Fast mode decision making for interframe encoding
A technology of coding mode and intra-frame mode, applied in the field of fast mode determination of inter-frame coding, which can solve problems such as increasing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
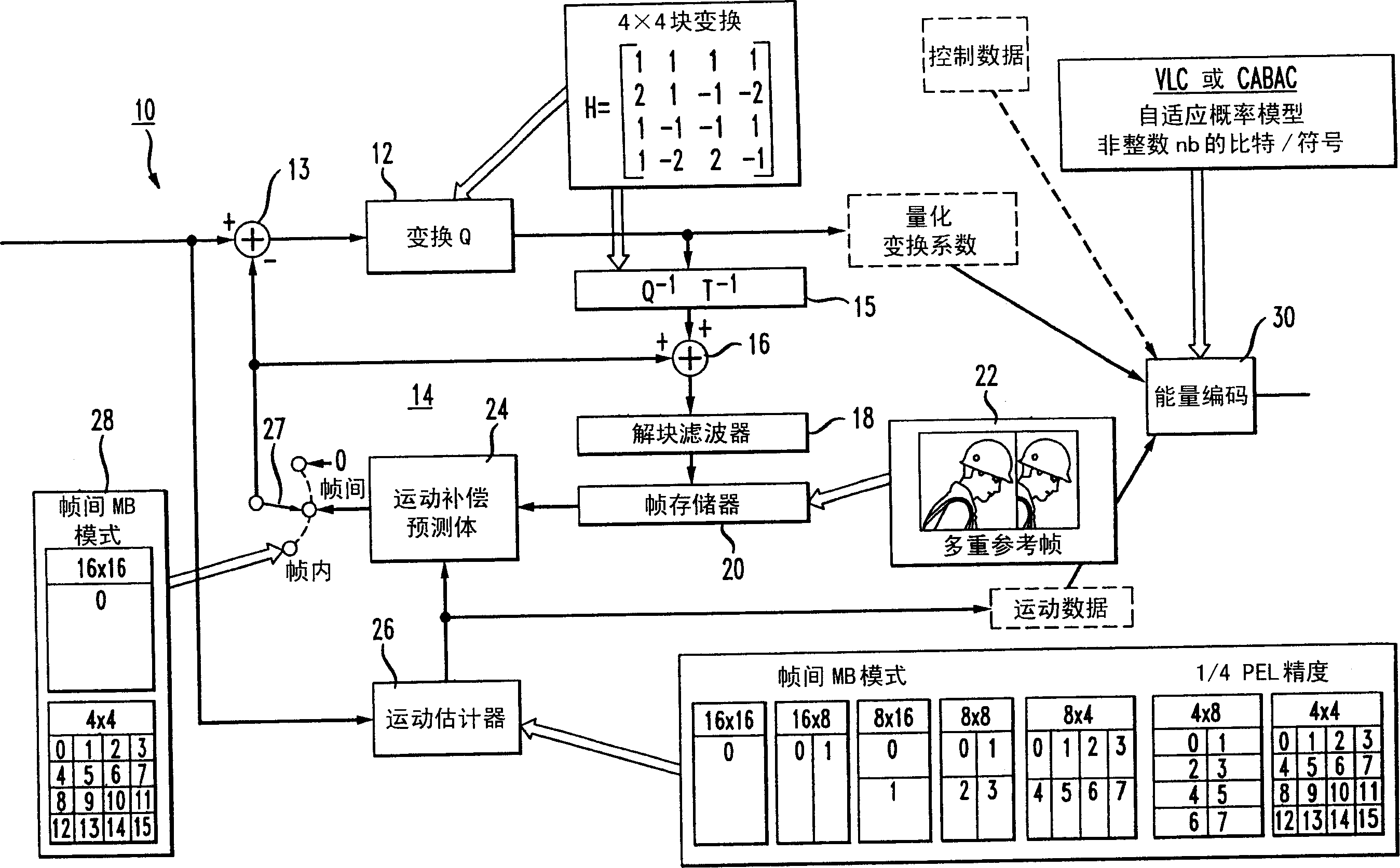
[0010] To better understand the encoding method of this principle, refer to figure 1 , figure 1 A block diagram showing the structure of a typical JVT encoder 10 for encoding an input video stream. The encoder 10 comprises a first block 12 for receiving at its positive input the output of a difference block 13 to which input video frames from a video source (not shown) are supplied. Block 12 quantizes each video frame received from difference block 13 and then performs a block transform to produce a quantized frame and a corresponding set of transform coefficients.
[0011] Loop 14 feeds back each quantized frame output by block 12 and the corresponding transform coefficients to enable the formation of predicted frames (P or B frames). The loop 14 comprises a block 15 which performs inverse quantization and inverse transformation respectively on the quantized frame and transform coefficients from block 12 to be received at a first input of a summation block 16 whose output i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com