Esophageal cancer marker and use thereof
a technology for esophageal cancer and tumor markers, applied in the field of esophageal cancer, can solve the problem of not having a definitive tumor marker for esophageal cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
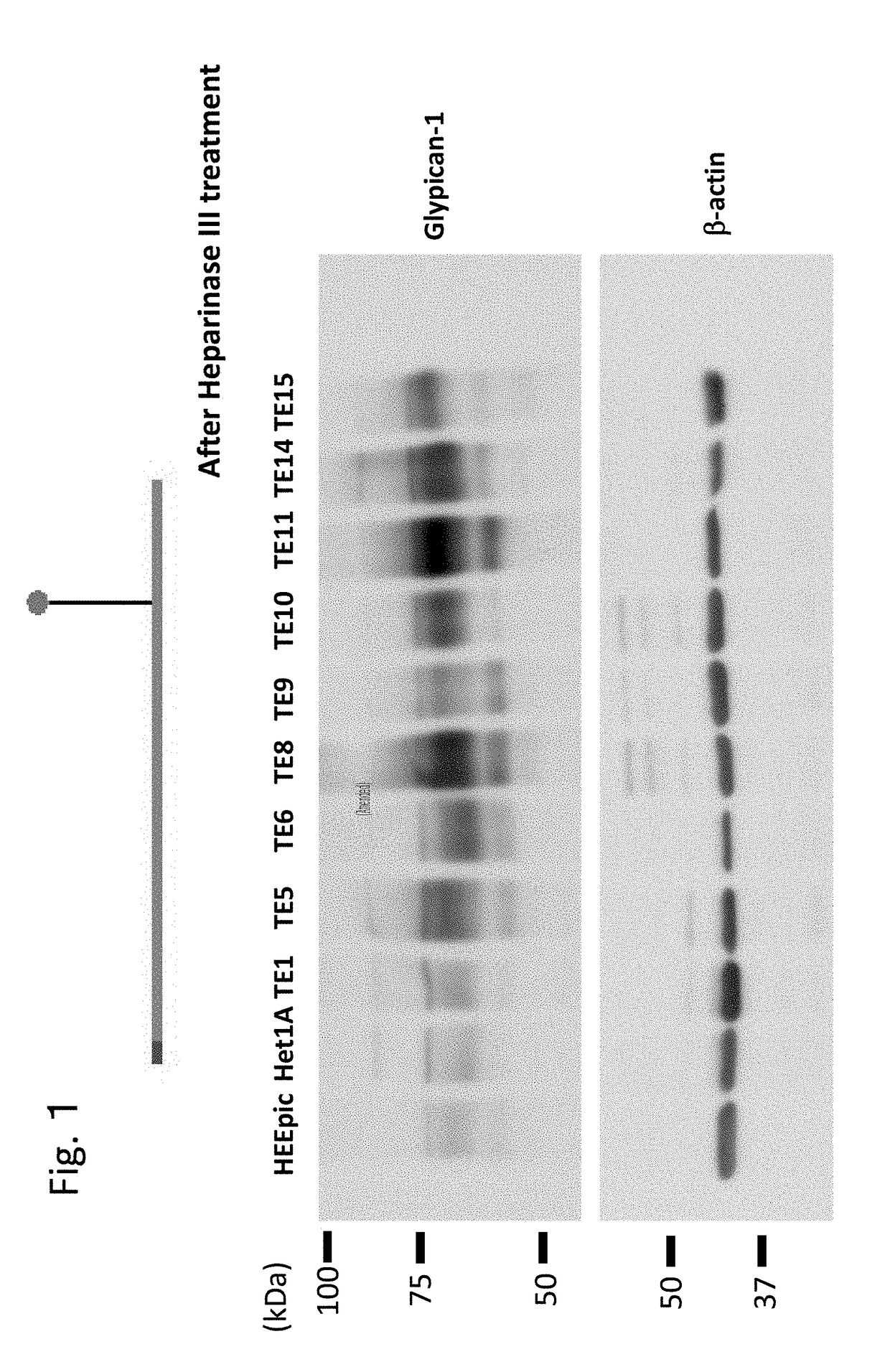
n of Glypican-1 in Various Cells by Western Blot
[0326]In the present example, the expression of Glypican-1 in various cells by Western blot was investigated.
(Western Blot Analysis)
[0327]Normal esophageal epithelial cells HEEpic and Het1A and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell strains TE1, TE5, TE6, TE8, TE9, TE10, TE11, TE14, and TE15 were washed with ice-cooled PBS (−), and then peeled off with a cell scraper. The cells were then recovered by centrifugation. The cells were lysed by a Lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (NACALAI TESQUE), 1× phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (NACALAI TESQUE)), The supernatant was recovered as a protein extract liquid by centrifugation (13,200 rpm, 4° C., 15 min). The protein concentration was quantified with a protein quantifying kit (DC Protein Assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.)) using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard.
[0328]A suger chain of Glypican-1 was enzymatically clea...
example 2
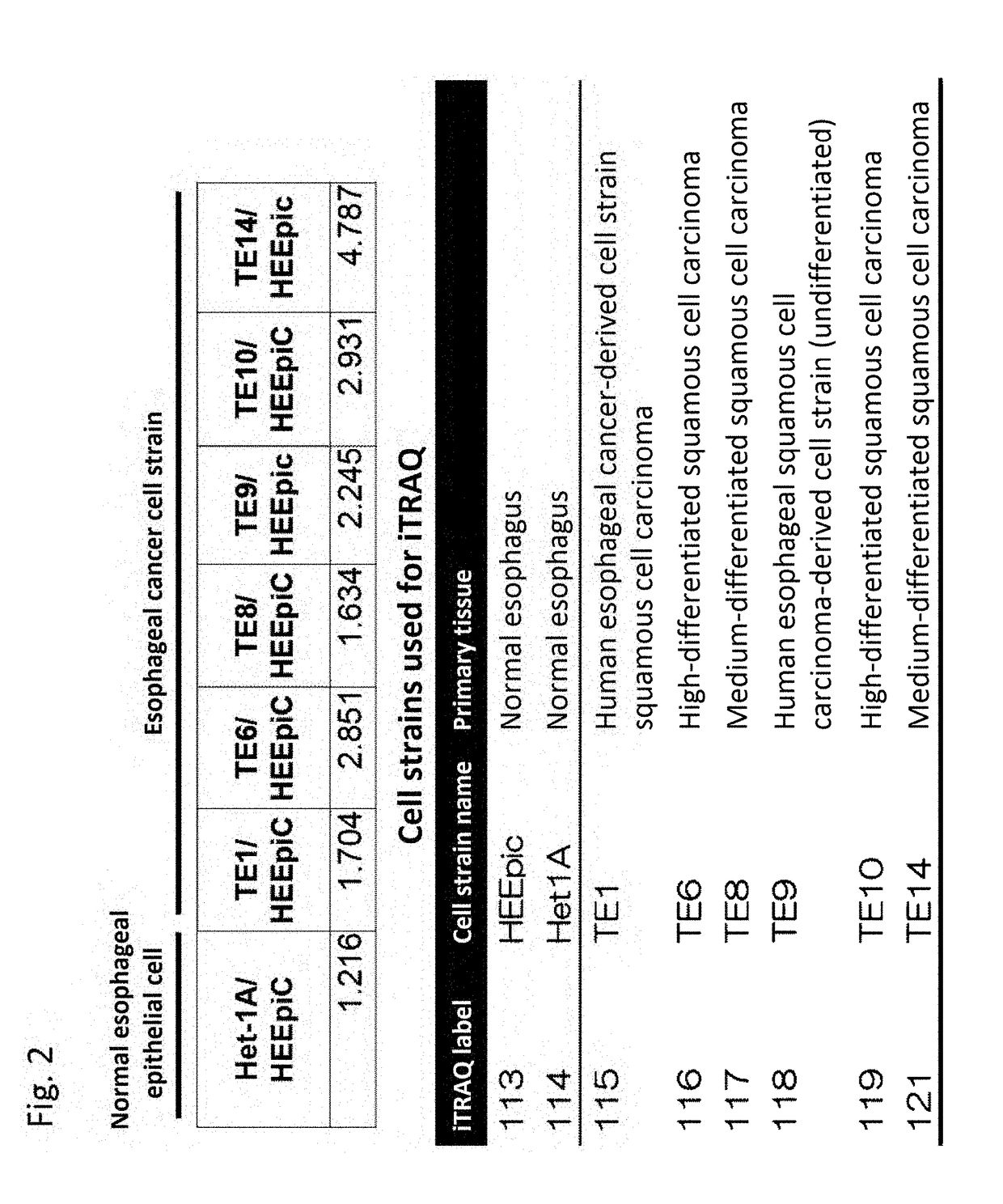
Expression Level of Glypican-1 (Accession No. P35052)
[0332]In the present example, the relative expression level of Glypican-1 (Accession No. P35052) was investigated in normal cells and various esophageal cancer cell strains.
(Techniques)
[0333]The expression level of Glypican-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell strains TE1, TE6, TE8, TE9, TE10, and TE14 was evaluated relative to normal esophageal epithelial cells HEEpic and Het1A.
[0334]For 8 types of cell strains cultured in 150 mm Petri dishes, a cell surface membrane protein comprising Glypican-1 was biotinylated with sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin. The extracted protein was purified by Neurto-avidin beads. At that time, in order to correct for the error among the samples, sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin-labeled bovine serum albumin was added to each in an equal amount as an internal standard, and was used for correction of quantification results from a mass spectrometer. The purified proteins were digested by trypsin and labeled with an iTRAQ ...
example 3
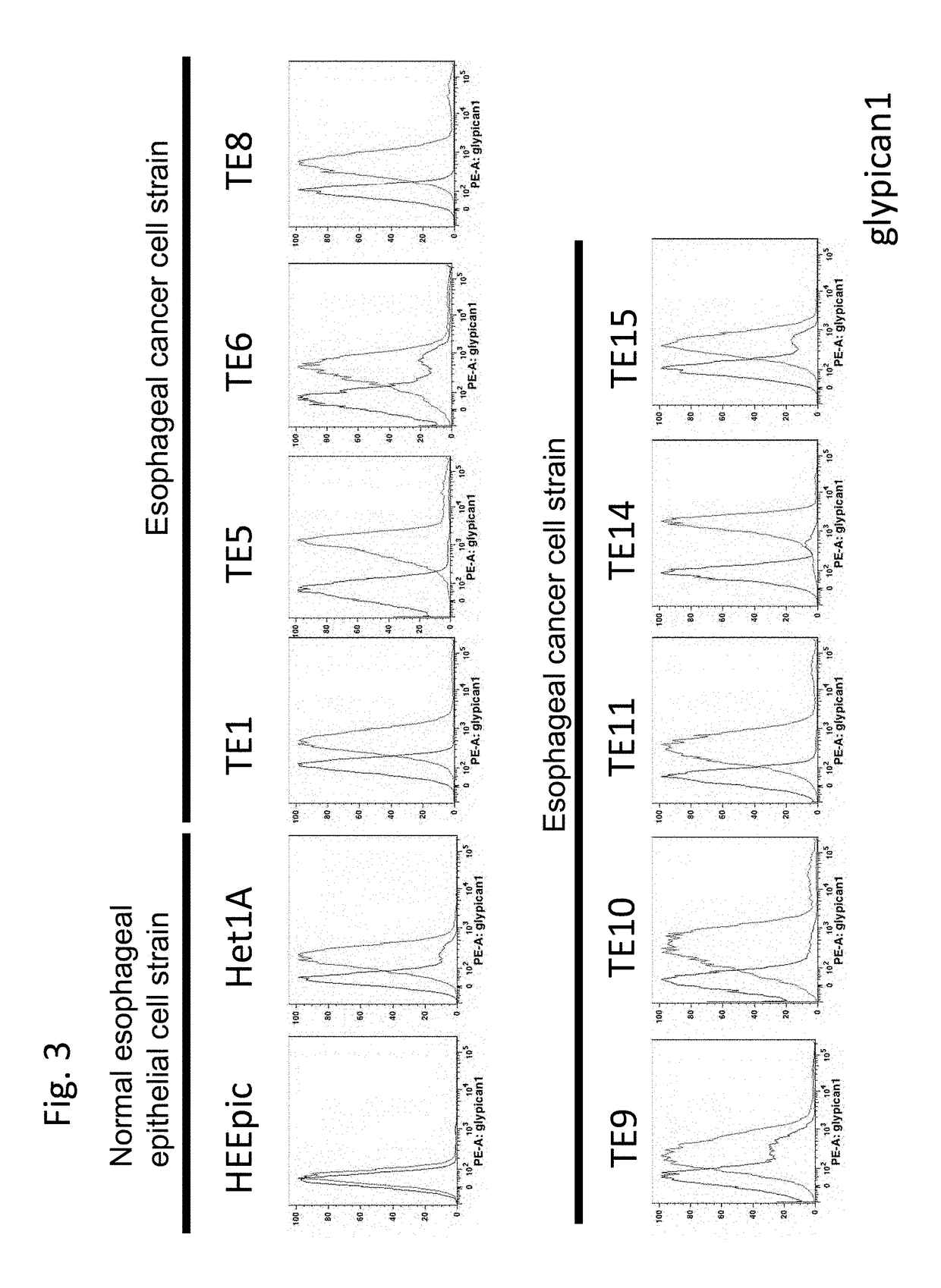
ysis to Show that Glypican-1 is Expressed on Cell Surface of Esophageal Cancer Cells
[0336]Then, in the present example, it was confirmed by FACS that Glypican-1 was expressed on cell surface of esophageal cancer cells.
(Facs Analysis)
[0337]Cells were washed with PBS (Nacalai Tesque) twice and peeled off from a dish by 0.02% EDTA solution (Nacalai Tesque). The cells were washed with a FACS staining buffer (PBS supplemented with 1% FBS and 0.1% sodium azide) twice, stained with a 5-time-diluted goat anti-human Glypican-1 antibody (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minn.), and subsequently stained with a 50-time-diluted PE-labeled anti-goat IgG antibody. The stained cells were measured by FACS Canto II (Becton Dickinson, Mountain View, Calif., USA) and the data was analyzed using FlowJo software (TreeStar, Stanford, Calif., USA).
(Result)
[0338]The result is shown in FIG. 3. As shown, while the expression of Glypican-1 in the normal cells was considered the background, it was shown that in all th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com