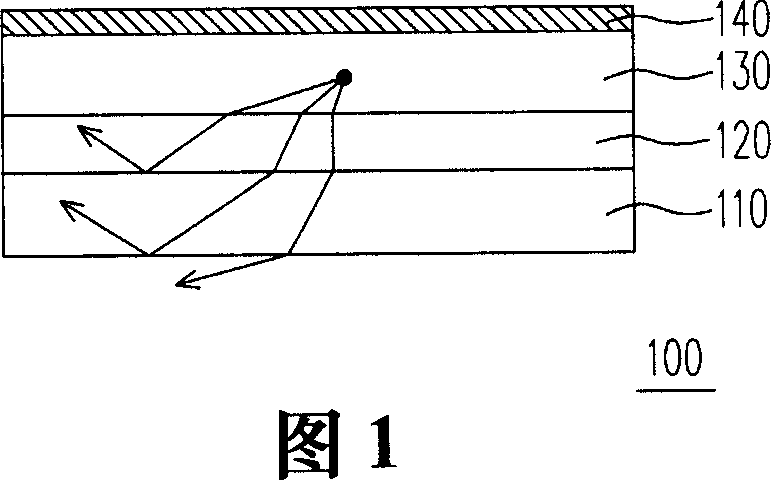
Organic electric luminous element
An electroluminescent element and luminescent technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electric solid devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low luminous efficiency, reflection or refraction, and inability to provide double-sided light emission of the light-emitting element 100
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
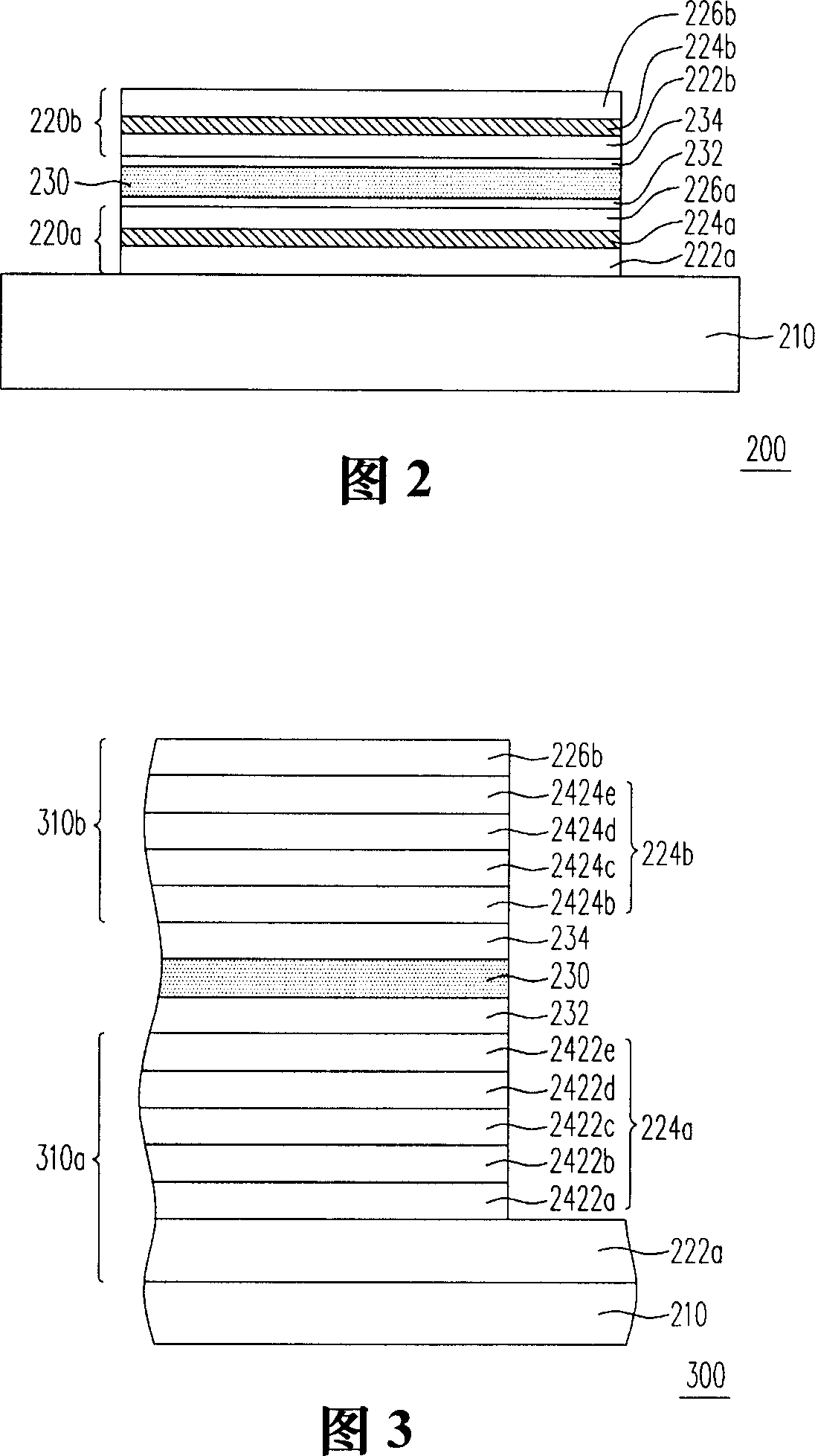
[0042] FIG. 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view of an organic electroluminescent device according to a first embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 2, the organic electroluminescent device 200 of this embodiment includes a transparent substrate 210, a plurality of organic electroluminescent units 220a, 220b and a reflective electrode layer 230, wherein these organic electroluminescent units 220a and 220b are stacked on the transparent substrate 210, and the reflective electrode layer 230 is disposed between the organic electroluminescence units 220a and 220b. In addition, the transparent substrate 210 is, for example, a glass substrate, a quartz substrate, a plastic substrate or a flexible substrate. In this embodiment, the organic electroluminescent element 200 further includes a first-type doped layer 232 and a second-type doped layer 234, and the reflective electrode layer 230 is disposed on the first-type doped layer 232 and the second-type doped layer. ...
no. 2 example
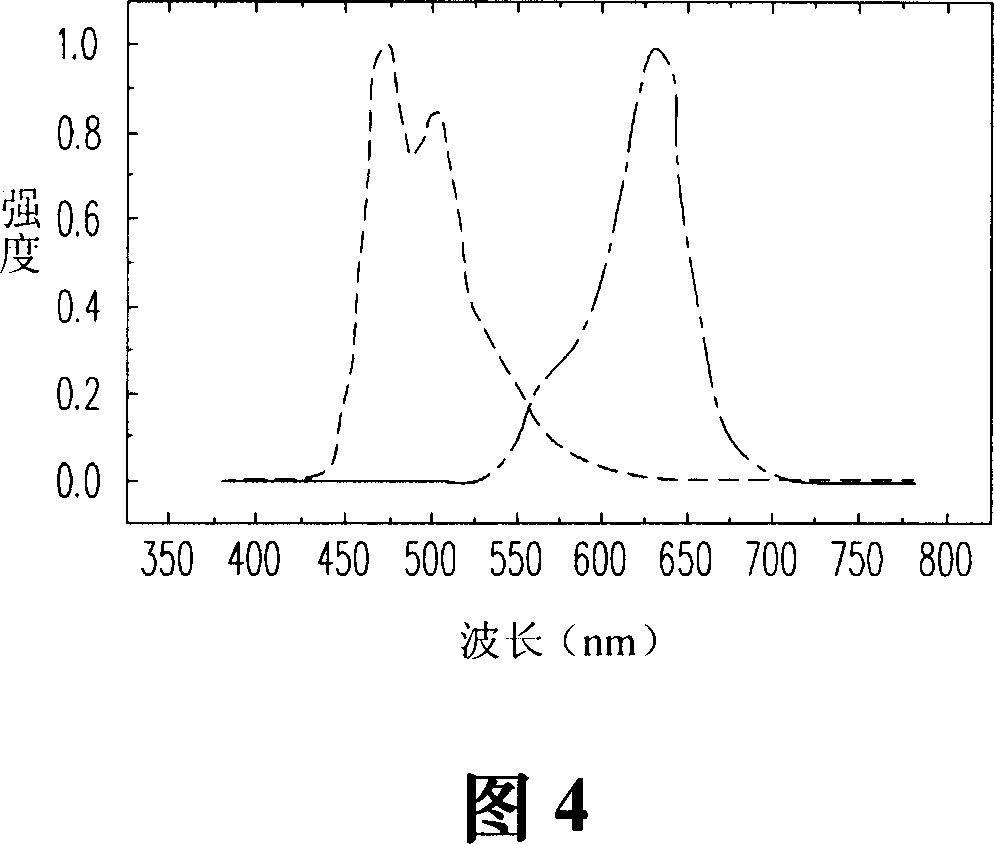
[0049] 3 is a schematic cross-sectional view of an organic electroluminescent device according to a second embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to FIG. 3 , the second embodiment is similar to the first embodiment, the difference is that: in the organic electroluminescence device 300 of this embodiment, the reflective electrode layer 230 is used as the common electrode layer. In other words, the reflective electrode layer 230 is disposed between two adjacent organic functional layers 224a and 224b. It is worth mentioning that since the reflective electrode layer 230 can be formed by vapor deposition, the organic functional layer 224 a will not be damaged during the process of forming the reflective electrode layer 230 .
[0050] More specifically, the reflective electrode layer 230 , the organic functional layer 224 a and the transparent anode layer 222 a constitute the organic electroluminescent unit 310 a, so the reflective electrode layer 230 is a cathode layer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com