Threshold on unblocking a processing node that is blocked due to data packet passing
A technology of threshold and count value, applied in the threshold field of unblocking processing nodes blocked due to data packet transmission, which can solve problems such as deadlocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
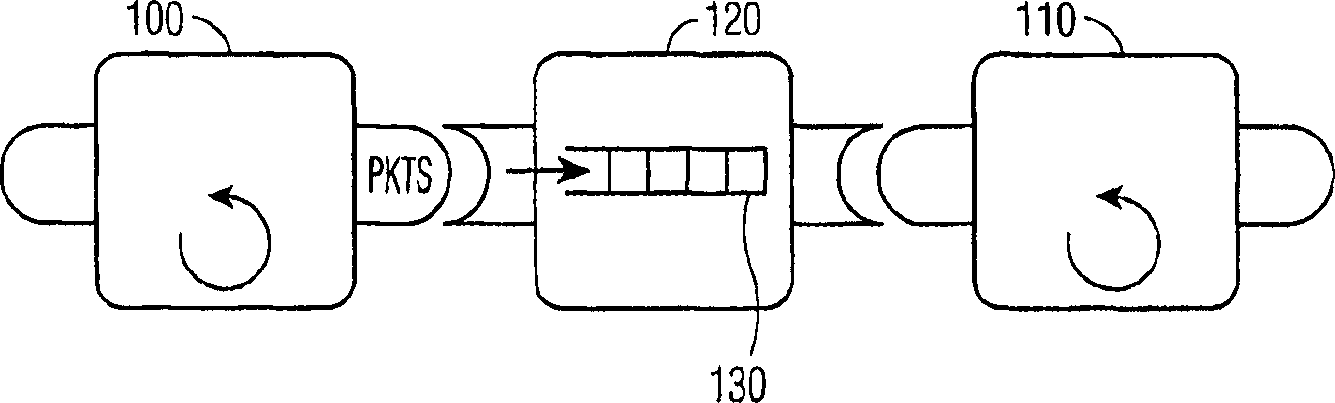
[0028] The system and method of the present invention reduce the number of environment switches that are the result of passing packets to higher priority flow components in a system that has a preemptive priority based on a scheduler. The reduction in the number of environment switches generally results in better performance at the expense of increased latency.
[0029] In a preferred embodiment, the buffer threshold is a mechanism that delays the signaling of blocked consumer components until sufficient packets are available in the buffer, that is, the threshold amount of packets appears in the buffer, The blocked consumer component waits for the packet. When the threshold of the buffer is set to x, only when x packets are available in the buffer, the waiting, i.e. blocked component associated with that buffer is signaled.
[0030] figure 1 Illustrated are low-priority producer components 100 that are all located on the same processor and connected to high-priority consumer com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com