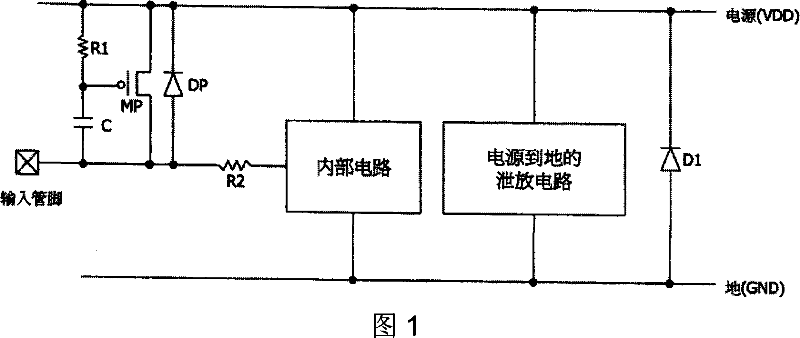
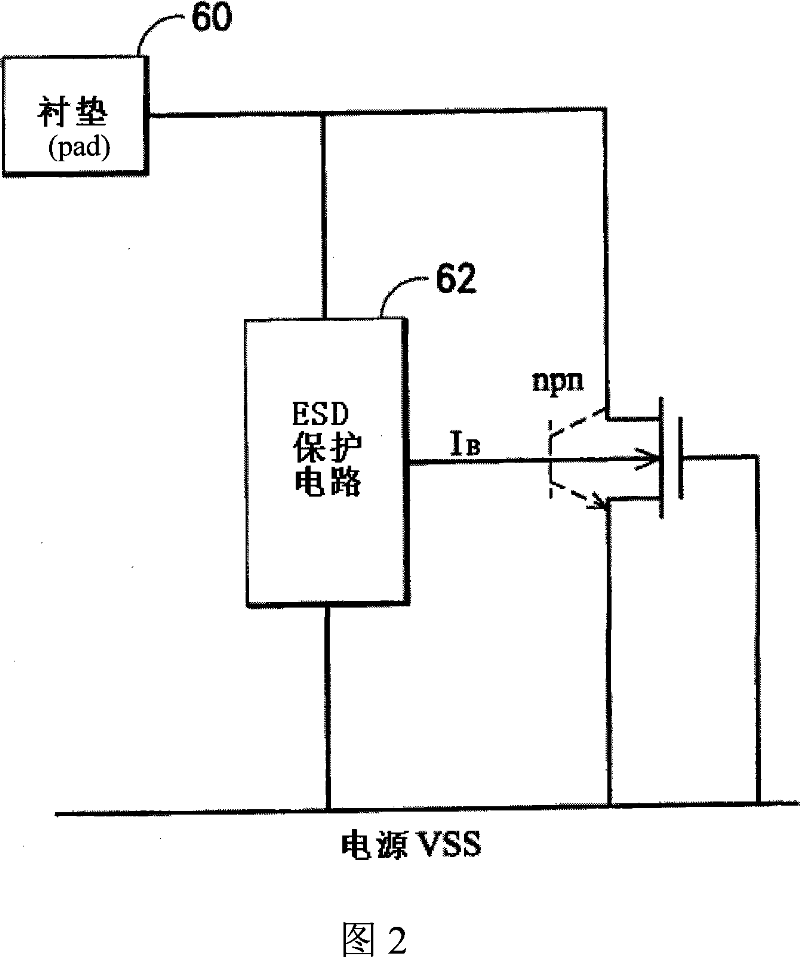
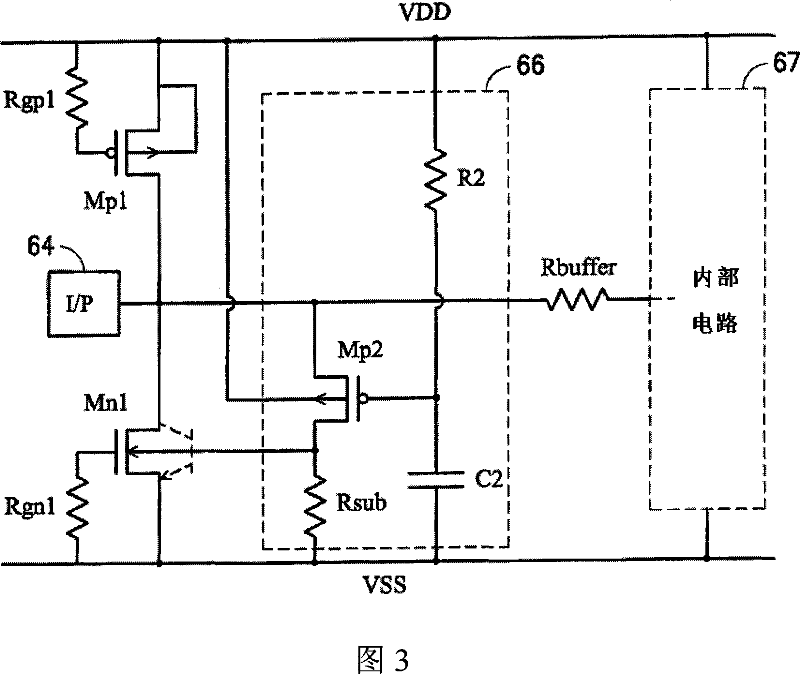
Improved electrostatic discharge protecting circuit
An electrostatic discharge protection and electrostatic discharge technology, which is applied to emergency protection circuit devices, emergency protection circuit devices for limiting overcurrent/overvoltage, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as increasing chip size, and achieve size saving and simplification. The effect of the design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The substrate-driven scheme shown in Figure 3 can be simplified to be compatible with standard CMOS processes. If the substrate is connected to the gate using the ESD MOS shown in Figure 4, no detection circuit is required.
[0039] Similar to the gate drive structure, when the ESD negative pulse from VM to VDD occurs, the body of the MP will be coupled low (relative to the MP) due to the existence of the large parasitic capacitance Cgd of the MP (the capacitance between the gate and the drain of the MP). In terms of the voltage of VDD, it is lower than the voltage of VDD and closer to the voltage of VM). At the same time, a current flowing out of the MP substrate is generated at the substrate of the MP. This substrate bias current will flow through the bulk resistance and create a voltage drop across it. If the voltage drop is greater than the V required to trigger the parasitic PNP BE Positive bias value, the parasitic PNP will be triggered, and the static electric...
Embodiment 2
[0047] On the basis of the ESD protection circuit 1 shown in Figure 4, a capacitor C is added between the gate of MP and VM, as shown in Figure 5, to obtain the ESD protection circuit 2 for negative input voltage pins.
[0048] In the ESD protection circuit 2, on the one hand, the increase of C is the same as the prior art (Fig. 1), which will increase the coupling voltage between the drain and the gate of MP during electrostatic discharge; When a fast ESD pulse voltage is applied, the capacitor C needs to be charged first (the initial voltage of the capacitor C is zero), a part of the charging current will flow out from the N well of MP, and the increase of C will also increase the output from the N well of MP. The outflow current, the latter can enhance the ESD discharge capability of the MP tube.
[0049] The ESD protection circuit 2 works the same as the ESD protection circuit 1 when electrostatic discharge occurs, except that the capacitor C will further enhance the disch...
Embodiment 3
[0054] FIG. 6 shows the ESD protection circuit 3 for common input voltage pins according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, including resistors R1 and R2 , NMOS transistor MN and diode D. One end of resistor R1 is connected to the gate of MN, the other end is grounded to GND; the drain of MN is connected to a voltage VI, the source is grounded to GND, the gate is connected to the substrate, VI is connected to the internal circuit through the resistor R2, and the positive electrode of diode D Ground GND, the negative pole is connected to voltage VI, and an ESD protection circuit is connected between the power supply and the ground.
[0055] When a positive ESD pulse is generated from VI to GND, the static electricity will be discharged through the reverse breakdown of MN; when a negative ESD pulse is generated from VI to GND, the static electricity will be discharged through the forward conduction of the diode D. When a positive ESD pulse is generated from VI to VDD, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com