Golf club shaft and golf club
a golf club and shaft technology, applied in the field of golf club shafts, can solve the problems of not allowing one of the shafts to primarily operate, low stiffness at this non-overlapping part, and high friction, so as to increase the initial speed of the ball, increase the launch angle of the ball, and increase the driving distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
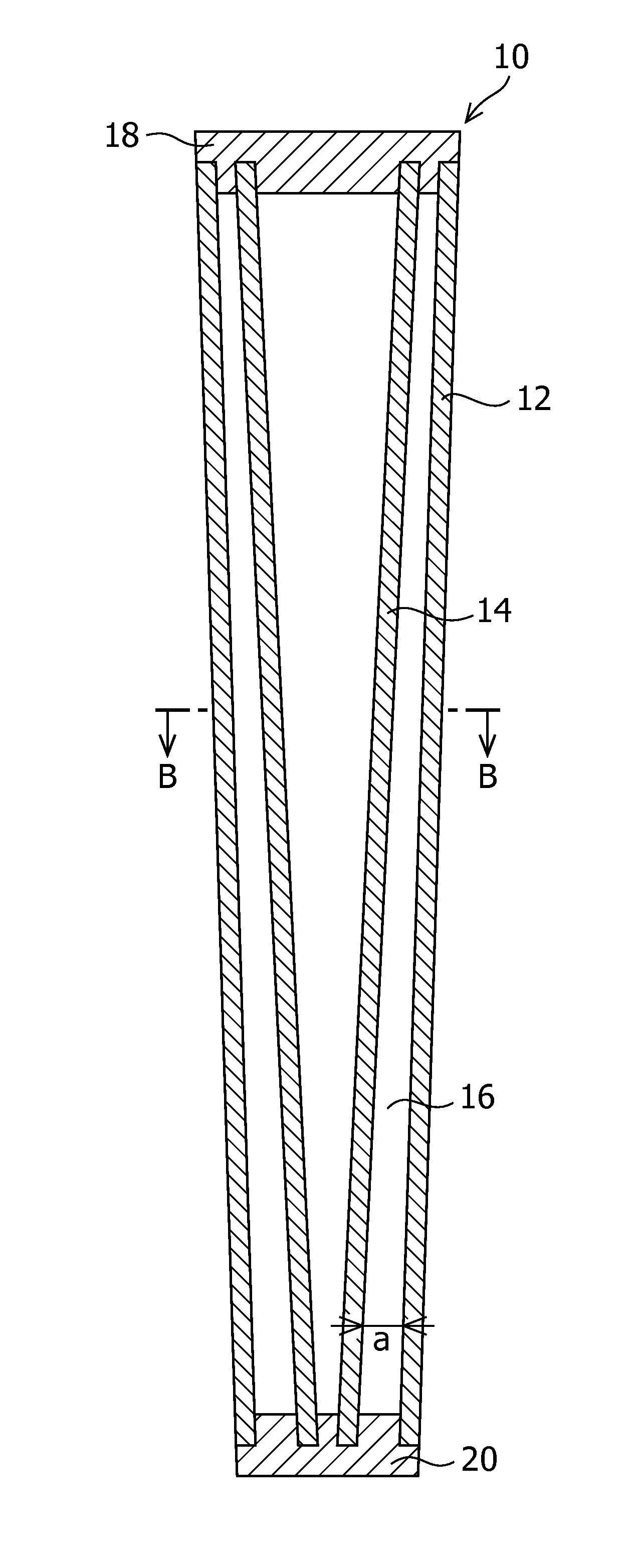
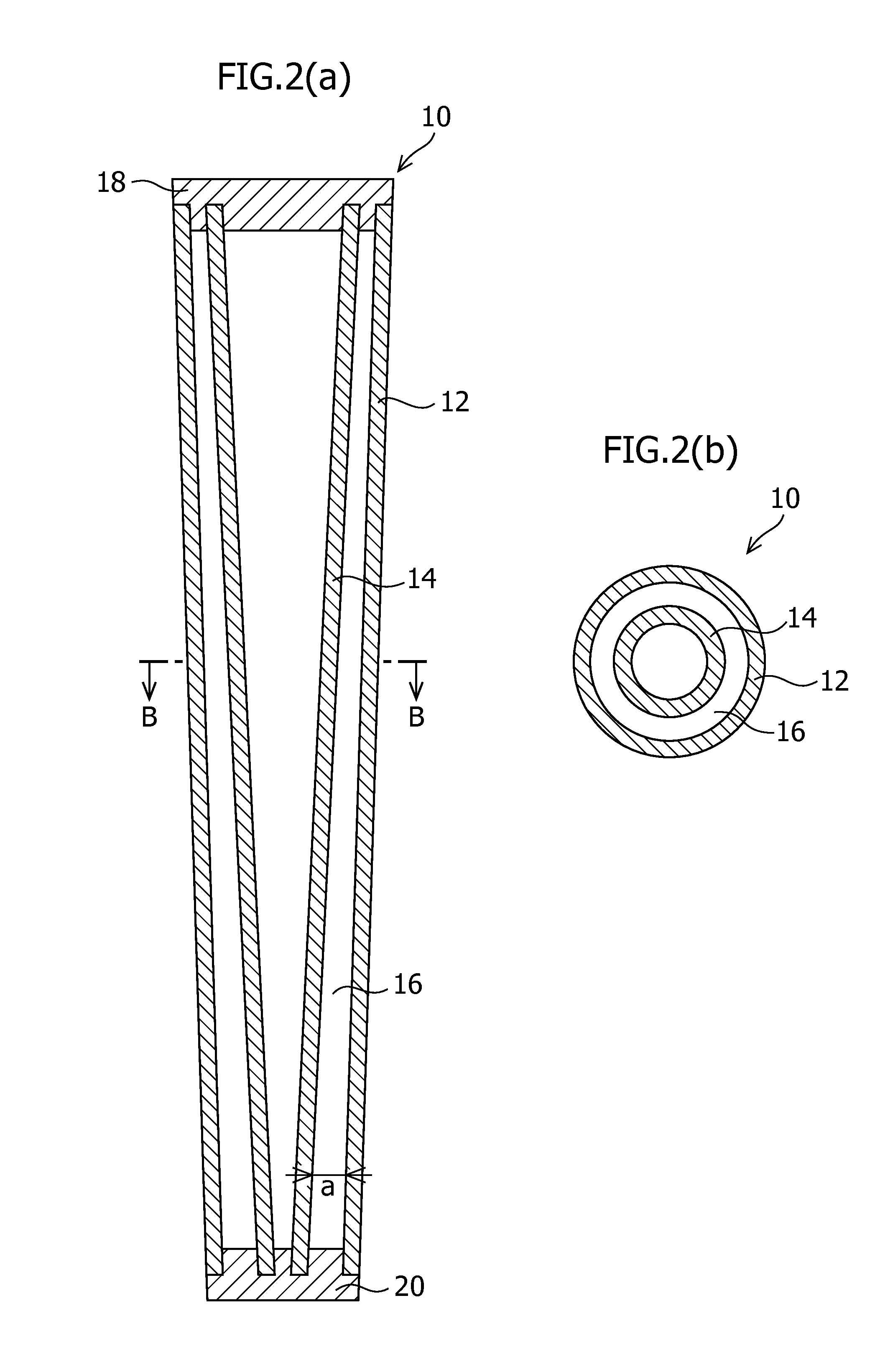
[0025]FIGS. 1, 2A and 2B illustrate a first embodiment of a golf club shaft according to the present invention. In FIGS. 2A and 2B, a grip 11 is not illustrated. A shaft 10 of the first embodiment includes an outer shaft 12 and an inner shaft 14 disposed in a hollow portion of the outer shaft 12. A void portion 16 is formed between the outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14. In the first embodiment, each of the outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14 has a hollow tapered conical shape such that the diameter is gradually reduced toward the tip end. The outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14 have almost equal lengths. The outer shaft 12 preferably has a length with a lower limit of approximately 787 mm and an upper limit of approximately 1219 mm. The outer shaft 12 preferably includes a distal end having an outer diameter with a lower limit of approximately 8.4 mm and an upper limit of approximately 10 mm; a proximal end having an outer diameter with a lower limit of approximately 14 mm a...
second embodiment
[0032]FIGS. 3A and 3B illustrate a second embodiment of a golf club shaft according to the present invention. In FIGS. 3A and 3B, a grip 11 is not illustrated. A shaft 30 of the second embodiment includes an outer shaft 12 and an inner shaft 14 disposed in a hollow portion of the outer shaft 12. A void portion 16 is formed between the outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14. In the second embodiment, the outer shaft 12 has such a hollow tapered conical shape that the diameter is gradually reduced toward the tip end. The inner shaft 14 has such a hollow cylindrical shape that the diameter at the proximal end is the same as the diameter at the distal end. The outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14 have almost equal lengths. The outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14 may each have a length, outer diameter, and thickness of the wall portions which are the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0033]The void portion 16 has a width a, at the distal end, with a lower limit of preferably approx...
third embodiment
[0035]FIGS. 4A and 4B illustrate a third embodiment of a golf club shaft according to the present invention. In FIGS. 4A and 4B, a grip 11 is not illustrated. A shaft 40 of the third embodiment includes an outer shaft 12 and an inner shaft 14 disposed in a hollow portion of the outer shaft 12. A void portion 16 is formed between the outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14. In the third embodiment, the outer shaft 12 has such a hollow tapered conical shape that the diameter is gradually reduced toward the tip end. The inner shaft 14 has such a solid cylindrical shape that the diameter at the proximal end is the same as the diameter at the distal end. The outer shaft 12 and the inner shaft 14 have almost equal lengths. The outer shaft 12 may have the same length, outer diameter, and thickness of the wall portions as that in the first embodiment. The inner shaft 14 may have the same length and outer diameter as that in the first embodiment.
[0036]The void portion 16 has a width a, at the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com