Method for choosing the defect detection mode of an optical storage device
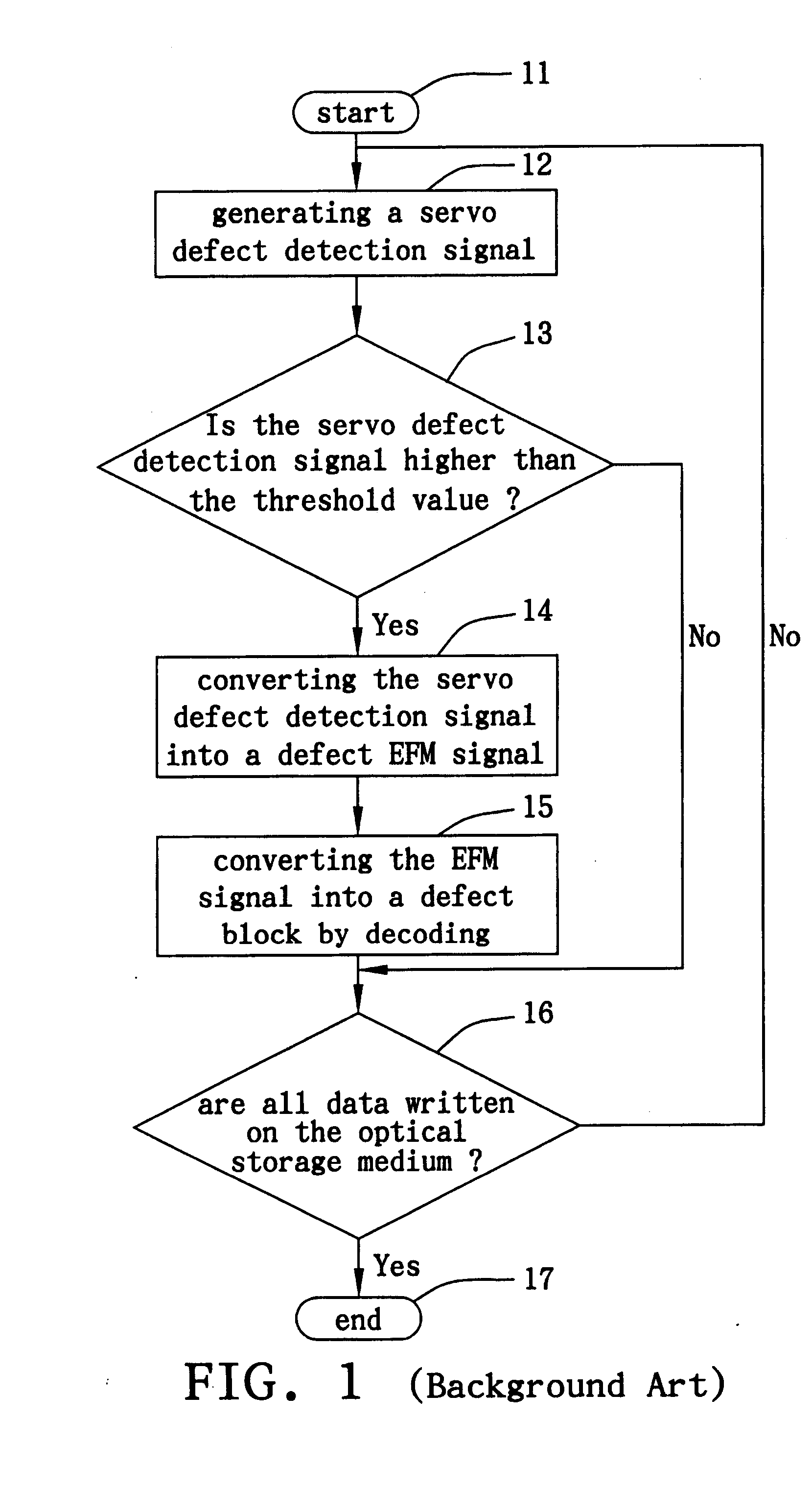
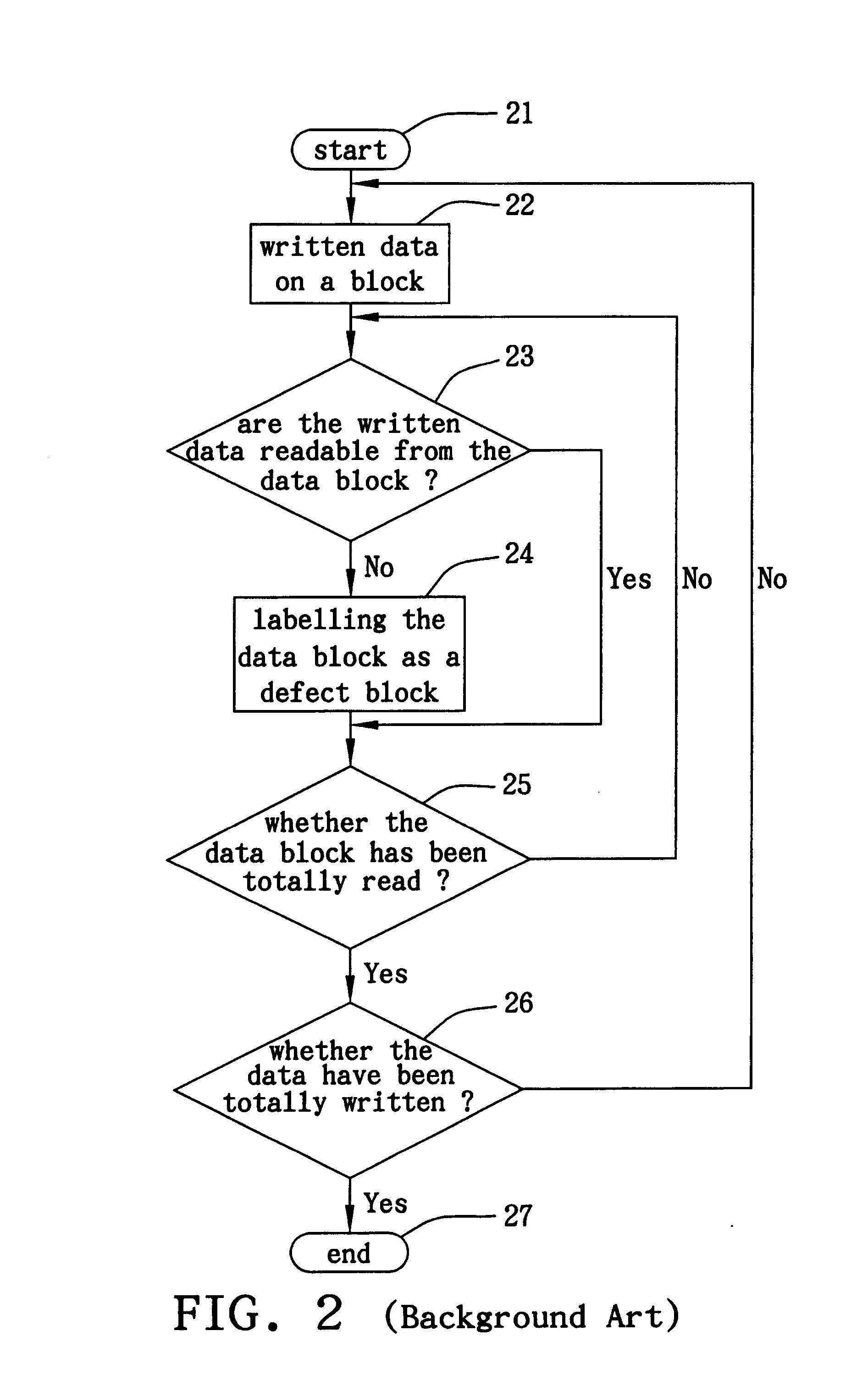
a technology of optical storage and defect detection mode, applied in the direction of digital signal error detection/correction, instruments, recording signal processing, etc., can solve the problem of absence of related defect records
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
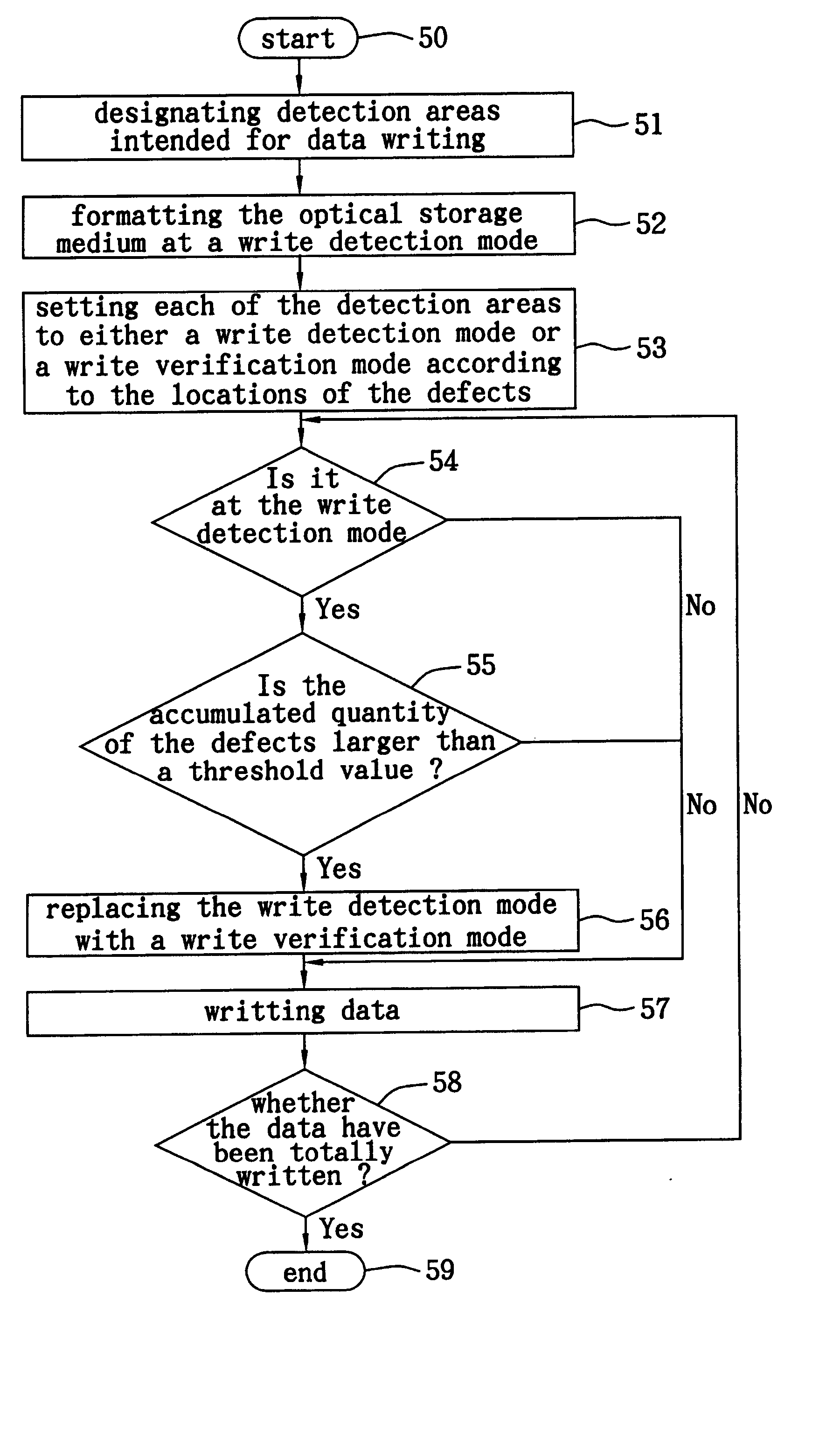
[0023] FIGS. 4(a)-4(c) are schematic diagrams about choosing a defect detection mode in accordance with the present invention. The present preferred embodiment may be applied to a formatted optical storage medium. There are four default detection areas, intended to store data and disposed on the optical storage medium, as shown in FIG. 4(a). The quantity and the locations of the defects in the program area are recorded in a defect table when the optical storage medium is formatted, thus it is possible to know the number of the defects in the detection areas 1-4. The quantity of the defects either in the detection area 1 or in the detection area 4 is smaller than a threshold value; thus both of the detection areas 1 and 4 are set to a write detection mode D first, as shown in FIG. 4(b). The quantity of the defects either in the detection area 2 or in the detection area 3 is greater than the threshold value; thus both of the detection areas 2 and 3 are initially set to a write verific...
second embodiment
[0026] FIGS. 6(a)-6(b) are schematic diagrams about choosing a defect detection mode in accordance with the present invention. The present preferred embodiment may be applied to an optical storage medium which is unformatted or whose defect distribution remains unknown. Assuming eight detection areas intended for data storage are disposed on the optical storage medium, as shown in FIG. 6(a), it is impossible to know the number of the defects in the detection areas 1 through 8 since the optical storage medium has not yet been formatted. It is expedient to set all the detection areas to the write detection mode D first. If it is found from the detection areas 2, 3 and 7 that the respective accumulated quantity of defects is greater than a threshold value within the duration of a data writing operation and defect detection operation, the corresponding detection area would be changed from the write detection mode D to the write verification mode V, as shown in FIG. 6(b).
[0027]FIG. 7 is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| intrinsic structural defect | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| defect detection | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| defect | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com