Method for treatment of malignant and infectious chronic diseases
a chronic disease and infectious technology, applied in the field of treatment, can solve the problems of poor success of combining specific active immunotherapy with chemotherapy, inability to induce an effective tumoral regression in humans, and inability to achieve effective tumoral regression. , to achieve the effect of increasing the autoimmune respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
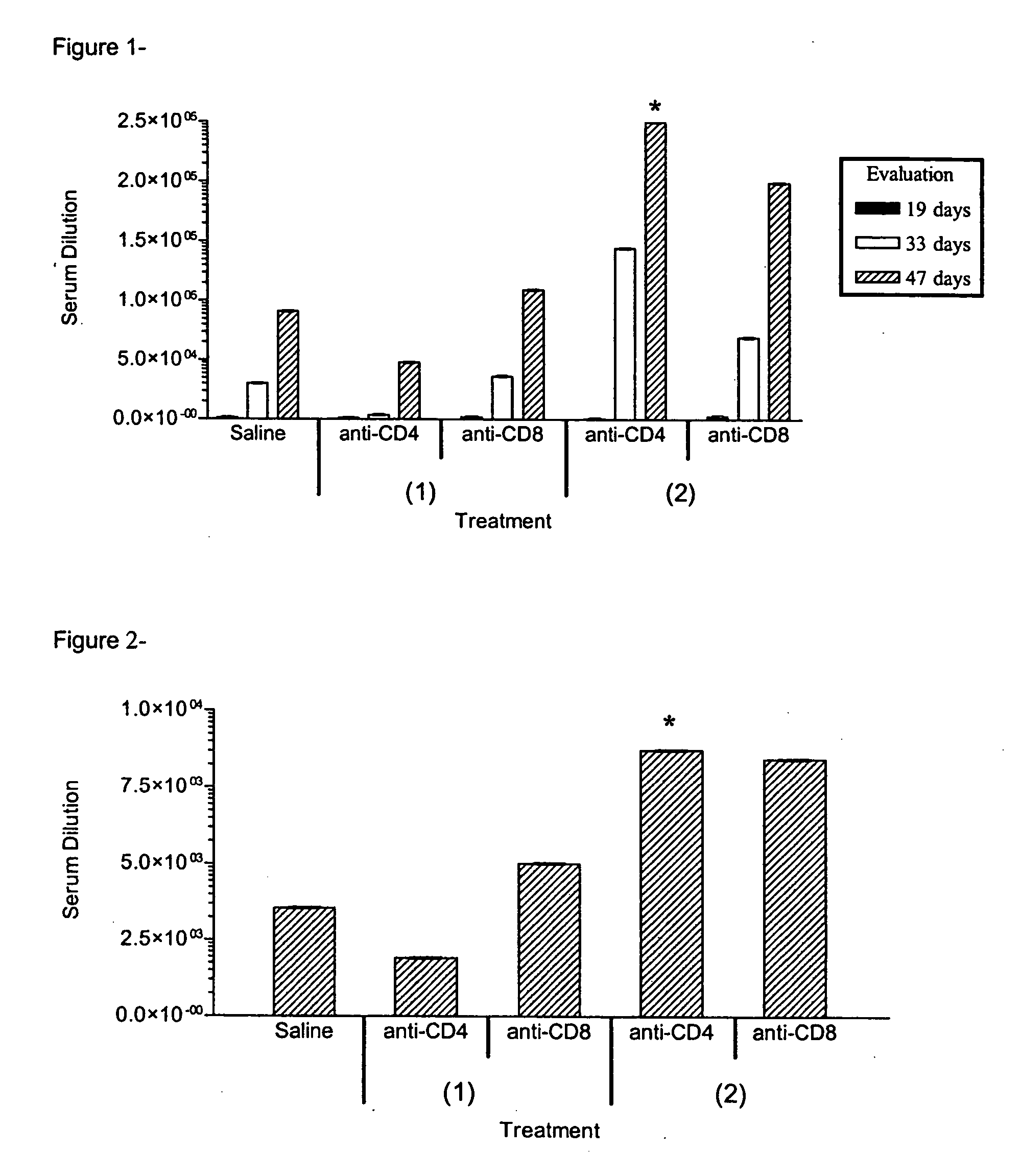
Comparison Between Two Treatment Schemes on the Induction of Antibodies Against Human EGF in Healthy Mice (VIV vs IVV). Immune Modulating with Anti-Mammalian T Cells Antibodies
[0060] The transitory immune modulation with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 Monoclonal Antibodies increases the antibody response against Epidermal Growth Factor and it depends on the treatment scheme used.
[0061] BALB / c mice were immunized using two combined protocols: According to the scheme, (1) the mice were injected by intravenous route with a dose of 0.5 mg of anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Five days later mice were immunized by subcutaneous route with 50 μg of human Epidermal Growth Factor (hu-EGF) in Complete Freund Adjuvant, two weeks later, the mice were re-immunized by subcutaneous route with a second dose of 50 μg of hu-EGF in Incomplete Freund Adjuvant (IFA).
[0062] According to the scheme (2), the mice were injected by subcutaneous route with 50 μg of human Epidermal Growth Factor (hu...
example 2
Comparison Between Two Treatment Schemes on the Induction of Antibodies Against Autologous EGF in Healthy Mice (VIV vs IVV). Immune Modulating with Anti-Mammalian T Cells Antibodies
[0063] The transitory immune modulation with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies increases the antibody response against the autologous Epidermal Growth Factor.
[0064] BALB / c mice were immunized using two protocols combined similar to that described in Example 1 and the IgG antibody response against murine EGF (autologous) was measured. FIG. 2 shows that the immune modulation with both anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 Mabs using the scheme (2) also increases the of IgG antibody response against the murine EGF, the one that was significantly higher than the response exhibited by the mice immunized twice with hu-EGF and treated with saline solution, which were used as control. It is shown the geometric average of the IgG antibody titers for each group at day 47 after the first immunization.
example 3
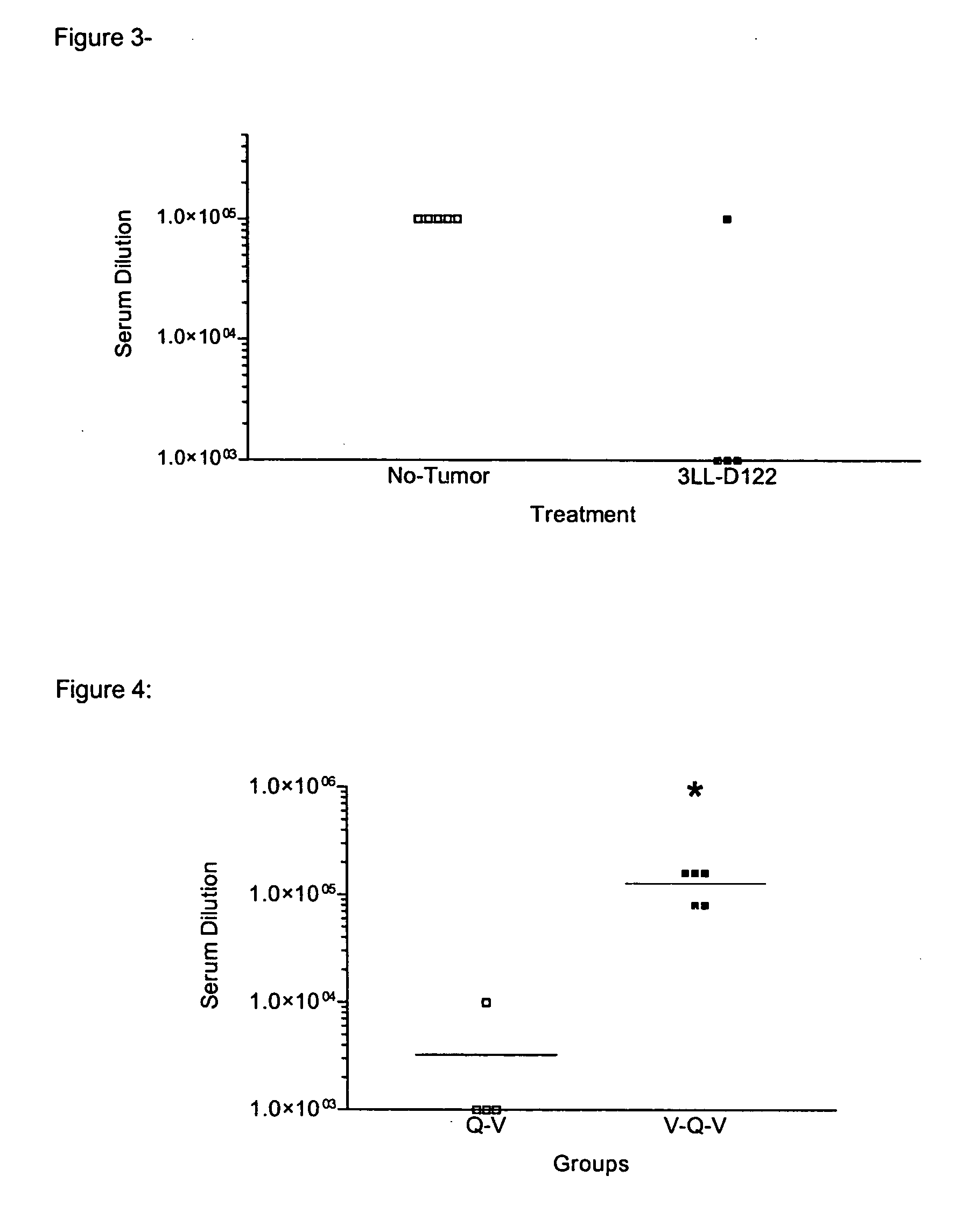
Tumor Effect on the Induction of an Antibody Response Against Vaccine Antigens
[0065] The immune response against vaccine containing self-antigens diminishes by the presence of tumor in the immunized subjects.
[0066] C57BL / 6 mice were injected by intramuscular route with a vaccine that contains 4 μg of human EGF conjugated to the P64 protein (EGF-p64) in Montanide ISA 51 (100 μl final volume) and two weeks later were re-immunized by intramuscular route with a second dose of said vaccine. A group of these animals was inoculated with the syngeneic tumor 3LL-D122 (200 000 cells / animal) in the right plantar pad 2 days previous to the first immunization.
[0067]FIG. 3 shows that the presence of the syngeneic tumor influences negatively in the induction of the immune response against the vaccinal antigen. The individual titers of IgG+IgM antibodies are shown for each group day 47 after the first immunization.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap