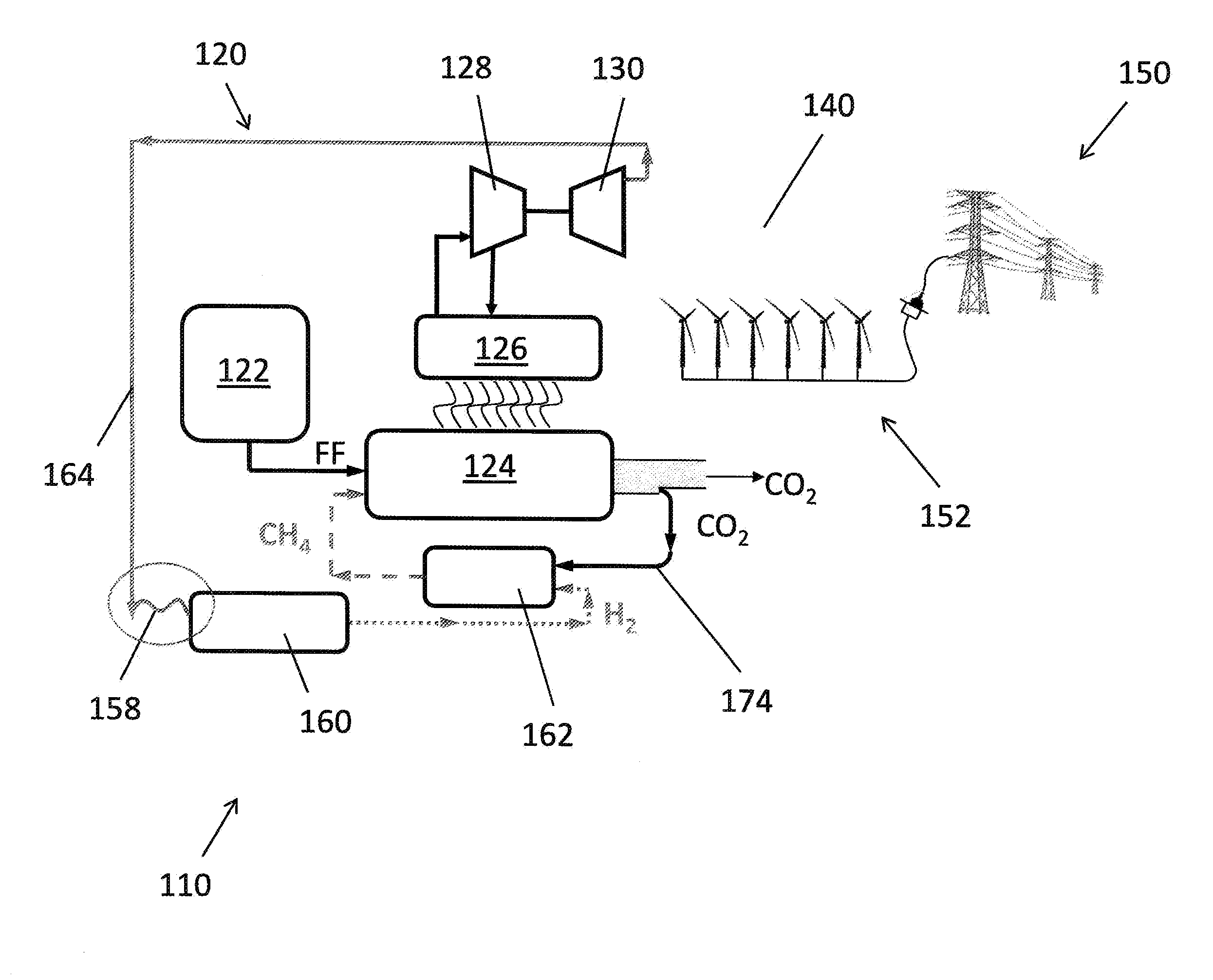
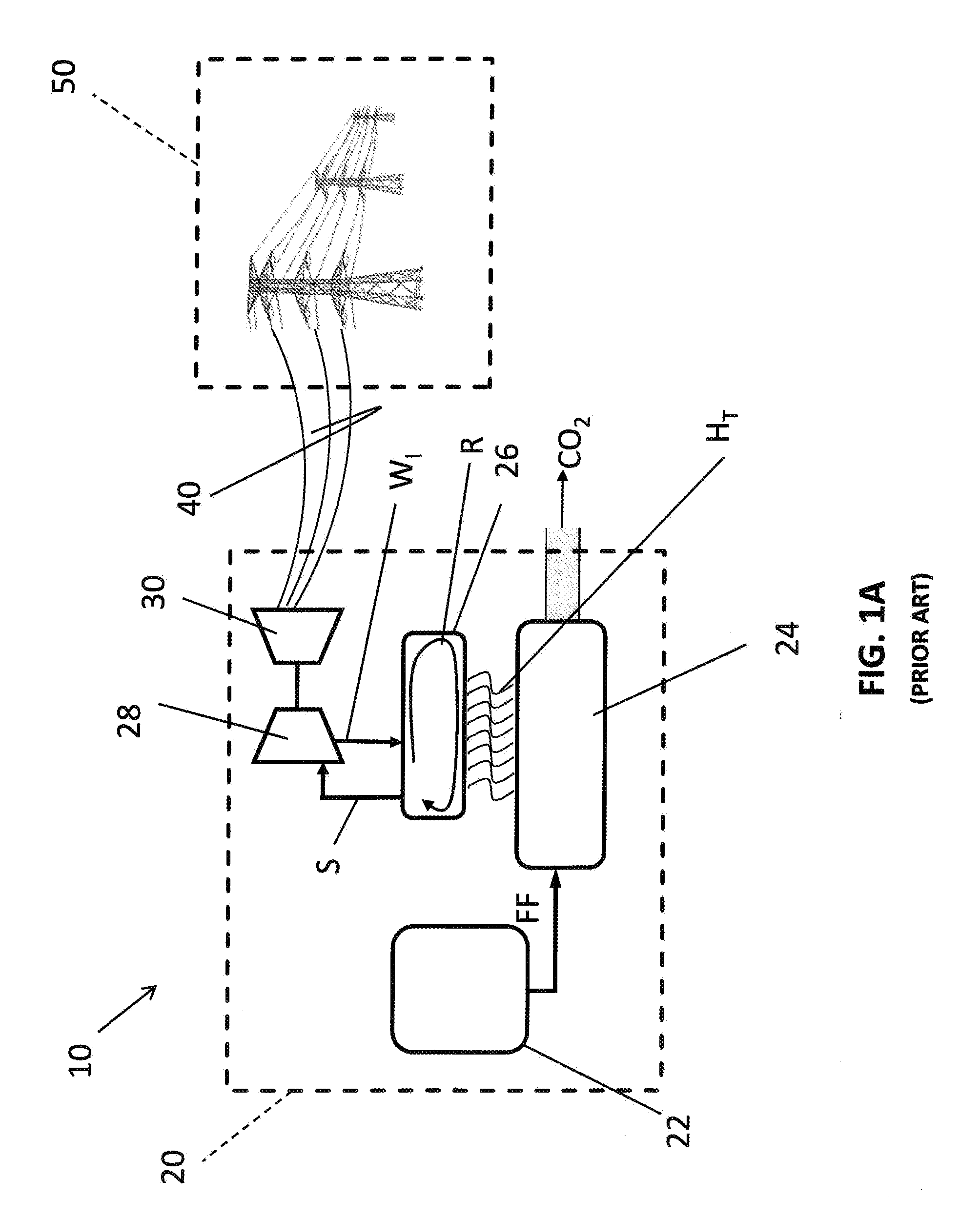
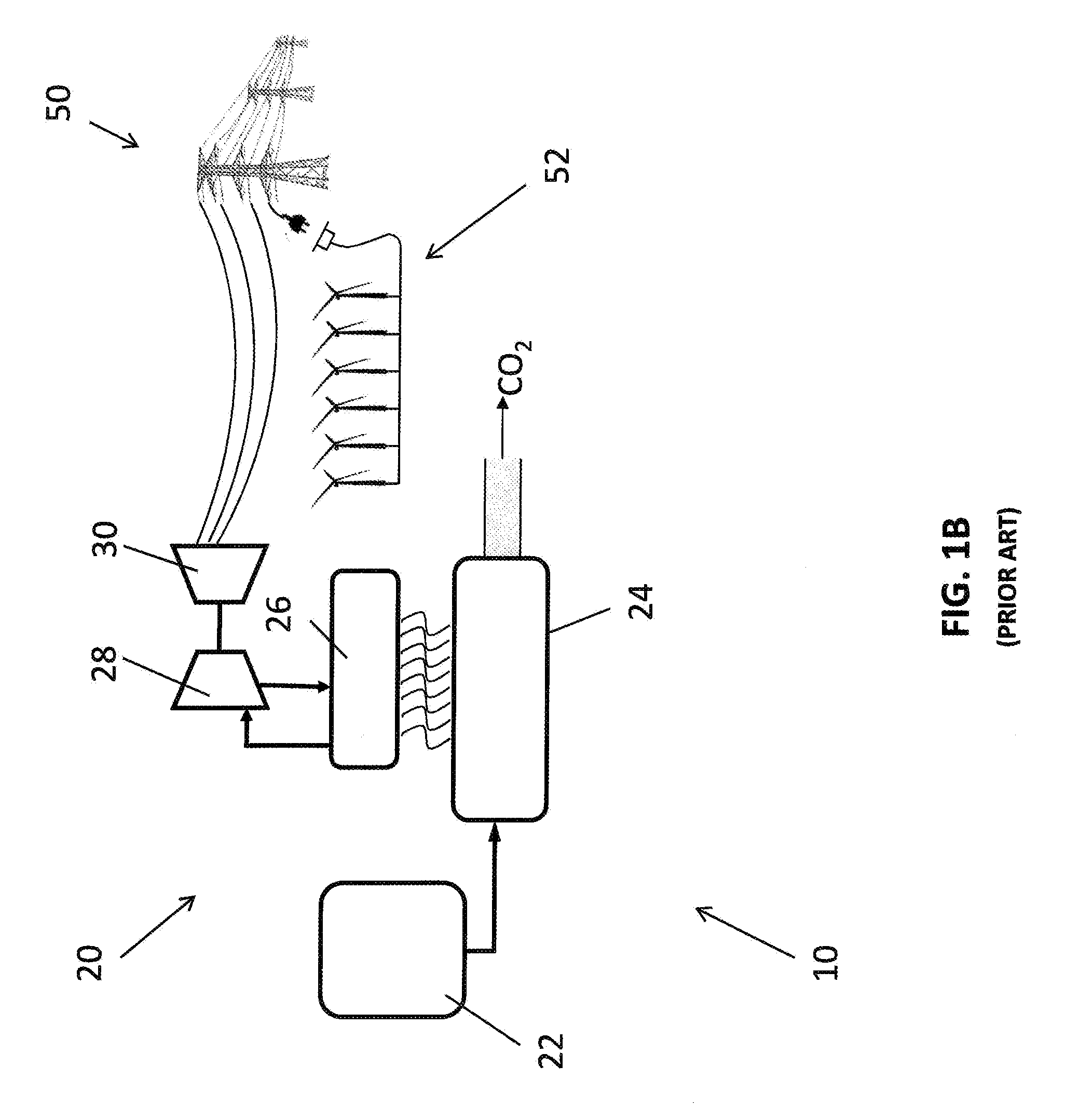
Method of Electricity Distribution Including Grid Energy Storage, Load Leveling, and Recirculating CO2 for Methane Production, and Electricity Generating System
a technology of electricity generation and grid energy storage, applied in steam engine plants, steam generation using hot heat carriers, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of slowing the commissioning of new nuclear power plants in the united states, fickle wind power, and inability to generate electricity from wind farms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023]FIG. 1A is a simplified representation of an electric generating system 10. The electric generating system 10 includes a fossil fuel electric generating plant 20 (or “fossil fuel plant”) that generates electricity by burning a fossil fuel such as natural gas, coal, fuel oil, or other suitable and available fuels. As described in the present disclosure, the electric generating system 10 also provides for the transmission of the generated electricity to commercial and residential consumers. The electric generating system 10 is, therefore, described as including transmission lines 40 and an electrical grid 50 connected to the fossil fuel plant 20 by the transmission lines 40. Further, the electrical grid 50 is interconnected with commercial and residential consumers as well as wholesale consumers that operate local distribution networks. As sometimes used herein for purposes of describing certain aspects of the invention, the term electric generating system 10 may include the tra...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap