A downlink service resource allocation method and radio network controller
An allocation method and technology for business resources, applied in the field of supporting mobile communications, and can solve problems such as decreased user experience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
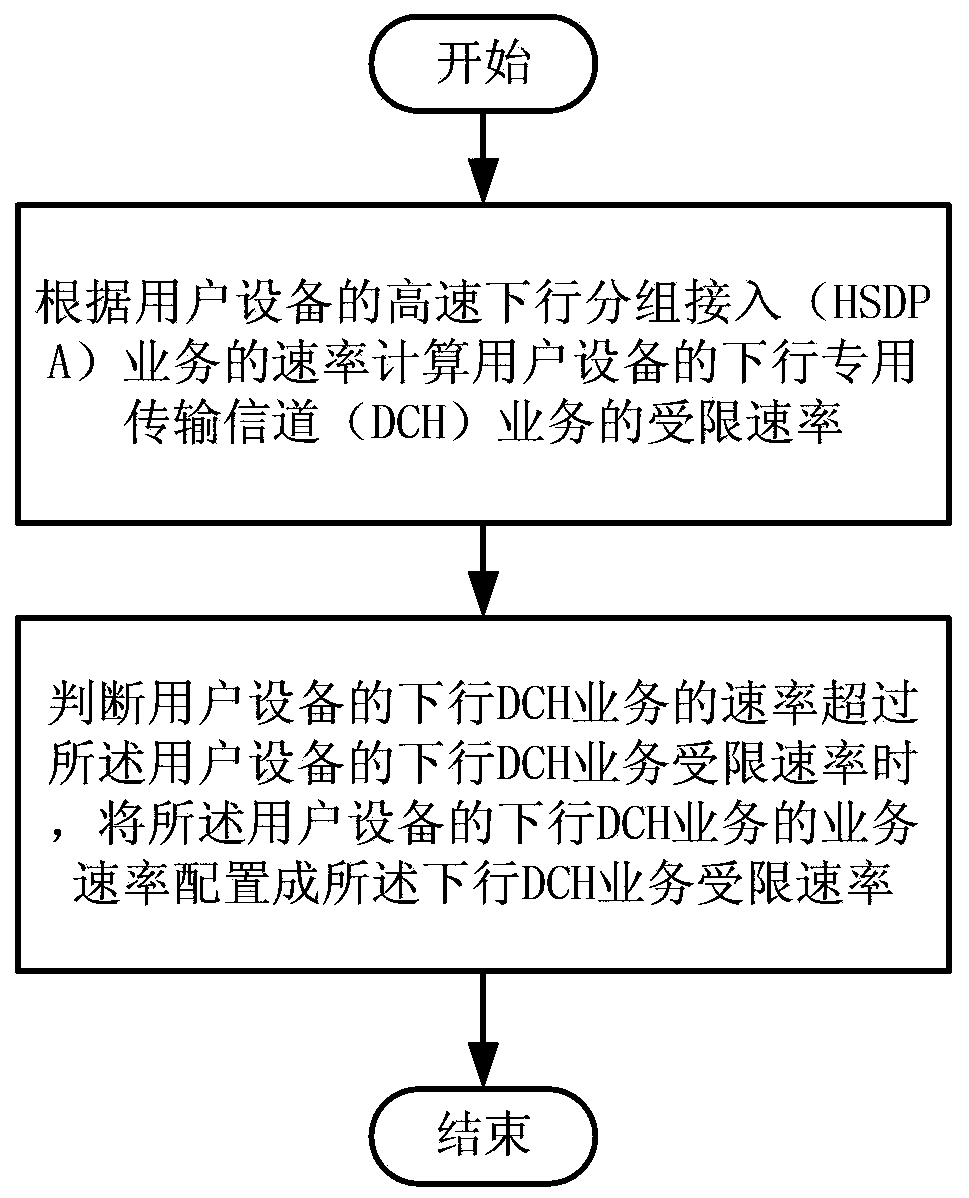
[0072] For the allocation of code resources in this specific embodiment, this solution is implemented on the RNC, and the RNC controls the HS-DPSCH code resources.
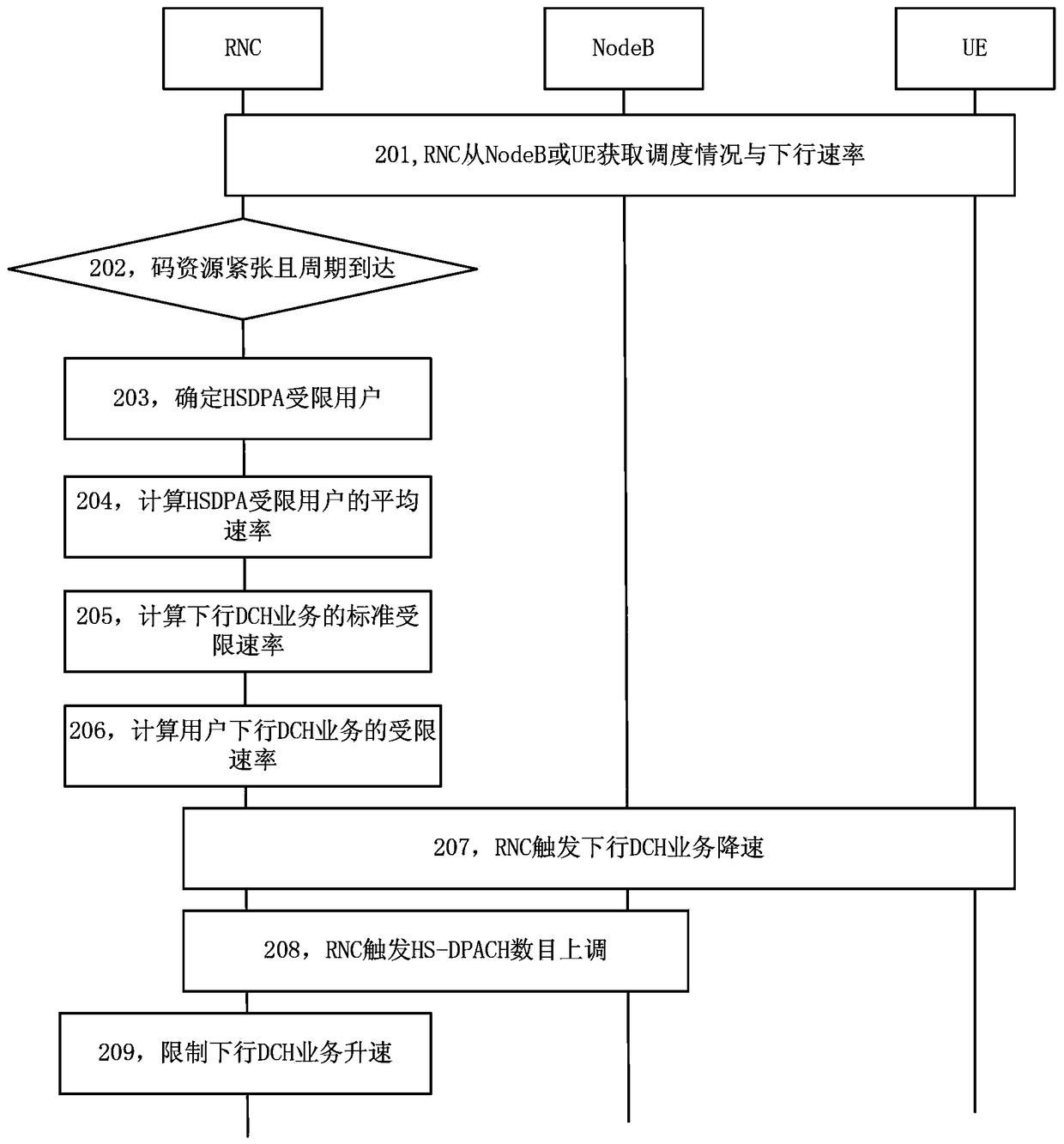
[0073] Such as figure 2 As shown, the resource allocation method includes steps 201 to 209.
[0074] In step 201, the RNC obtains the scheduling situation and downlink rate from the NodeB or UE, and the RNC records them for data preparation for subsequent decisions.
[0075] Step 202, when the RNC judges that code resources are insufficient and the set fairness algorithm judgment period is reached, the RNC is triggered to make a series of subsequent judgments.
[0076] Step 203, RNC traverses all UEs in the cell, compares the scheduling situation and downlink rate with the maximum contracted rate and UE capability, and determines whether the UE is an HSDPA restricted user.
[0077] Step 204, the RNC calculates the average rate of the HSDPA restricted users on the cell.
[0078] In step 205, the RNC obtains the...
specific Embodiment 2
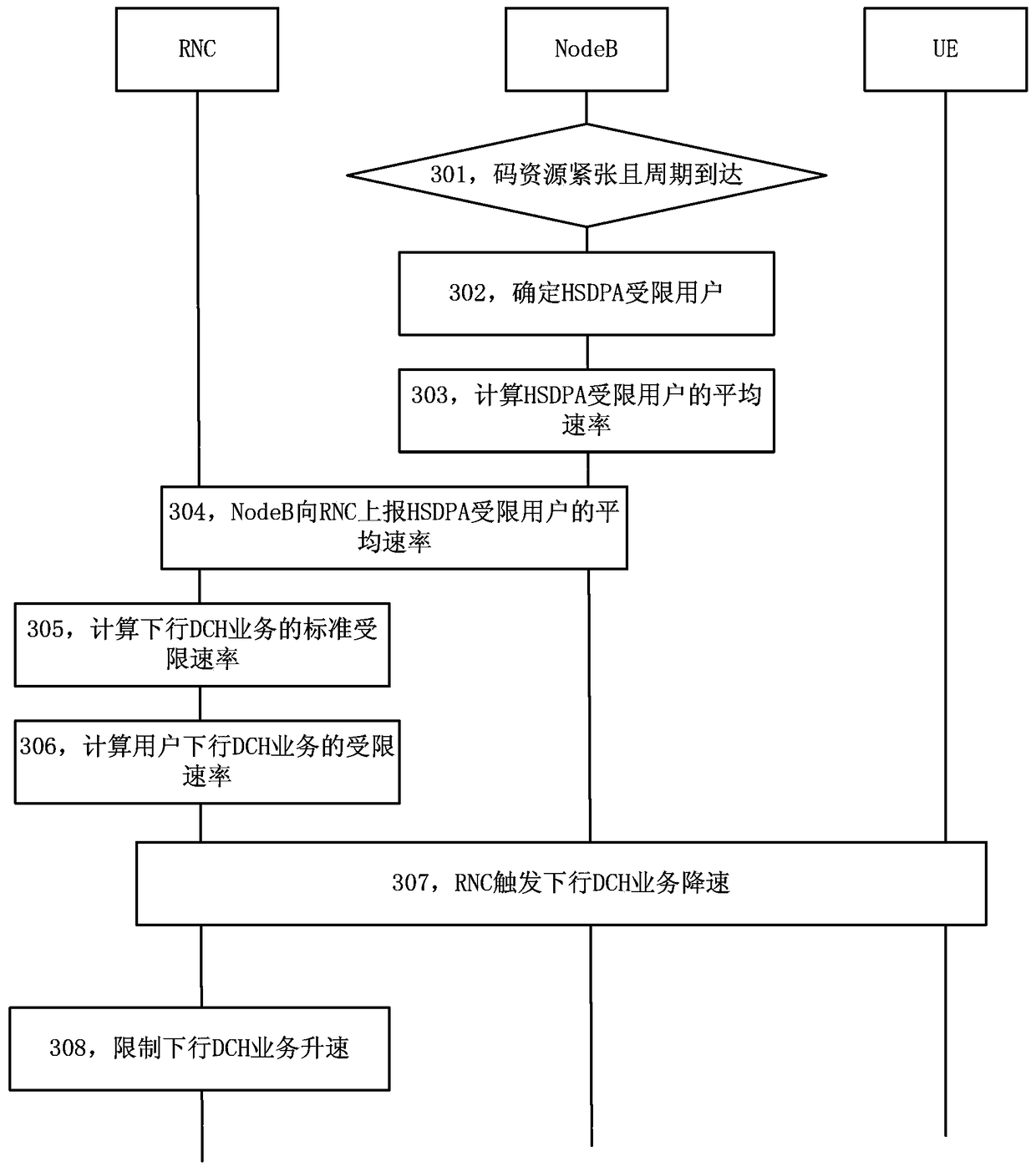
[0085] For the allocation of code resources in this specific embodiment, this solution is implemented on the NodeB, and the NodeB controls the HS-DPSCH code resources.
[0086] Such as image 3 As shown, the resource allocation method includes steps 301 to 308.
[0087] In step 301, when the NodeB determines that the code resource is insufficient and the set fairness algorithm judgment period is reached, the NodeB is triggered to perform a series of subsequent judgments.
[0088] In step 302, the NodeB traverses all UEs in the cell, and determines whether the UE is an HSDPA restricted user according to the scheduling situation.
[0089] In step 303, the NodeB calculates the average rate of the HSDPA-restricted users on the cell.
[0090] In step 304, the NodeB reports the average rate of the HSDPA-restricted users on the cell to the RNC.
[0091]In step 305, the RNC obtains the standard restricted rate of the downlink DCH service of the cell according to the rate level mapp...
specific Embodiment 3
[0095] For the allocation of power resources in this specific embodiment, this solution is implemented on the RNC, and the HS-DPSCH code resources are controlled by the RNC.
[0096] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the resource allocation method includes steps 401 to 409 .
[0097] In step 401, the RNC obtains the scheduling situation and downlink rate from the NodeB or UE, and the RNC records them for data preparation for subsequent decisions.
[0098] Step 402, when the fairness algorithm decision period set by the RNC arrives, the RNC is triggered to make a series of subsequent decisions.
[0099] Steps 403 to 407 are the same as steps 203 to 207.
[0100] In step 408, the RNC uses the power resources vacated by the UE's speed reduction to trigger an increase in the maximum allowable transmission power of HSDPA.
[0101] Step 409, when the UE's packet service is initially established on the downlink DCH, or when the rate of the downlink DCH service is dynamically adjusted, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com