Managing modulation transfer function values for image data
a modulation transfer and image data technology, applied in the field of image processing apparatus, image processing method, information processing apparatus, information processing method, etc., can solve the problems of optical character recognition, unreadable characters scanned by the scanner, drop in image quality, etc., to solve individual differences in the mtfs of scanners, suppress variance in reading results, and stable mtf
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0090](First Embodiment)
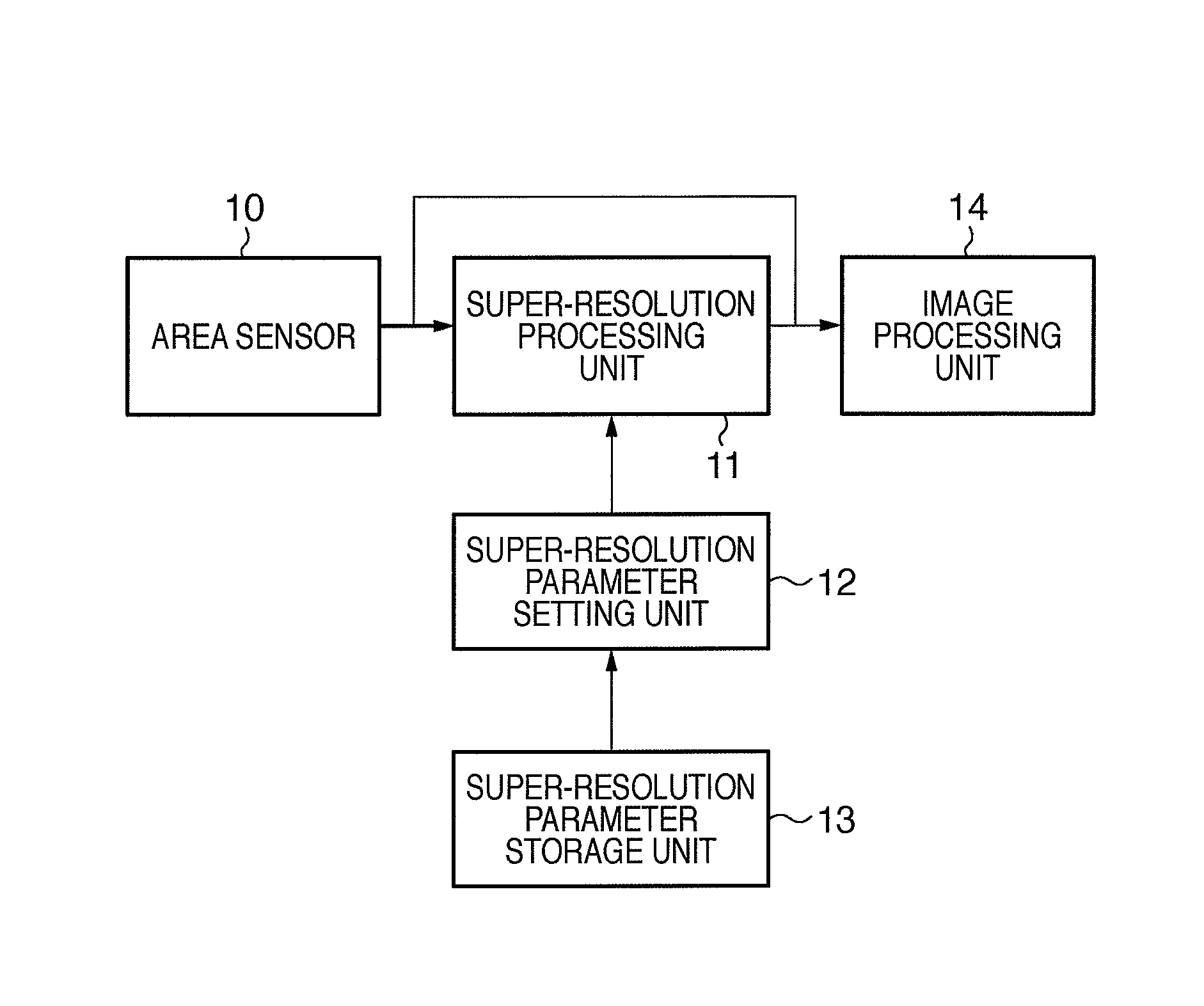
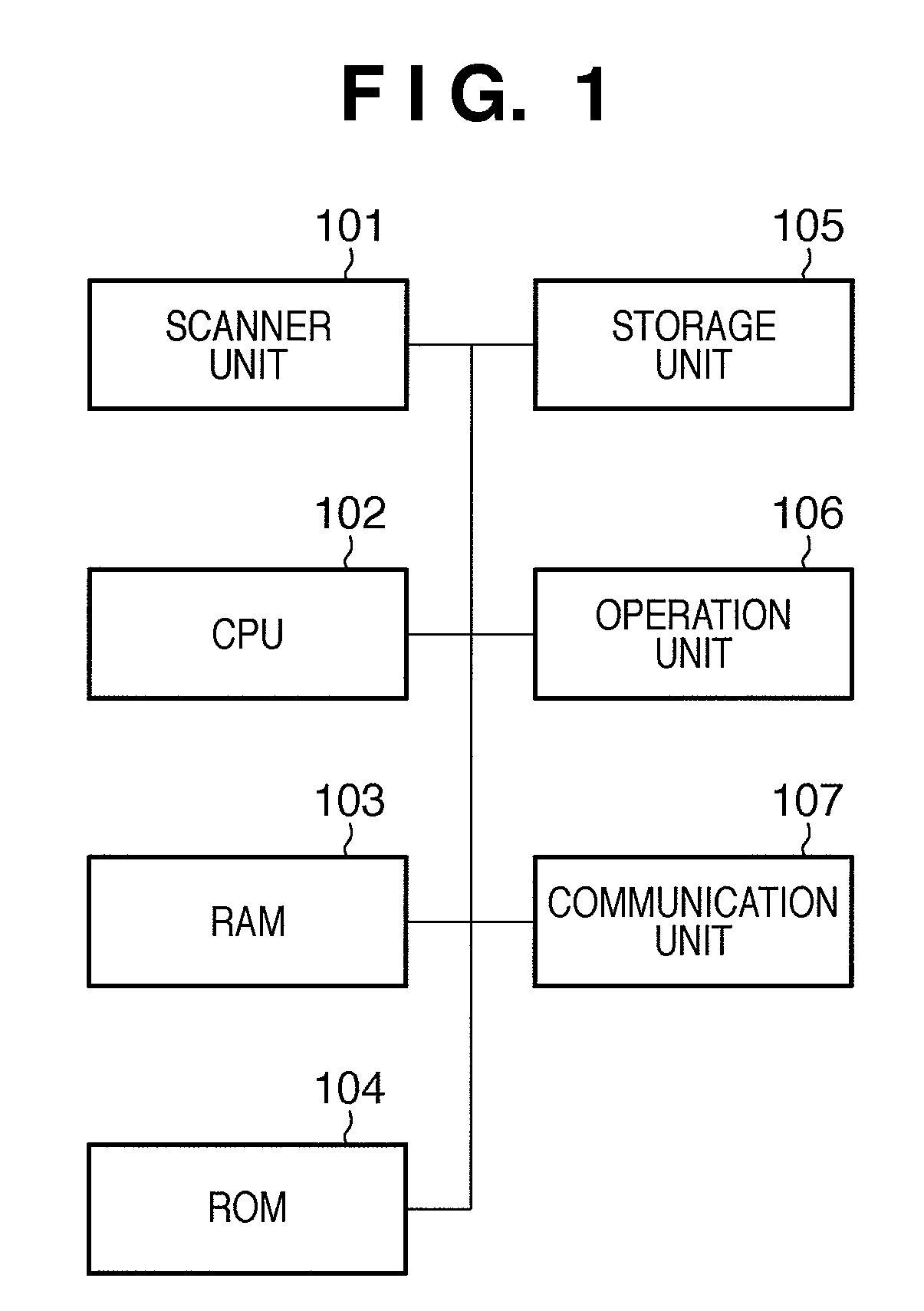
[0091]An image processing system that corrects variances in the MTF and outputs stable scan data by setting, when shipping a scanner, a number of images to undergo super-resolution processing, which is a first embodiment of the present invention, shall be described hereinafter. This image processing system includes an information processing apparatus such as a computer and an image processing apparatus such as a scanner, and it is preferable for the two to be connected to each other. This is to make it possible for information to be collected from and sent to the scanner online, but the present embodiment can be realized as long as information can be input / output to / from the apparatuses, even if the apparatuses are not connected to each other and are offline.
[0092]
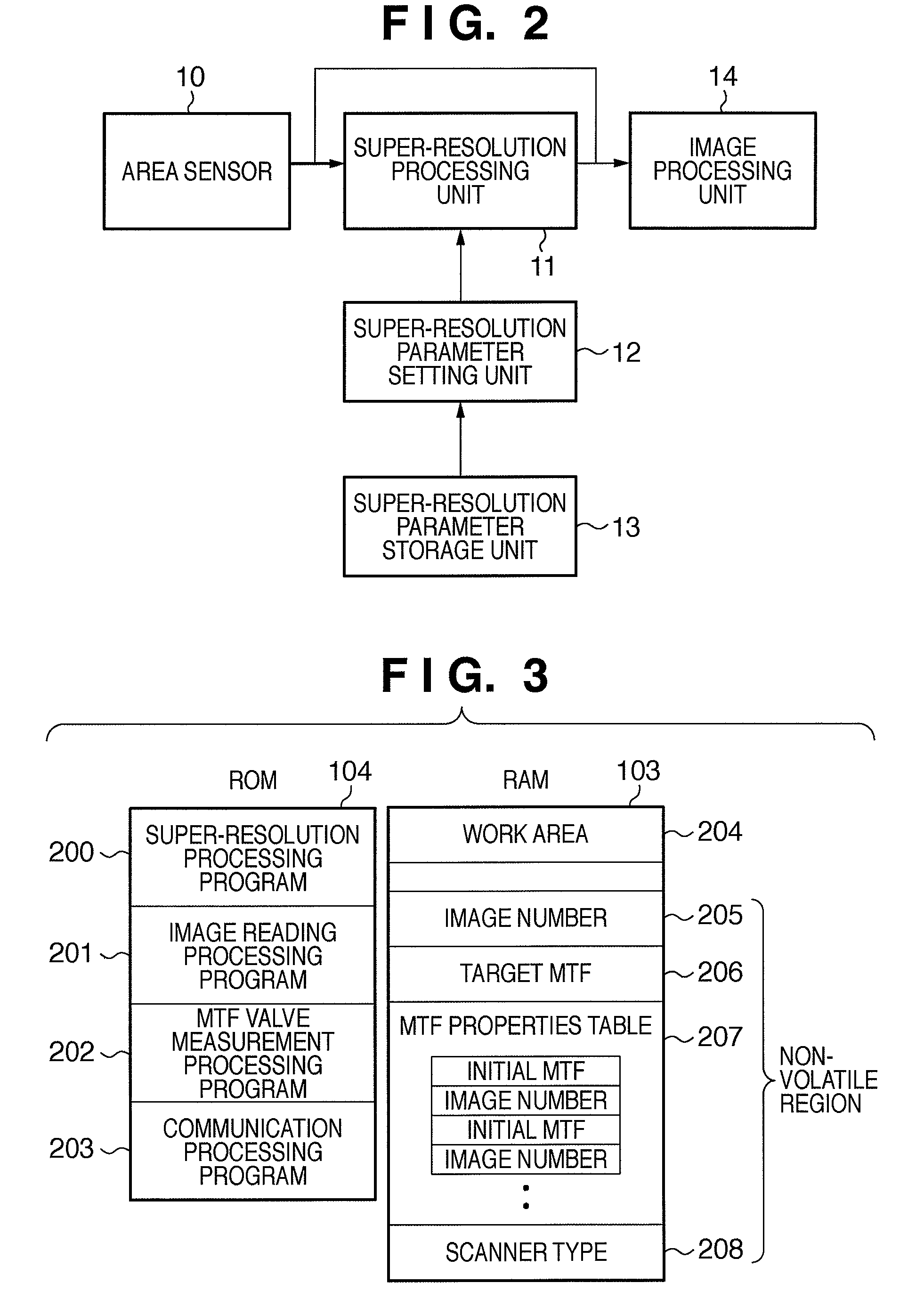
[0093]Various reading devices are used in image processing apparatuses such as digital multi-function peripherals (MFPs). Here, in order to make it possible to identify the variance properties of th...
second embodiment
[0113](Second Embodiment)
[0114]Next, a method aligning target reading MTF values within a group, thereby making the reading accuracies uniform within the group, shall be described as a second embodiment of the present invention. In the present embodiment, the processing performed up until the shipping process is the same as that in the first embodiment, and thus detailed descriptions thereof shall be omitted.
[0115]
[0116]The parameter setting procedure in the shipping process shall be described using the flowchart in FIG. 14 and the schematic diagram in FIG. 15. In the shipping process, an image processing apparatus 301 acquires images using an MTF measurement chart (S400), and measures the MTF using an MTF measurement device (S401). As a result, an initial reading MTF value (of, for example, 50) is obtained. Then, the necessary number of pieces of low-resolution image data with respect to the initial reading MTF value is calculated based on an MTF properties table for a scanner (in ...
third embodiment
[0133](Third Embodiment)
[0134]Next, a method for maintaining a constant MTF in generated image data by changing the number of low-resolution images in the super-resolution processing in response to MTF degradation caused by deterioration over time in the scanner shall be described as a third embodiment of the present invention. The scanner unit of an image processing apparatus according to the present embodiment is configured as shown in FIG. 22. A resolution measurement unit 24 is located in a later stage of the super-resolution processing unit 11, and thus MTF values can be measured during the reading process. In the present embodiment, the processing performed up until the shipping process is the same as that in the first embodiment, and thus detailed descriptions thereof shall be omitted.
[0135]
[0136]The parameter setting procedure in the shipping process shall be described using the block diagram of the scanner unit in FIG. 22, the flowchart in FIG. 23, and the schematic diagram...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com