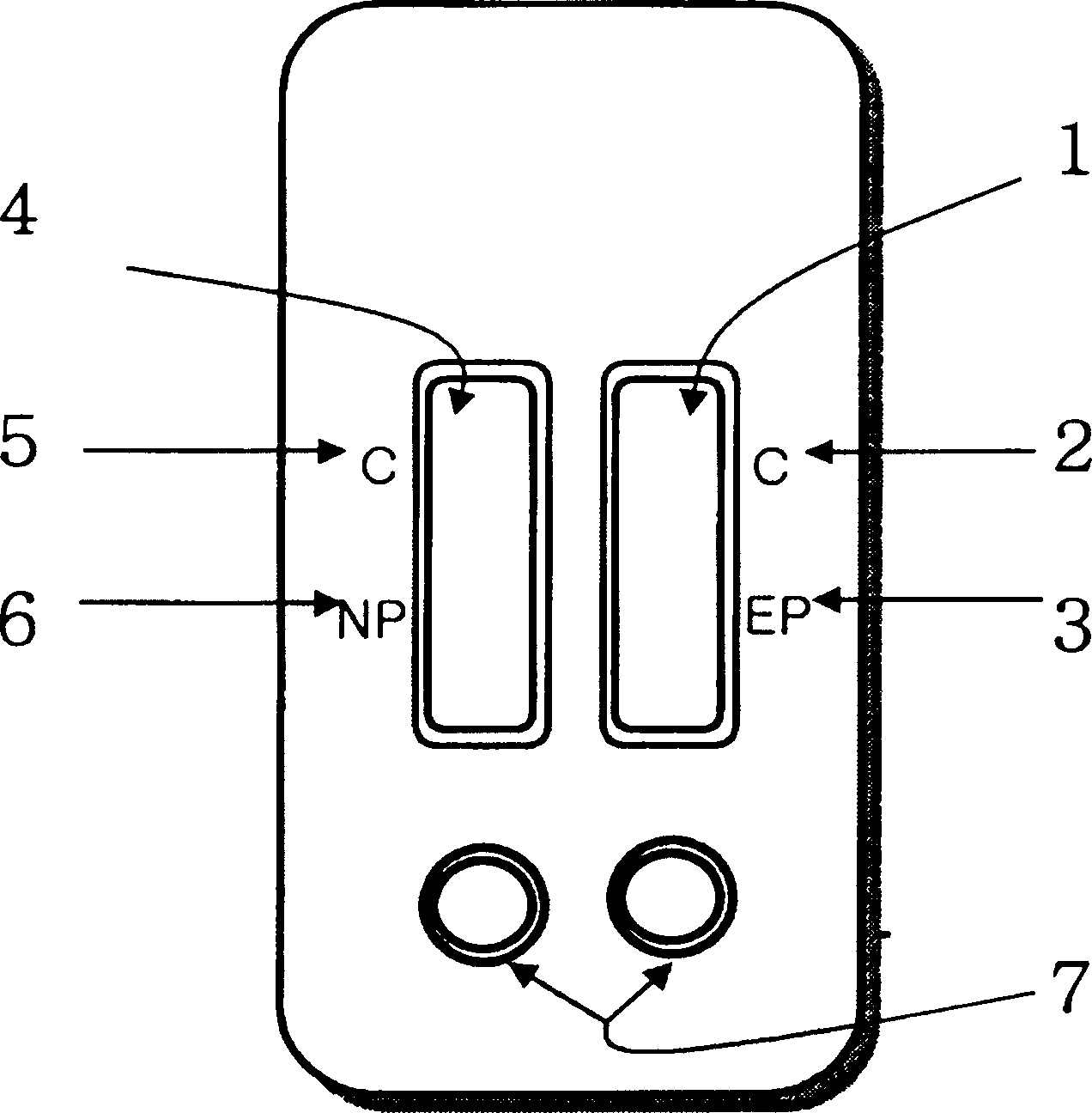
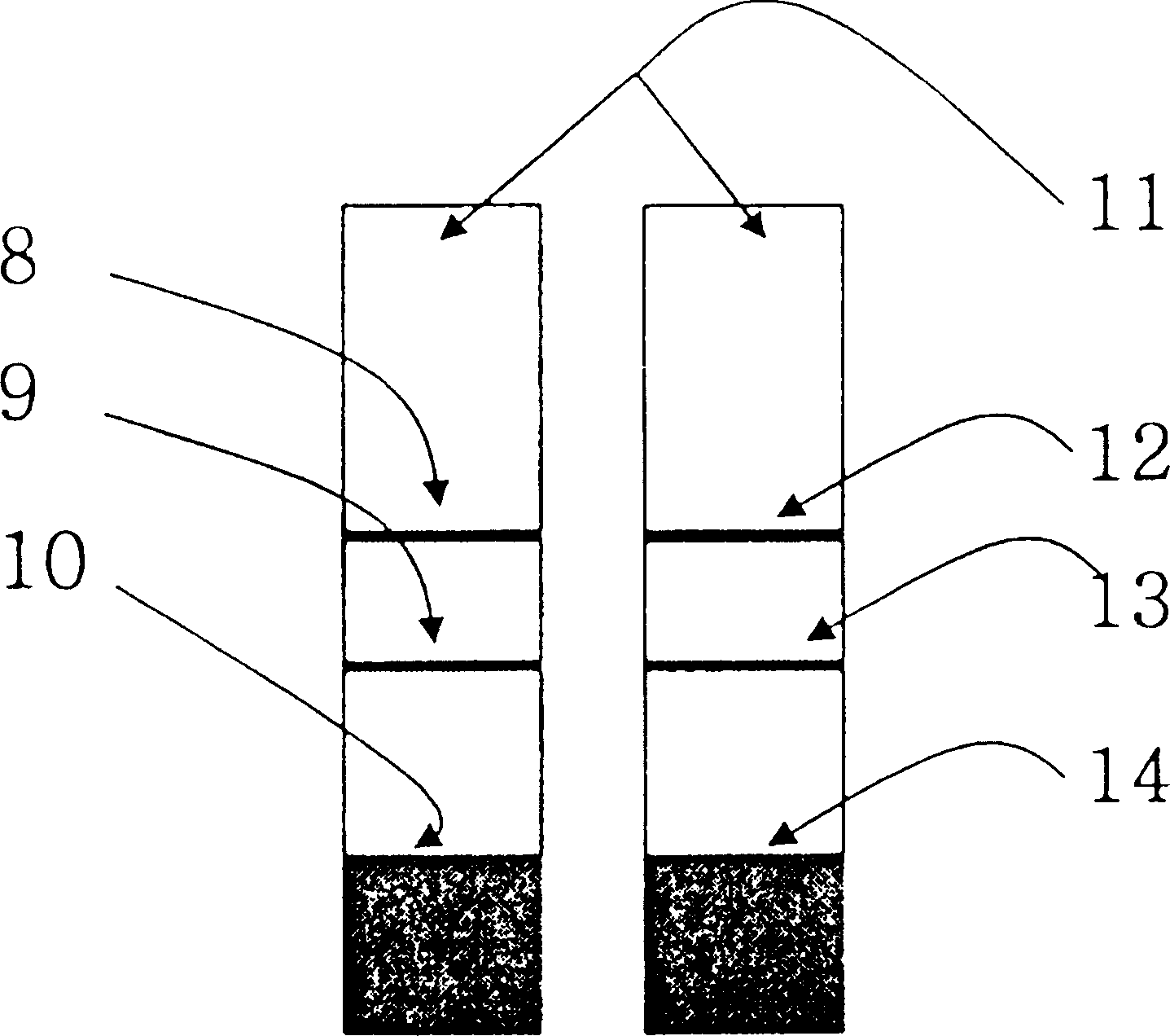
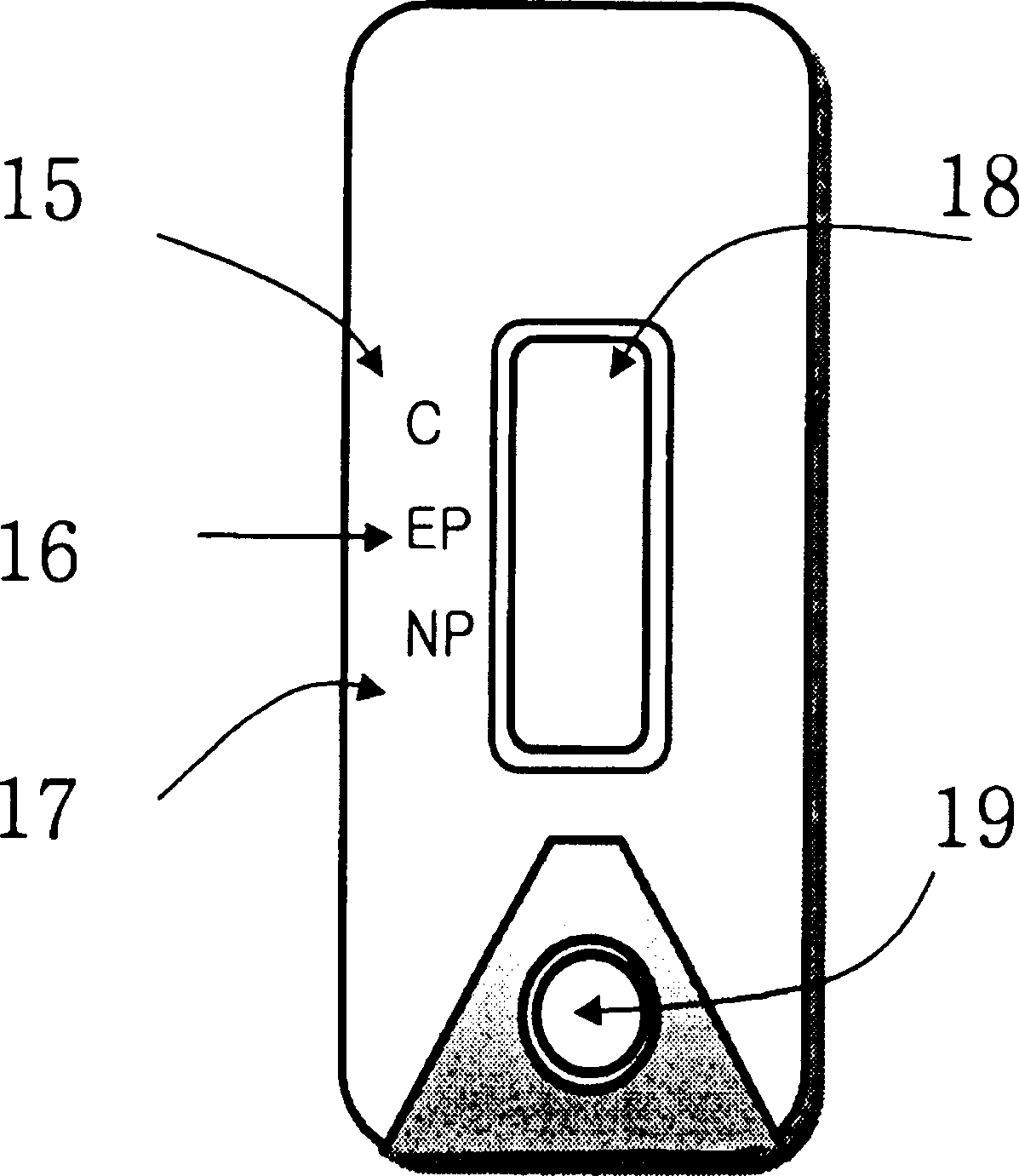
Diagnostic device for distingushing between normal and ectopic pregnancy and method for preparing the same
A technology for pregnancy diagnosis and ectopic pregnancy, which is applied in the direction of diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and measuring devices, and can solve the problems of difficult access and effective early identification of pregnant women's risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] the scope of the invention. Example 1: Preparation and Purification of Anti-I-hCG Monoclonal Antibody and Anti-α-hCG Monoclonal Antibody A: Immunization and Cell Fusion
[0032] The known cell fusion procedure (Galfre, G et al., 1981, Methods Enzymol. 73:3-46) was used to prepare monoclonal antibodies against I-hCG. First, 20 μg / 100 μl of I-hCG (Zymed, USA) was well emulsified with 100 μl of complete Freund's adjuvant and injected intraperitoneally into Balb / C mice (8 weeks). After 3 weeks, a second intraperitoneal injection was performed under the same protocol as the first injection, except for emulsification with 100 μl of Freund's incomplete adjuvant. After 1 week, blood samples were collected from the mice and antibody formation was determined by ELISA, after which 20 μg hCG was injected into the tail vein. After 3 days, splenocytes were recovered from the mice and subjected to cell fusion with pre-cultured Sp2 / O cells and PEG. Confluent cells were cultured in 9...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Splenocytes were obtained from mice that had previously been immunized three times with β-hCG antigen purchased from Zymed according to the same procedure as in Example 1, A. These cells were mixed with Sp2 / O cells and PEG was used for cell fusion. Confluent cells were cultured in 96-well plates supplemented with HAT medium. Next, cells secreting antibodies reactive to β-hCG and cells secreting antibodies reactive to modified hCGs but not to intact hCG were selected and cultured on a large scale. Next, the monoclonal antibody was purified from the large-scale culture according to the same purification procedure as in Example 1, B, dialyzed with phosphate buffer, adjusted for concentration, and then used for the preparation of a diagnostic kit. Embodiment 3: the preparation of colloidal gold (colored particle)
Embodiment 3
[0035]Colloidal gold with a particle diameter of 20 to 60 nm is used as the colored particles. To prepare colloidal gold, add 220 ml of double distilled water to a 500 ml round bottom flask. The flask was then placed on a hot plate (Corning, USA) and fitted with a reflux device (Pyrex, USA) to prevent evaporation of water. Turn on the hot plate to heat the suspended flask to 100 °C. When the temperature of the distilled water exceeded 100°C, 1.0 ml of 2% gold chloride (Sigma, USA) was added with mixing, followed by 2.0 ml of 1% sodium citrate (Sigma, USA). Continue heating for 30 minutes to produce colloidal gold. The colloidal gold thus obtained was filtered on 0.45 μm filter paper to remove impurities and aggregates, and then used in the preparation of diagnostic devices. Example 4: Preparation of Pads of Colored Particles Incorporating Colored Particles to which Monoclonal Antibodies are Binded
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com