Reinforced nonwoven fabric
a non-woven fabric and reinforced technology, applied in the field of reinforced non-woven fabrics, can solve the problems of no special requirements for weight reduction and mechanical stability in such applications, and the known instructions are inadequate for the manufacture of components subject to more stringent requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
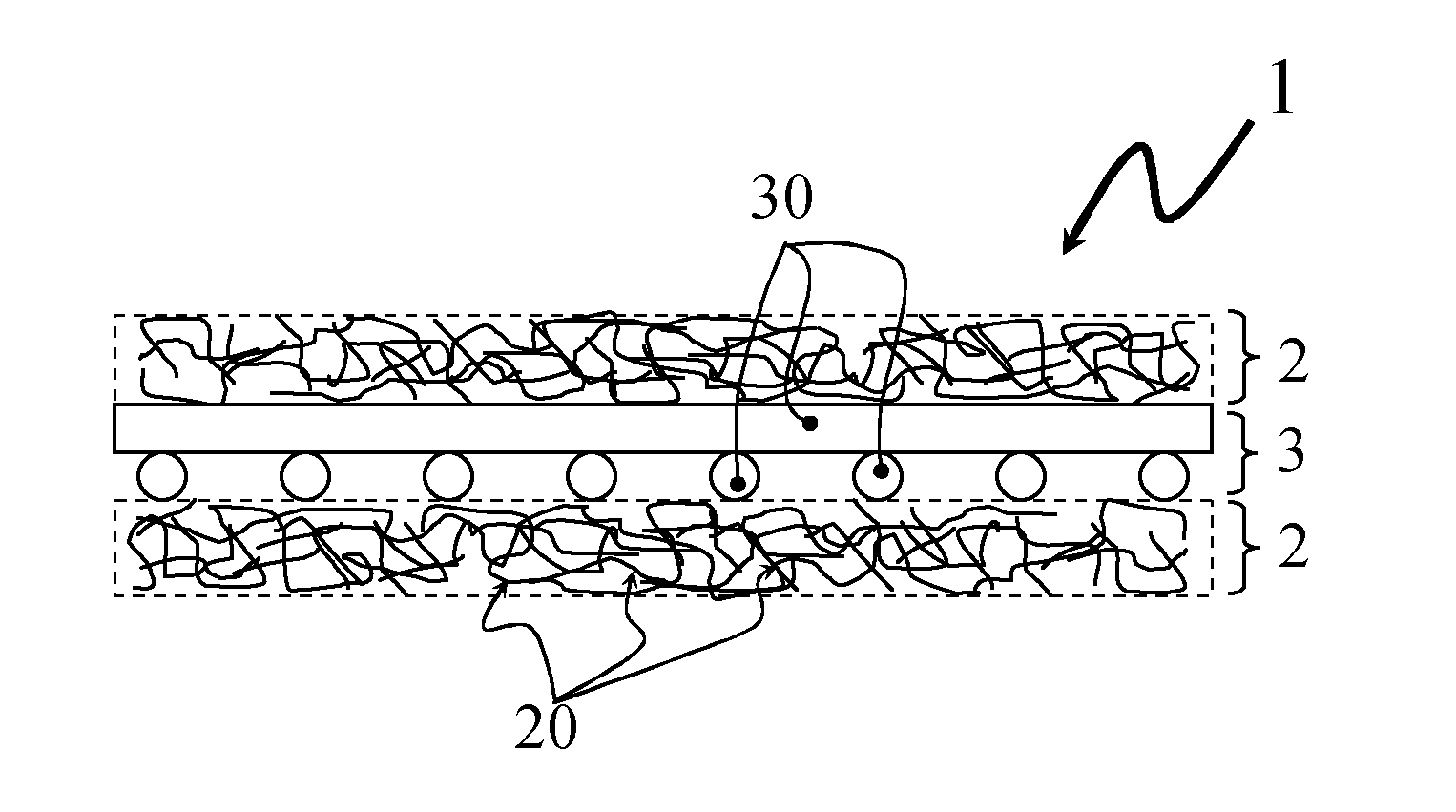
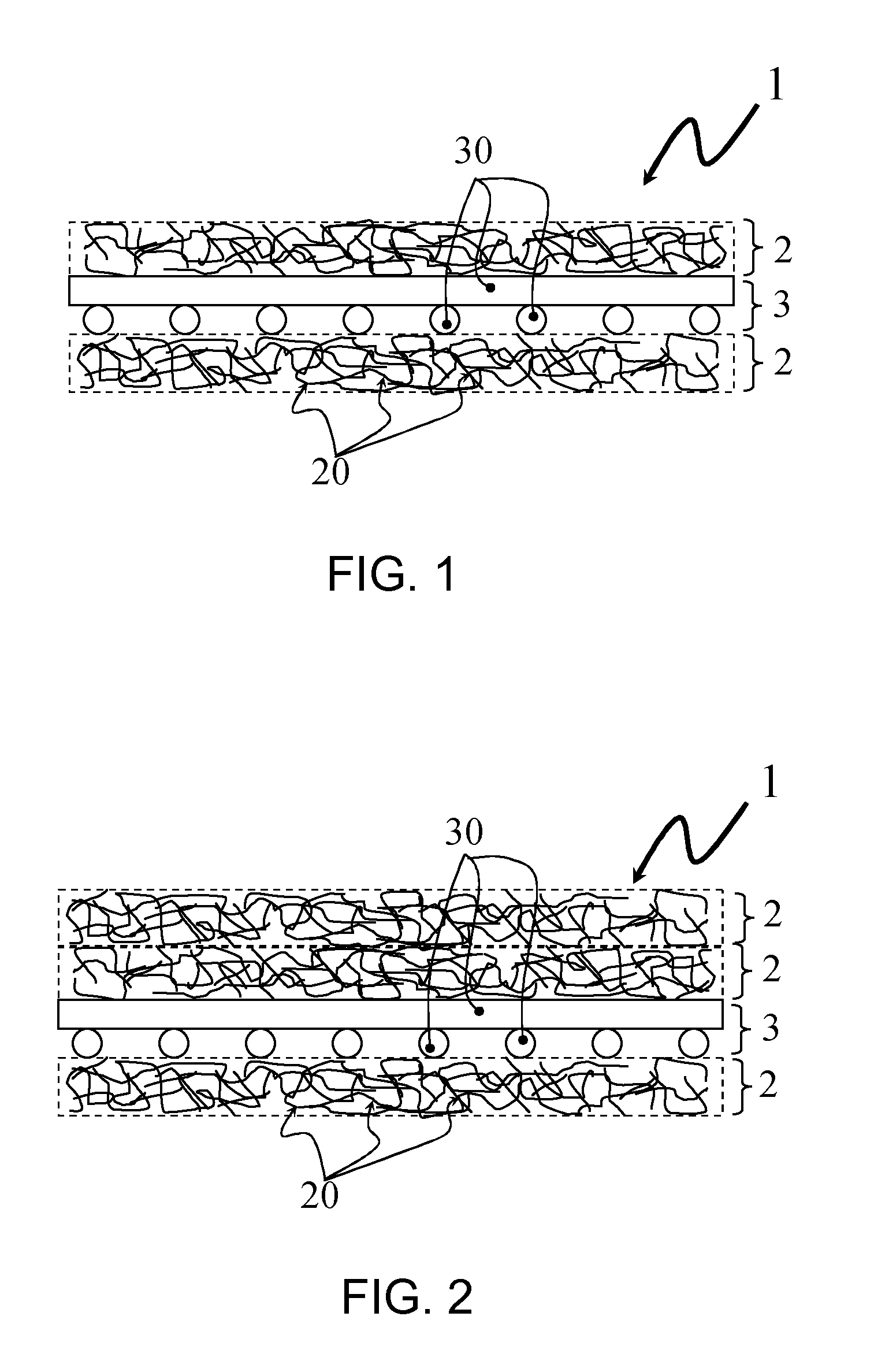
[0024]FIG. 1 shows the schematic structural design of a flat textile structure (1) according to one aspect of the present invention. The reinforcing grid (3) according to the invention, as represented by its grid braces (30), is here secured between two pile layers (2) according to the invention, as represented by its fibers (20).
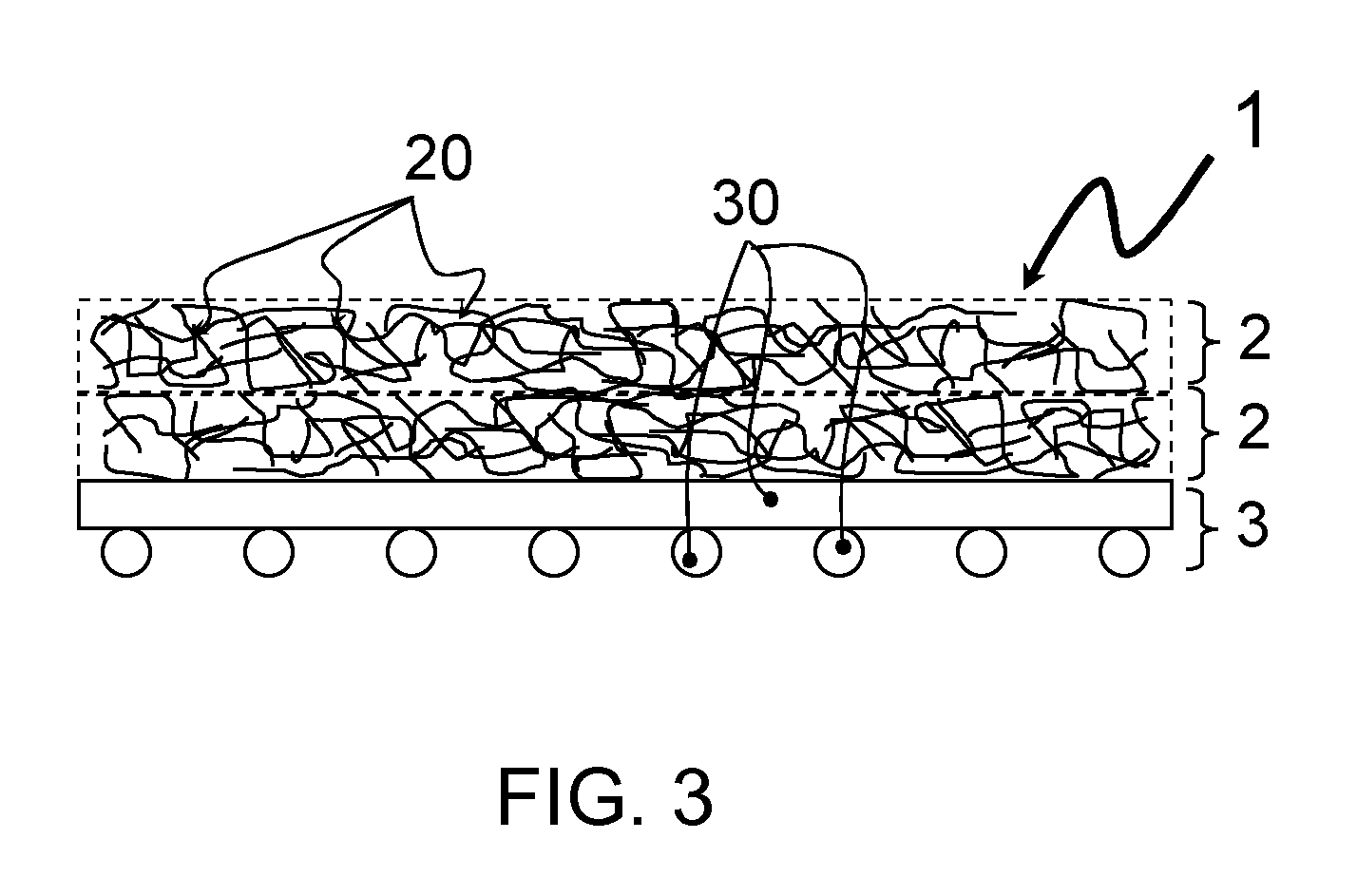
[0025]FIG. 2 shows the schematic structural design of a preferred embodiment of the flat textile structure (1) according to the invention. Two vertically stacked pile layers (2) here lie on one side of the reinforcing grid (3), while one pile layer (2) lies on the other side. This embodiment is preferred because the surface of the flat textile structure (1) exhibits better optical and tactile characteristics on the side with the two vertically stacked pile layers (2). This becomes advantageous when primarily only one side of the component is visible in the subsequent component that integrates the flat textile structure (1), for example in the case of vehicl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap