Method for minimizing the error of a measurable quantity
A technique of minimizing the measured variable, applied to measuring devices, instruments, special recording/indicating devices, etc., to achieve the effect of providing stability and avoiding feedback
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] Figure 1 shows the ideal situation for a noise-free signal. At t=0 the signal performs a jump from 0 to 3 MHz and then remains constant.
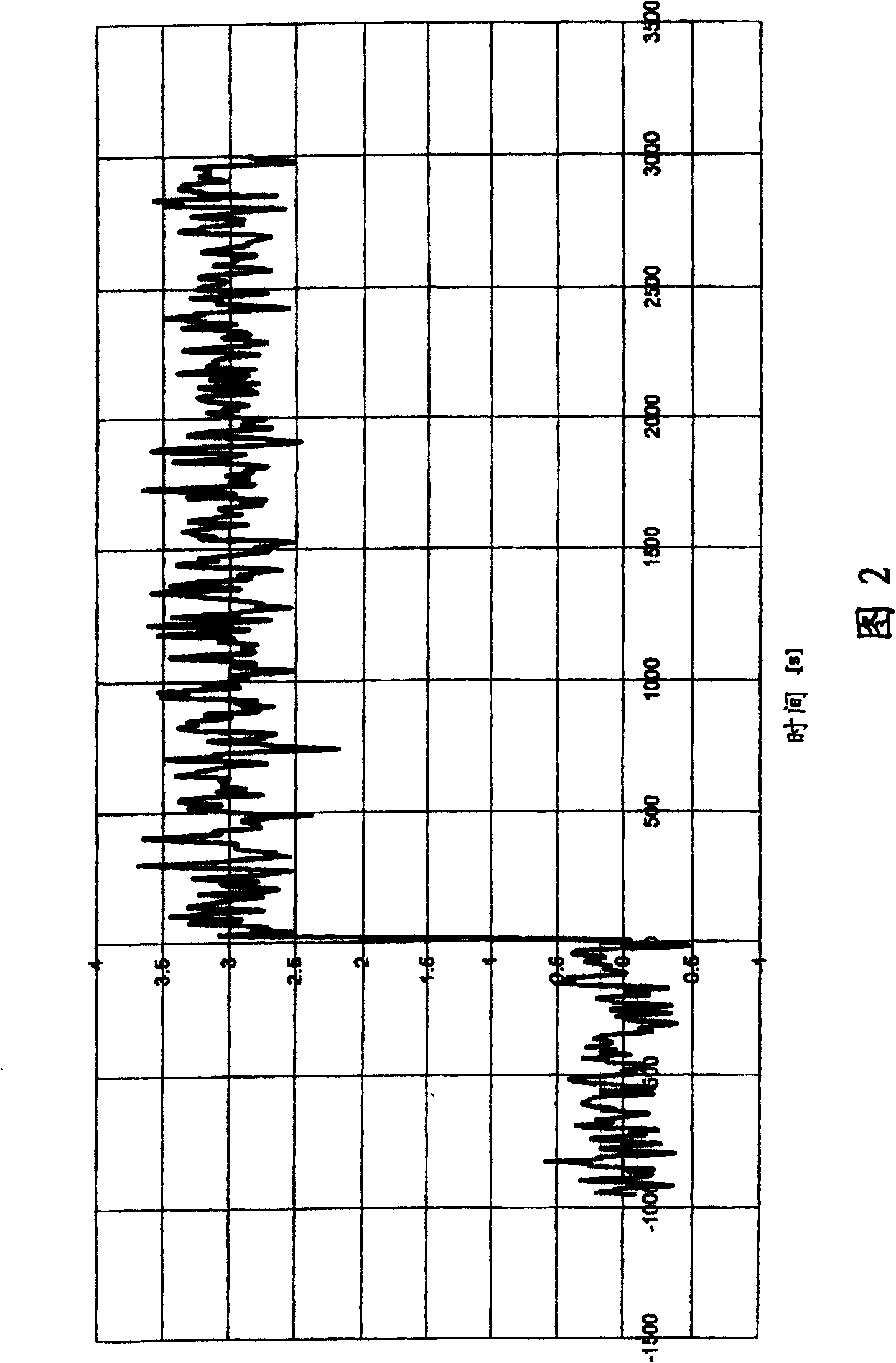
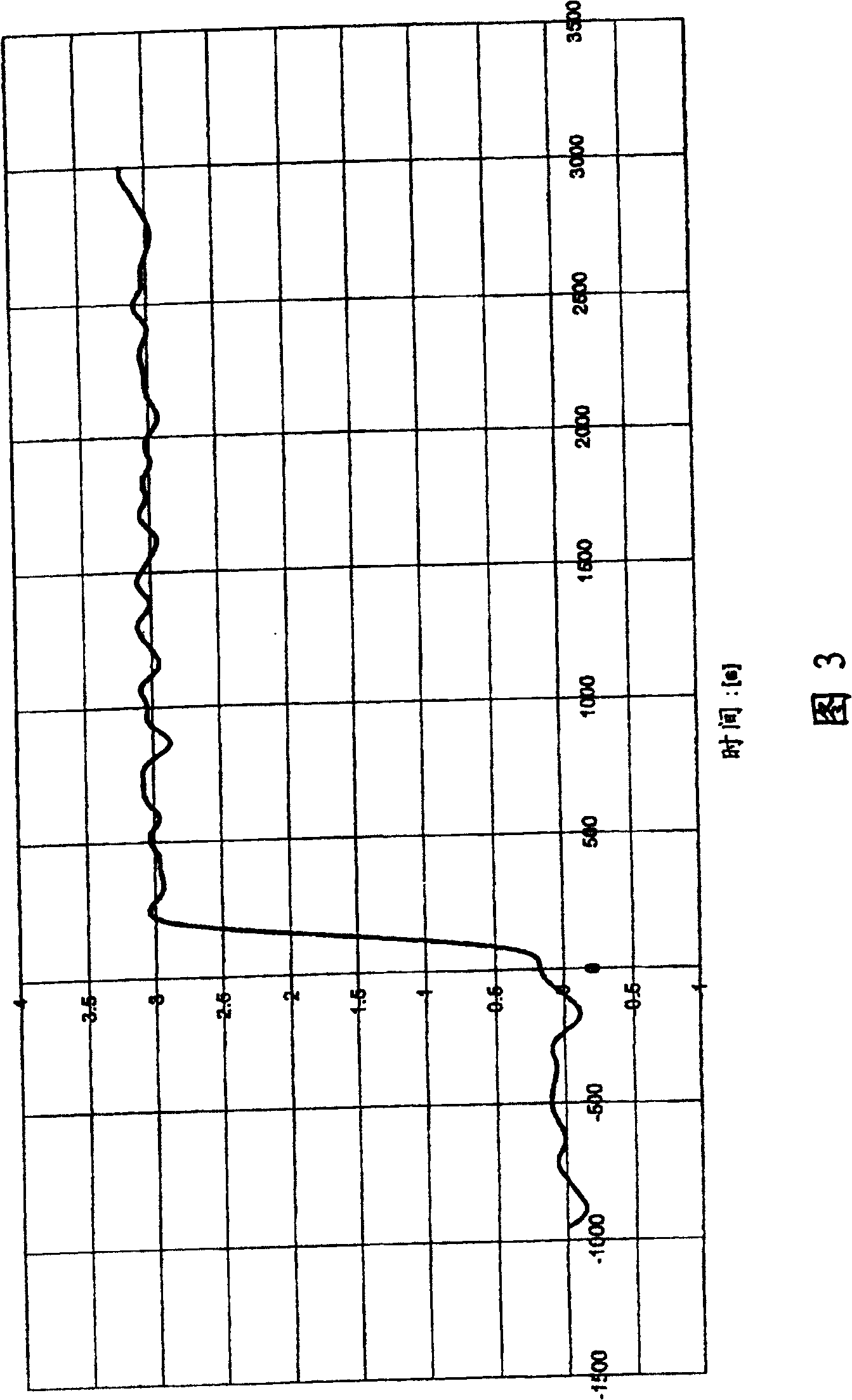
[0027] Figures 2, 3, and 4 provide realistic illustrations. In this case, the signal shown in Fig. 1 is shown as a signal with noise of different bandwidth and is passed through low-pass filters of different bandwidth for this purpose. The bandwidth in Fig. 1 is 25MHz [sic; 2], the bandwidth in Fig. 3 is 3MHz, and the bandwidth in Fig. 4 is 0.4MHz. As can be deduced from Figures 2, 3, and 4, the higher the bandwidth of the signal, the higher the noise amplitude; however, the higher the bandwidth frequency, the faster the jump at t=0.
[0028] Figure 5 shows the error signal with 3MHz bandwidth. The error signal is the difference between the information component shown in Figure 1 and the measured signal after passing through a low-pass filter (shown in Figure 3, which has a bandwidth of 3MHz). The error corresponds to the full he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com