Anti-bacterial plant compositions
a technology of plant compositions and antibacterial properties, applied in the field of isolation and use of extracted and purified plant compounds, can solve the problems of difficult control of mycobacterium, difficult identification of lead plant extracts, and difficult identification of mycobacterium /i>, and achieve the effect of inhibiting the growth of mycobacterium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
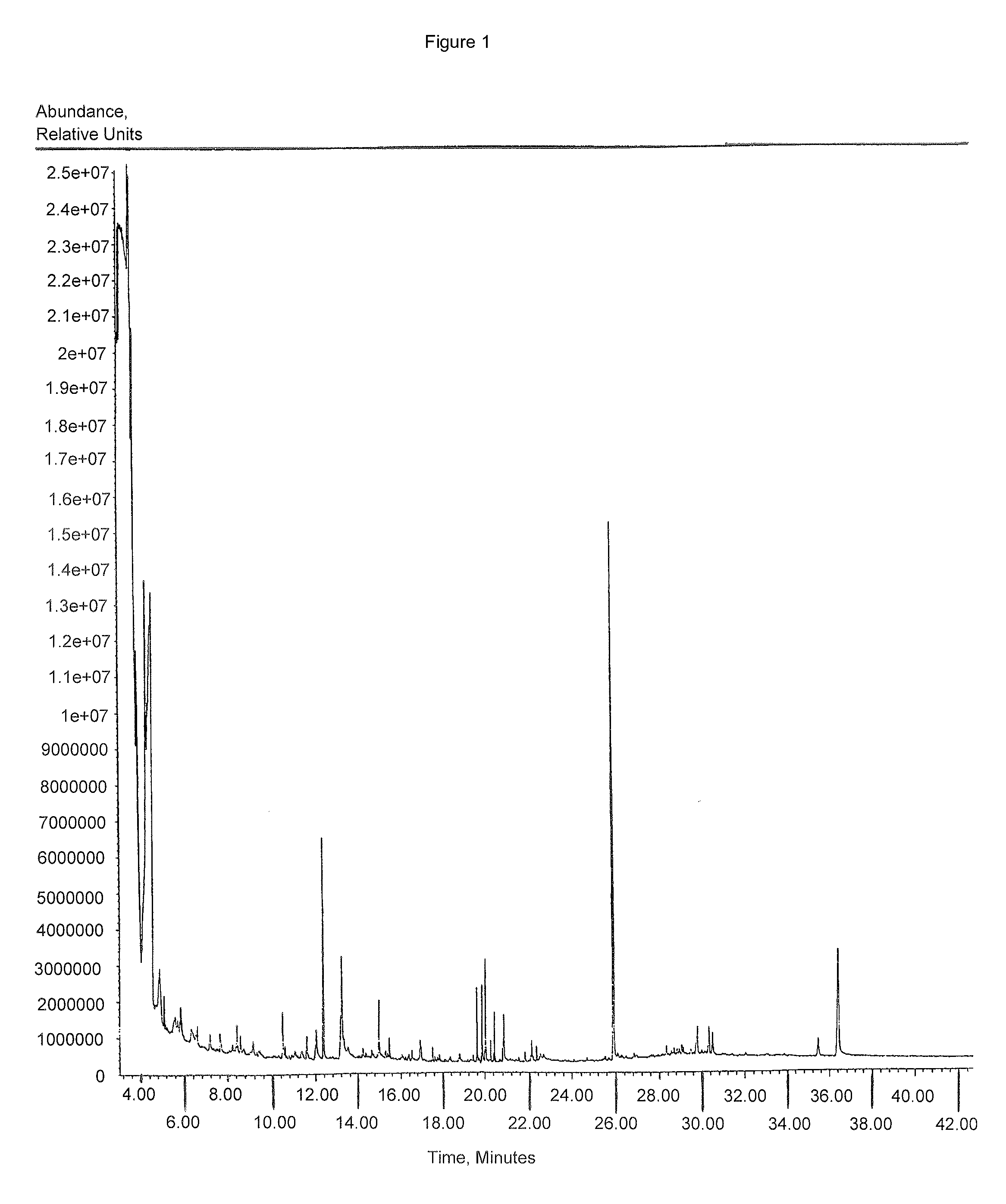
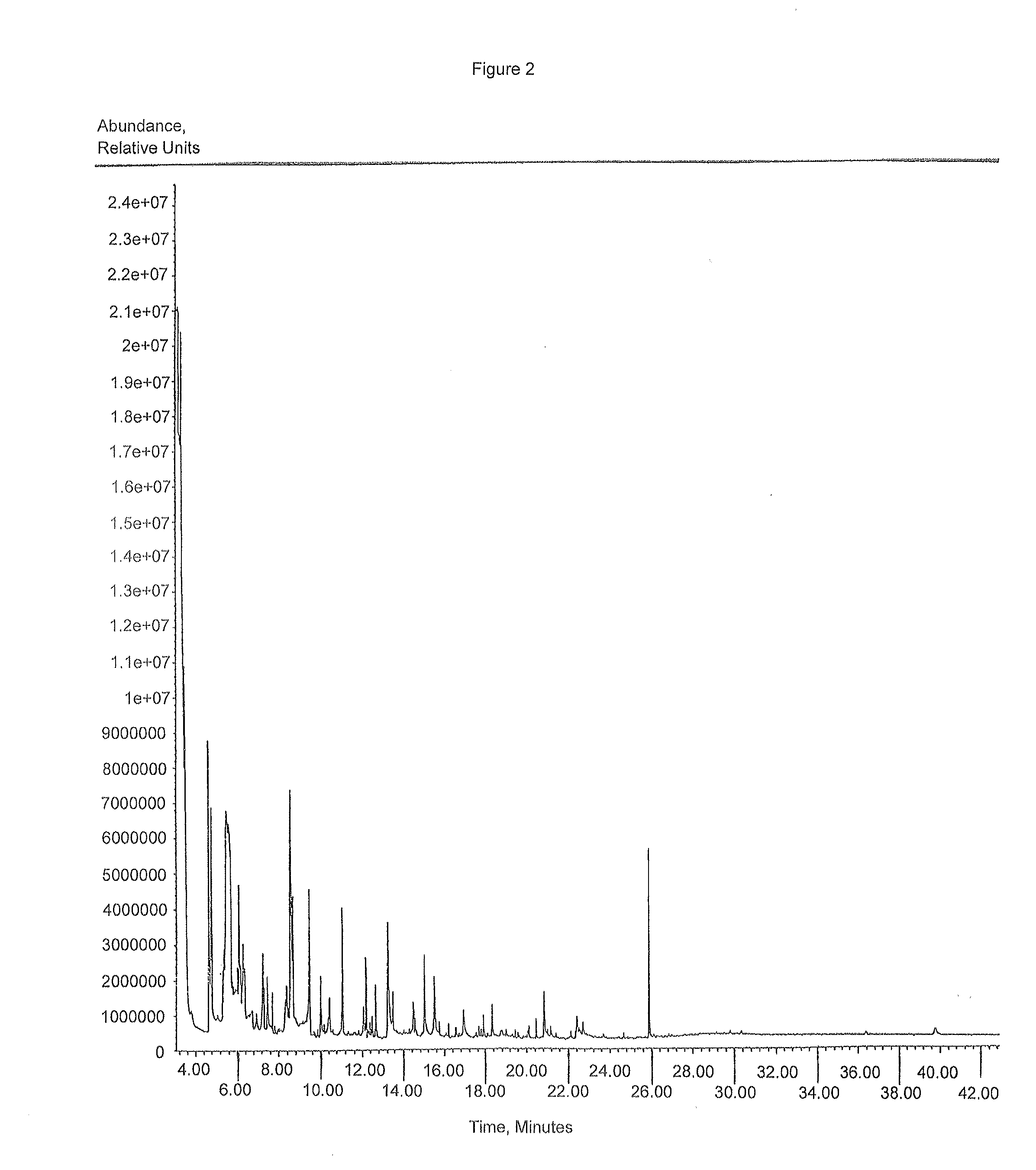
[0058]This example demonstrates that Mammea americana, Callistemon citrinus, and Marchntia polymorpha ethanolic plant extracts have significant anti-mycobacterial activity but limited toxicity to shrimp and no detectable toxicity to mammals.
[0059]Approximately 3 pounds of plant leaves from 50 plant species were oven dried at 42° C., and ground in a blender. 30 gr of the ground material were extracted in 300 ml of absolute ethanol (Spectrum Products laboratory, Garden, Calif.) by shaking at room temperature for 24-36 hrs. The liquid was then filtered on Whatman paper #4, then #2 (VRW Scientific Laboratory, Willard, Ohio) and evaporated at 40° C. on a Buchi / Beckman rotary evaporator (VRW Scientific Laboratory, Willard, Ohio). For testing, the material was resuspended in methanol, at the desired concentrations.
[0060]The activity of each extract was tested on M. smegmatis 607 (ATCC, Rockville, Md.). An agar-disk diffusion assay was performed, in parallel with assaying of extracts from o...
example 2
[0063]Shows that there is no significant toxicity to mammals associated with plant extracts of Mammea Americana, Callistemon citrinus, or Marchntia polymorpha.
[0064]Groups of 7 CF-1 outbread mice (50 day-old males, average weight 30 gr) SASCO, Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, Mass.) were tested by peritoneal administration to each group 500 μg of a plant extract resuspended in methanol, over a 15 day period, in daily injections of 100 μl. The plant extracts tested included Mammea Americana, Callistemon citrinus, and Marchntia polymorpha. Two groups of mice which received saline (100 μl) or saline and methanol mixture (50 μl each) were used as controls.
[0065]Mice remained under observation for a period of one month and the following parameters were measured on a daily basis: changes in activity, fecal consistency, hair condition, cutaneous lesions, eye changes, appetite (water and food intake), weight loss, temperature change and mortality.
[0066]In general, all six extracts de...
example 3
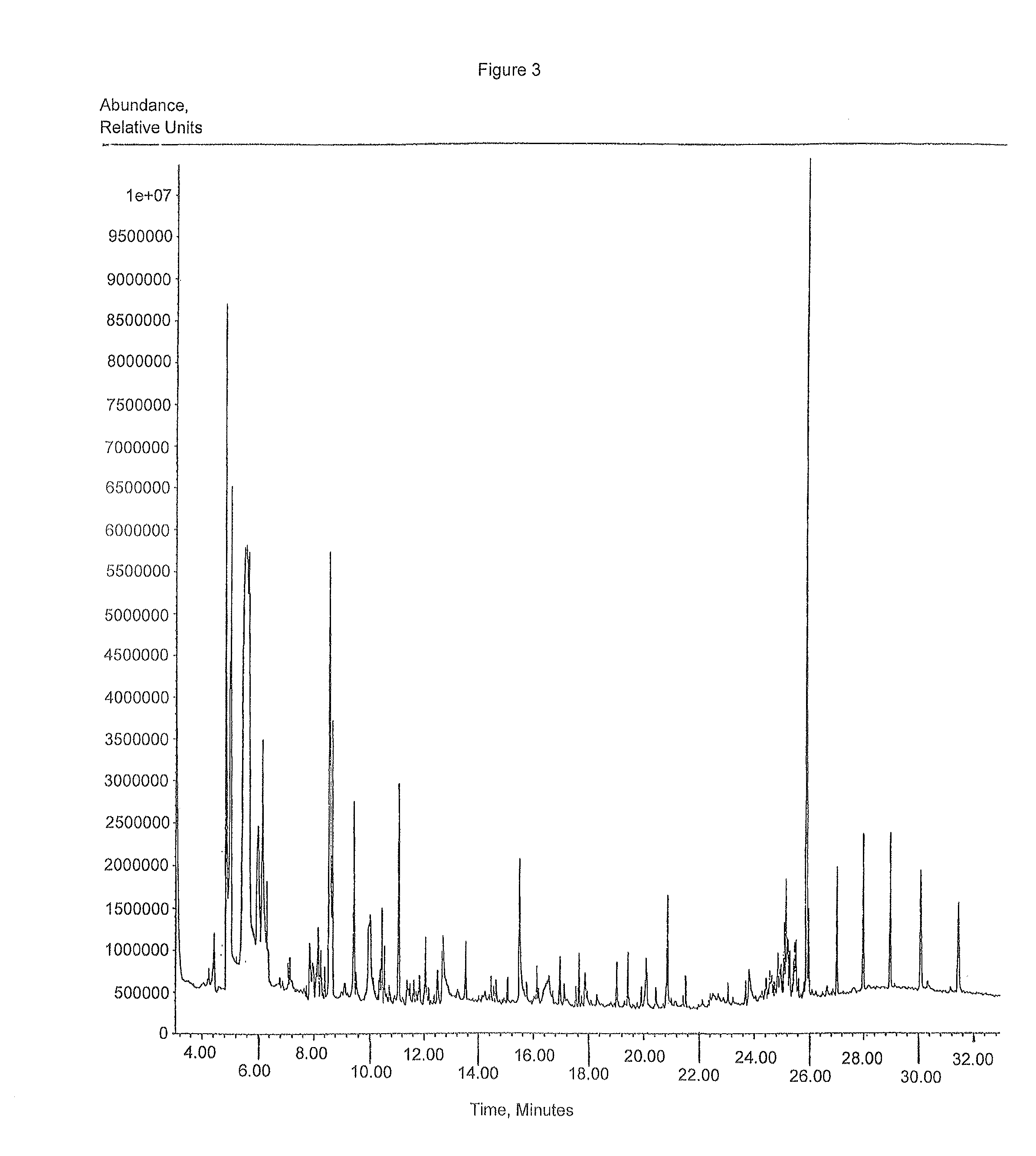
[0068]This example demonstrates that the anti-mycobacterial extract can be obtained by alternative extraction solvents and that a methylene chloride extract produces a more pure active fraction.
[0069]In a preliminary step which might indicate the likelihood of purifying an active compound from of Mammea Americana, Marchntia polymorpha, and Callistemon citrinus, an extraction with alternative organic solvents was undertaken. If an extract with anti-mycobacterial activity by extraction with alternative organic solvents can be obtained, it would increase the likelihood that the active component is a single compound or a very small group of compounds which could be isolated as a pure fraction. The alternative solvent tested was methylene chloride.
[0070]About 5 gr of powdered leaf tissue was extracted in 100 ml absolute methylene chloride by shaking for 4 hrs. at room temp. The extracted material was tested by agar diffusion assay, generally as described above for tests with ethanol extr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com