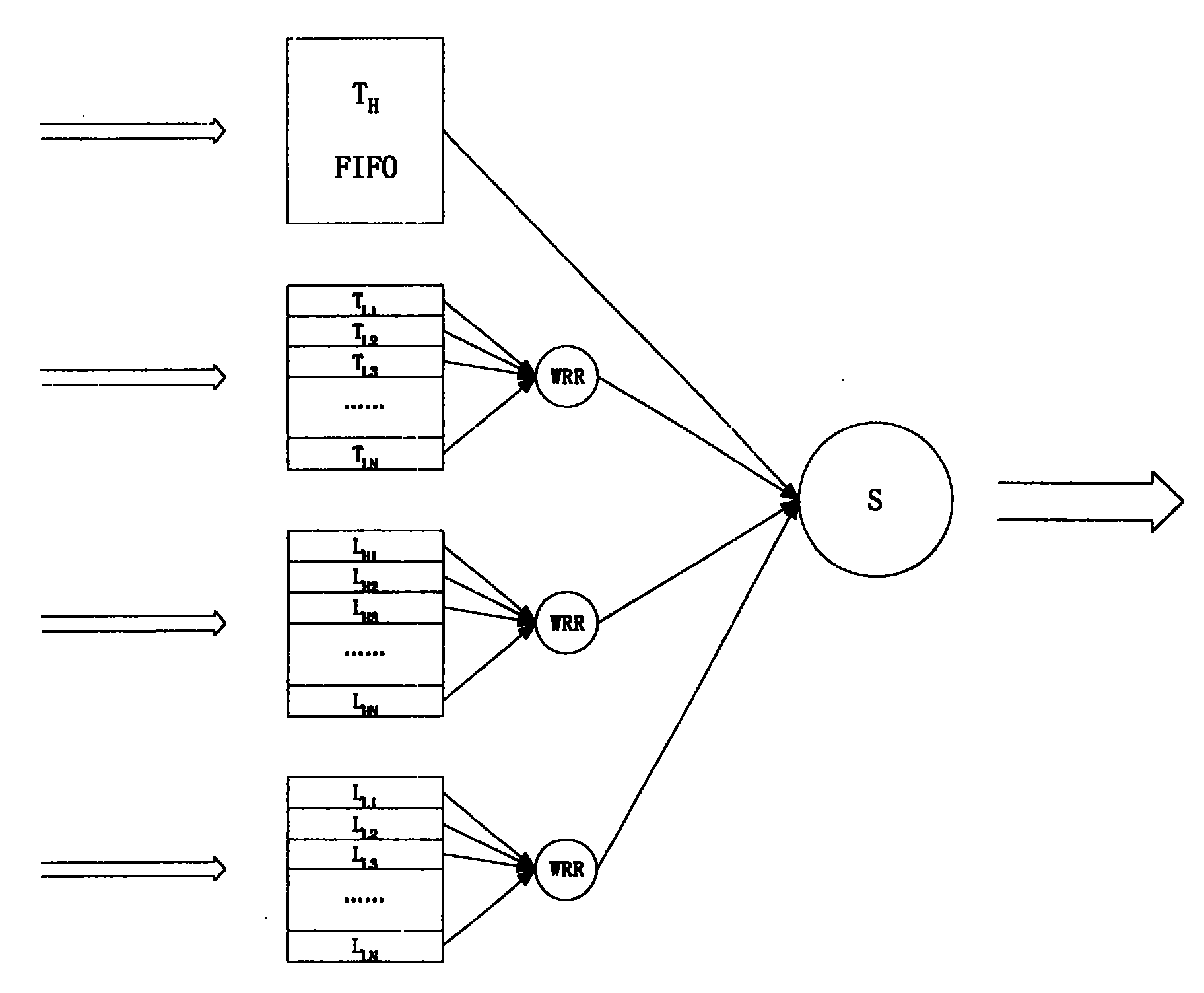
[0020] Figure 1 shows a queue scheduling block diagram of a node. Among them, T H Indicates forwarding high-priority packets, T L Indicates forwarding low-priority packets, L H Indicates local high-priority packets, L L Indicates local low-priority packets.
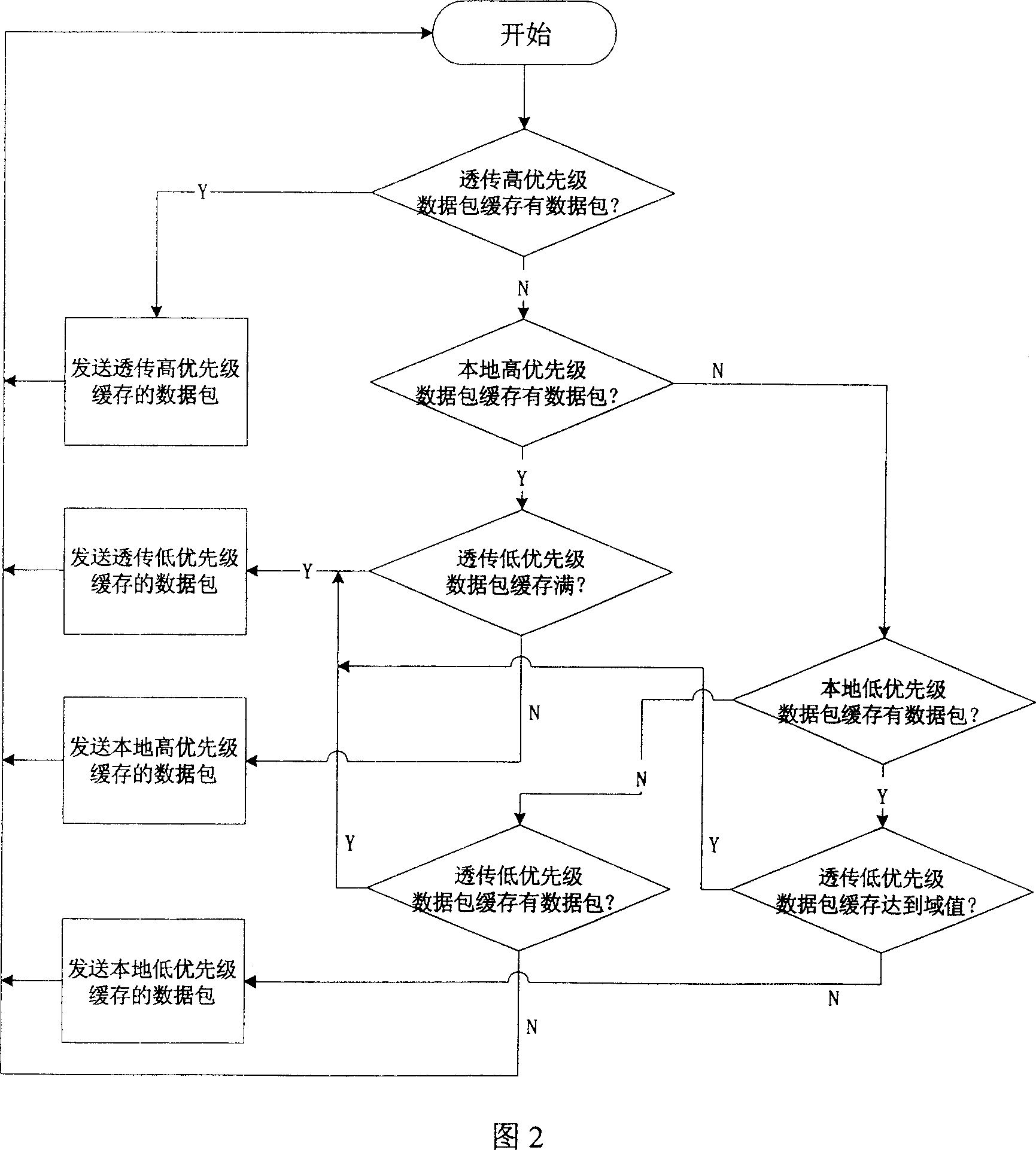
[0021] FIG. 2 shows a flow chart of a node's sending message processing.
[0022] In Figure 1, each station has four types of queues: forwarding high-priority message queues, forwarding low-priority message queues, local high-priority message queues, and local low-priority message queues. Each type of queue is subdivided according to the user (except for the forwarded high-priority message queue, because it can be sent out quickly). Firstly, weighted round-robin scheduling is performed on each type of queue, and then fair scheduling is performed on the four types of queues.
[0023] FIG. 2 is a flow chart of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com