Thin layer transfer method wherein a co-implantation step is performed according to conditions avoiding blisters formation and limiting roughness
A thin-layer, conditional technology, applied in the field of thin-layer structure of semiconductor materials, can solve the problems of inability to separately control surface roughness and bubble formation, undesirable bubble formation, poor roughness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
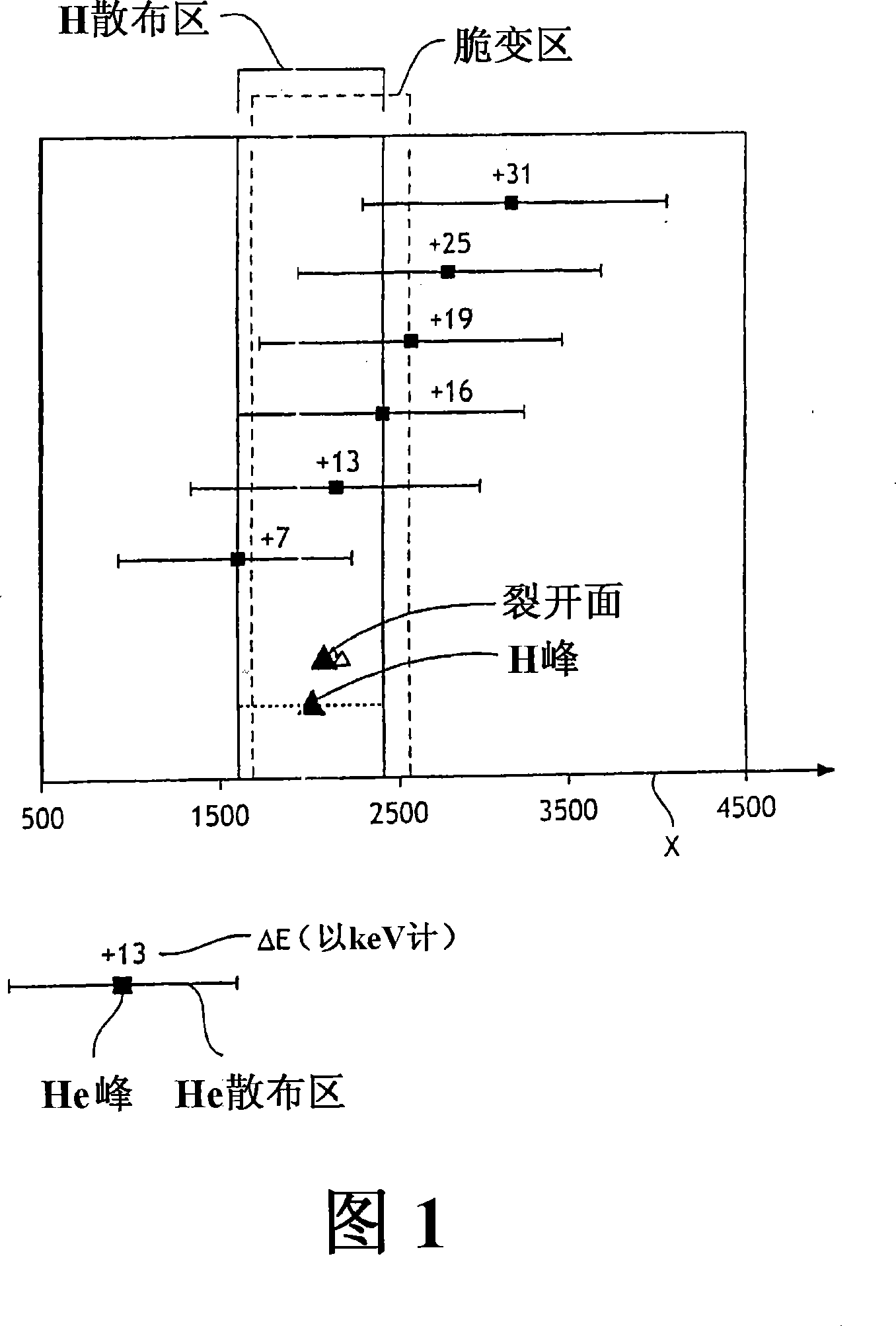
[0067] As already revealed, the present invention relates to a co-implantation step performed during the fabrication of a structure comprising a thin layer of semiconductor material on a support substrate through the level of the donor substrate previously embrittled by the implantation of the species obtained separately.
[0068] The present invention can help to improve the quality of structures obtained by using SMARTCUT-type transfer processes.
[0069] In general, the structure may be any type of structure comprising a thin layer of semiconducting material on a surface exposed to the external environment.
[0070] In a non-limiting manner, the thin layer of semiconductor material may be silicon Si, silicon carbide SiC, germanium Ge, silicon-germanium SiGe, gallium arsenide AsGa, or the like.
[0071] The substrate support can be made of silicon Si, quartz or the like.
[0072] It is also possible to insert a layer of oxide between the supporting substrate and the thin l...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap