Fluid treatment system and process
a fluid treatment system and fluid technology, applied in the direction of disinfection, chemical/physical/physical-chemical processes, energy-based chemical/physical/physical-chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of non-uniform irradiation of treated fluid, inability to accurately control fluid level, and inability to achieve accurate fluid level control. , to achieve the effect of reducing hydraulic head loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
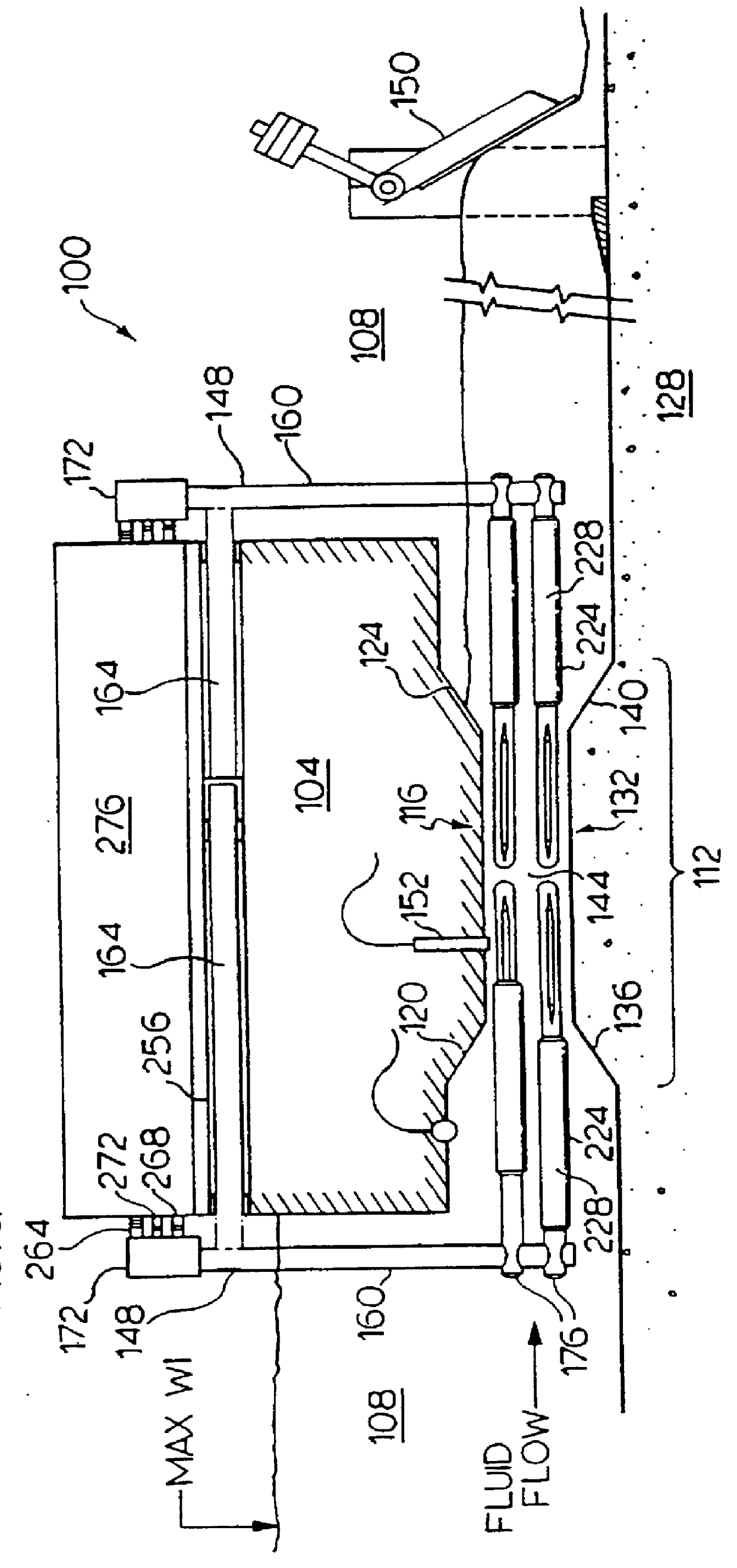
Embodiment Construction
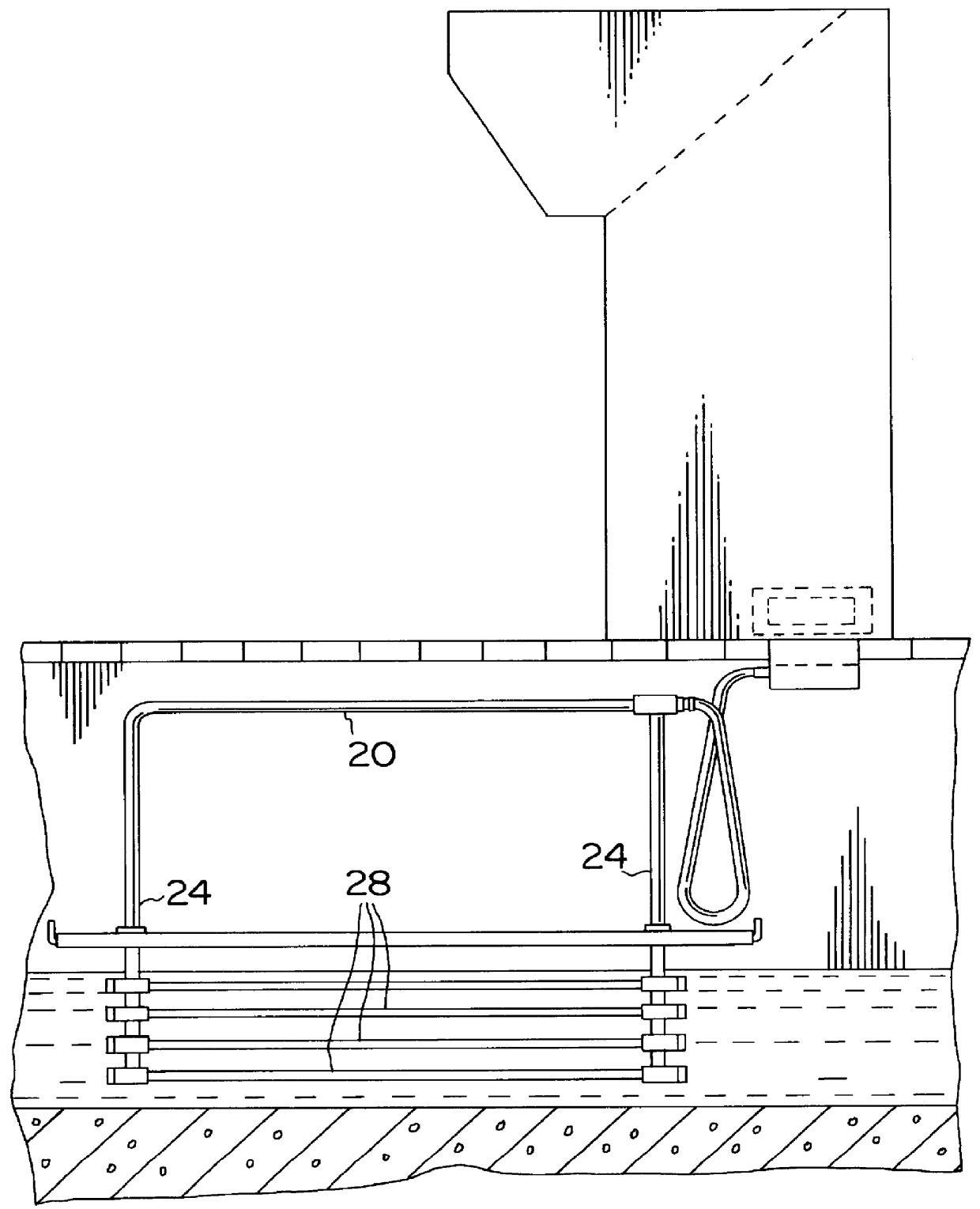
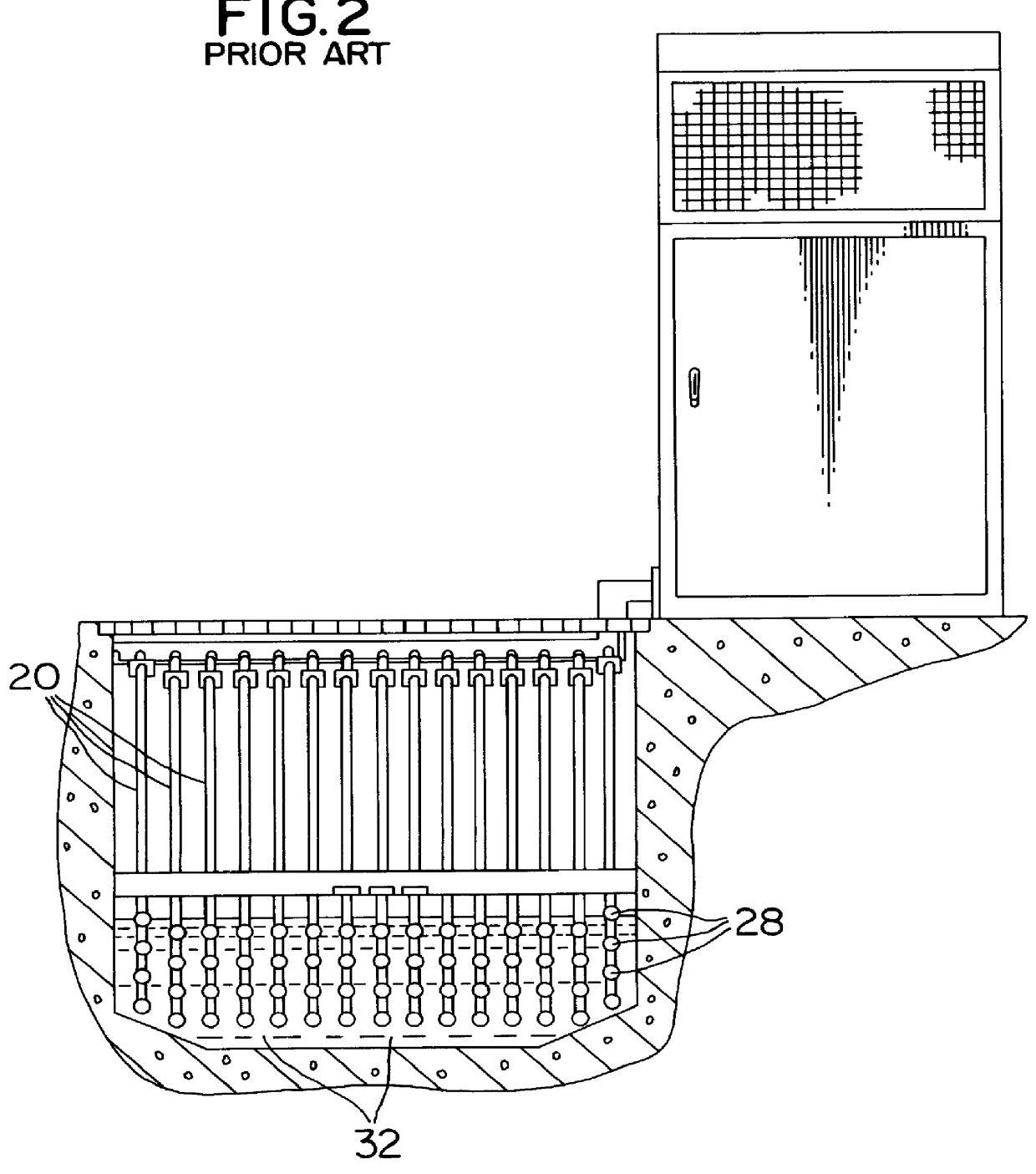
For clarity, a brief description of a prior art fluid treatment device will be presented before discussing the present invention. FIGS. 1 and 2 show a prior art treatment device as described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,482,809. The device includes a plurality of radiation source modules 20, each including a pair of frame legs 24 with UV lamp assemblies 28 extending therebetween. As best shown in FIG. 2, a plurality of lamp modules 20 are arranged across a treatment canal 32 with a maximum spacing between lamp modules 20 which is designed to ensure that the fluid to be treated is irradiated with at least a predetermined minimum dosage of UV radiation.
While this system has been successful, as discussed above it suffers from disadvantages in that the arrangement of the lamp modules 20 makes maintenance of the device relatively labour intensive. Specifically, replacing lamps or cleaning the sleeves surrounding the lamps is time consuming and expensive. Also, for treatment to continue when a lamp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com