Electric power steering apparatus
A technology for electric power steering and auxiliary devices, which is applied to electric steering mechanisms, automatic steering control components, steering mechanisms, etc., and can solve problems such as the limitation of the effect of compensation control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
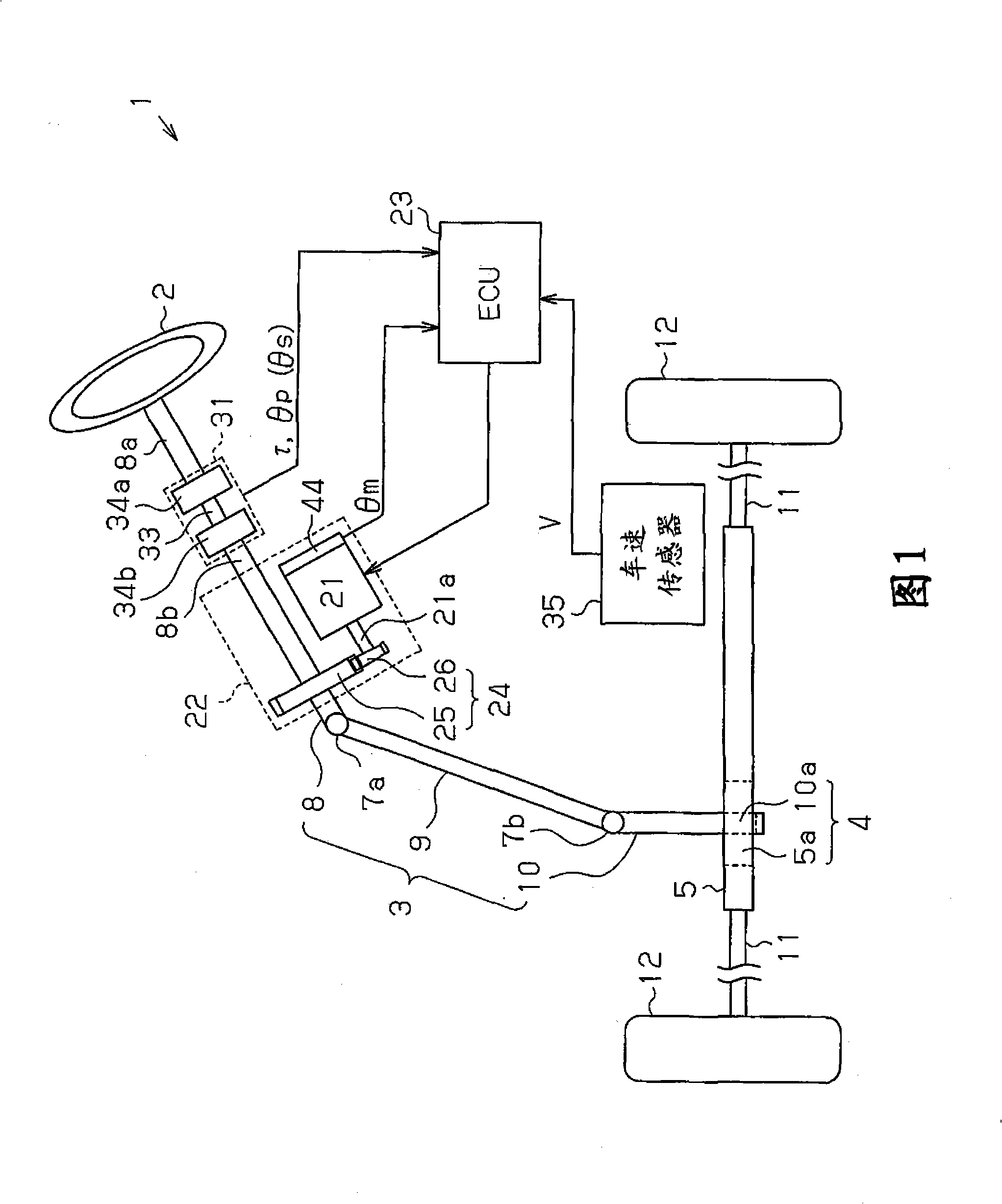
[0026] A description will be given below of a column type electric power steering apparatus (EPS) according to a first embodiment of the present invention with reference to the drawings.
[0027] As shown in FIG. 1 , a steering wheel 2 is fixed to a steering shaft 3 . The steering shaft 3 is connected to a rack shaft 5 via a rack and pinion mechanism 4 . The rotation of the steering shaft 3 following the steering operation is converted into the reciprocating linear motion of the rack shaft 5 by the rack-and-pinion mechanism 4 . Specifically, in the steering shaft 3, the column shaft 8 and the intermediate shaft 9 are coupled to each other via the universal joint 7a, and the intermediate shaft 9 and the gear shaft 10 are coupled to each other via the universal joint 7b. The pinion-rack mechanism 4 is composed of a pinion tooth 10a formed in an end portion of the pinion shaft 10 and a rack tooth 5a provided in the rack shaft 5 and meshing with the pinion tooth 10a. The recipro...
no. 2 approach
[0063] A description will be given below of a second embodiment of the present invention with reference to the drawings.
[0064] The main difference between the present embodiment and the first embodiment lies only in the control to suppress the vibration due to the stress applied to the steering wheel 12 . Therefore, for convenience of explanation, the same parts as those of the first embodiment are given the same reference numerals, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
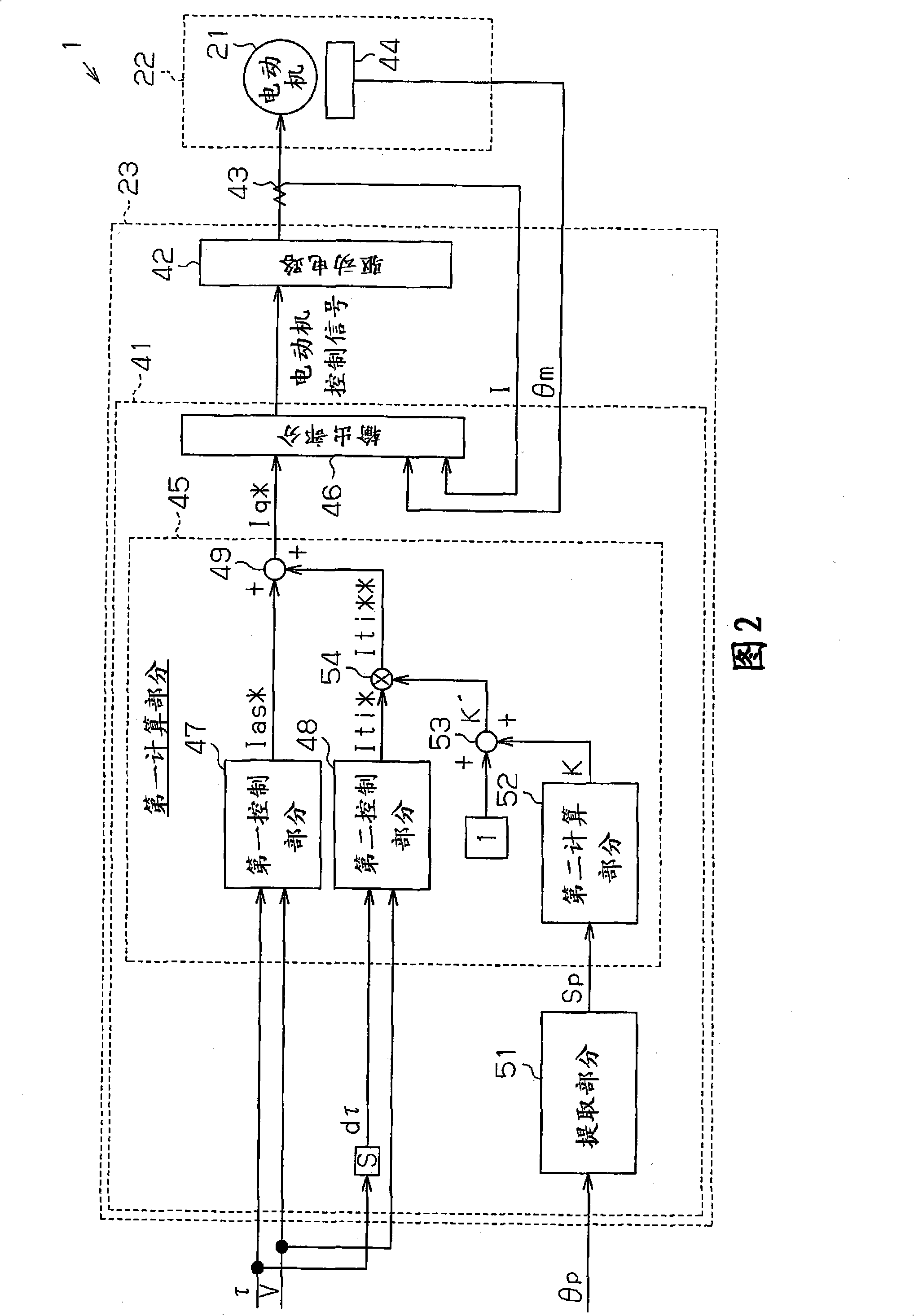
[0065] Such as Figure 6 As shown in , the microcomputer 41 is provided with a judging section 61 as judging means, and the judging section 61 judges whether the driver is performing a steering operation, that is, whether the EPS 1 is in a steering state. In the case where the determination section 61 determines that the steering operation is being performed, that is, during the steering operation, the microcomputer 41 does not execute the enhancement of the torque inertia compensation control, that is, d...
no. 3 approach
[0078] A description will be given below of a third embodiment of the present invention with reference to the drawings.
[0079] The main difference between the present embodiment and the first embodiment lies only in the control to suppress the vibration due to the stress applied to the steering wheel 12 . Therefore, for convenience of explanation, the same parts as those of the first embodiment are given the same reference numerals, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
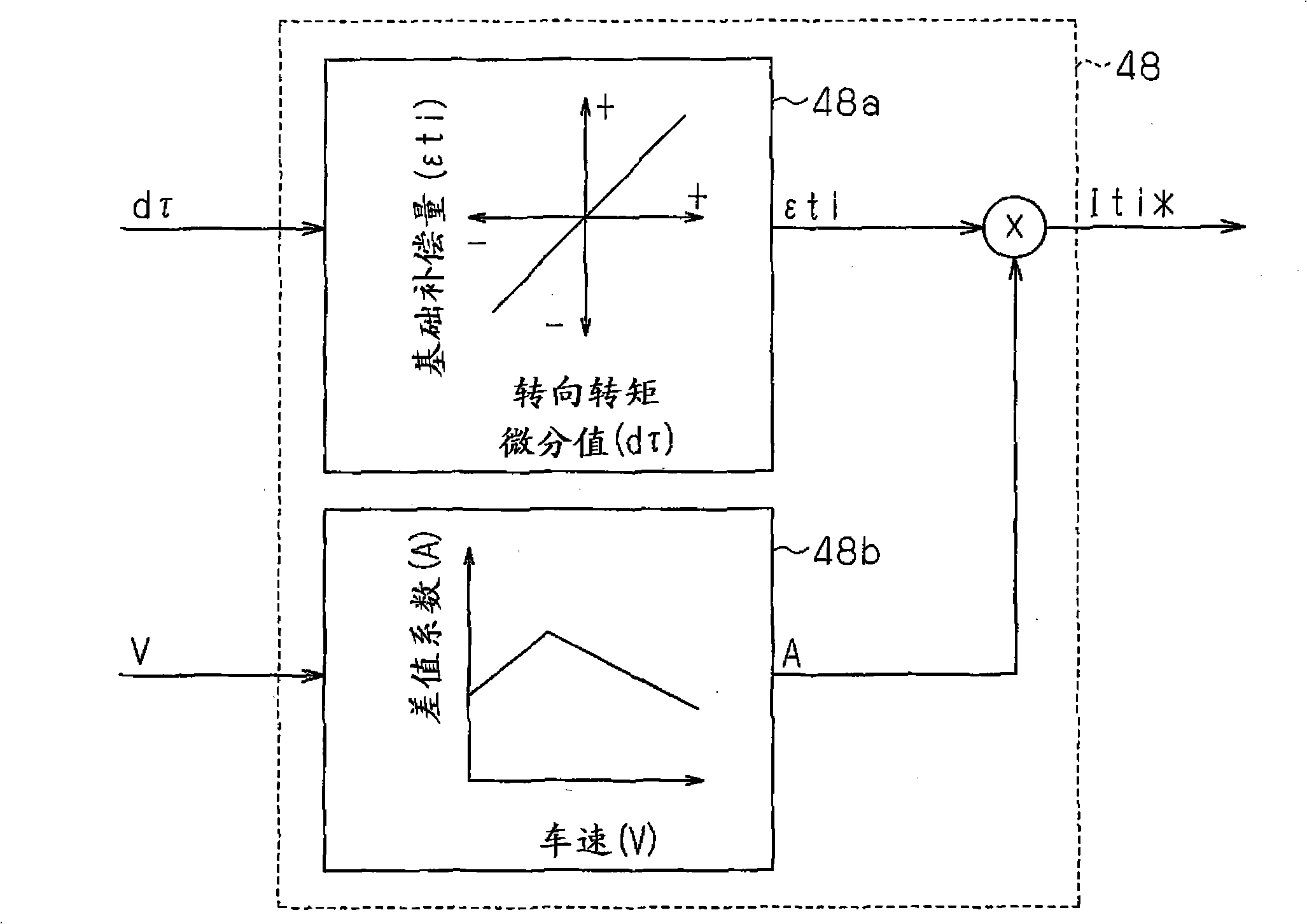
[0080] The microcomputer 41 is used as an uneven road surface determination device for determining whether the road surface on which the vehicle is traveling is uneven, that is, for determining whether the road surface is uneven. In the case where it is determined that the road surface to travel is an uneven road, the microcomputer increases the torque inertia compensation amount Iti corresponding to the compensation component based on the steering torque differential value in the same manner as in the firs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com